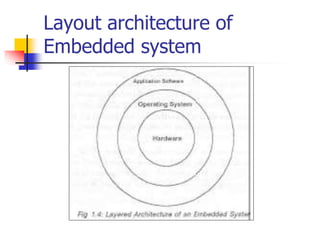
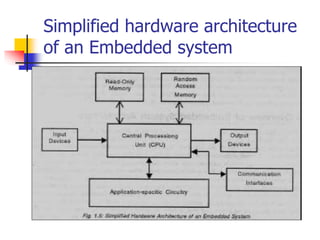
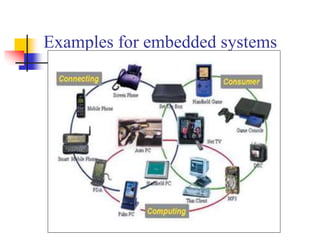
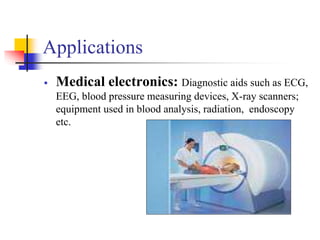
This document provides an overview of embedded systems. It defines an embedded system as having computer hardware with application software and an real-time operating system embedded within it. Embedded systems typically consist of custom hardware built around a CPU, software stored on memory chips, and an OS that runs applications. Common components include processors, memory, input/output devices, communication interfaces, and application-specific circuits. Embedded systems are found in devices like consumer appliances, industrial equipment, medical devices, networking gear, and more, performing specialized tasks in real-time.