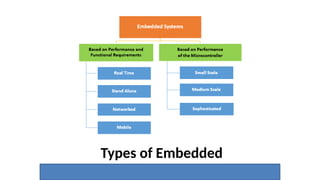
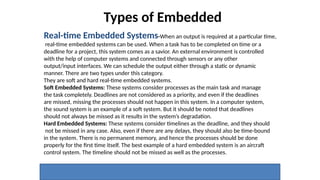
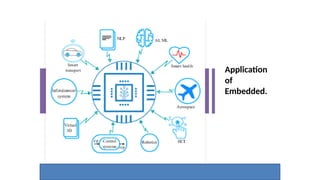
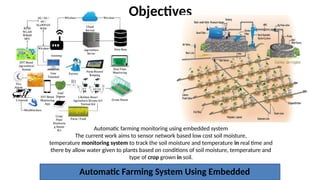
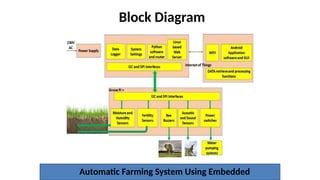
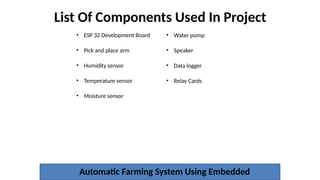
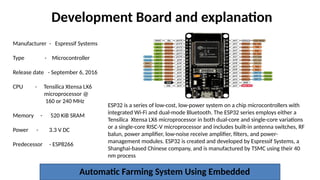
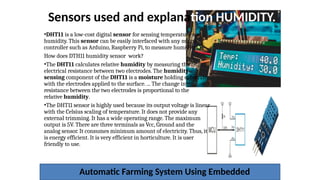
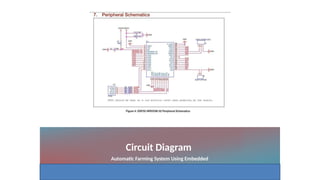
The document outlines the use of embedded systems in agriculture, detailing various types and applications including real-time, stand-alone, and network embedded systems. It discusses the advantages such as stability, efficiency, and resource optimization, and reviews current devices available in the market for smart farming. Additionally, it highlights the significance of automation through robotics in enhancing agricultural productivity and reducing labor costs.