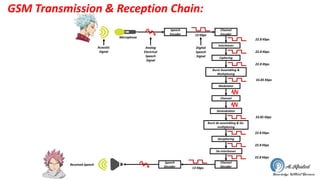
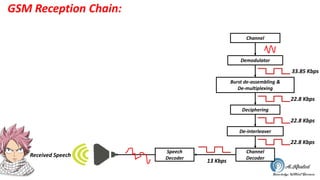
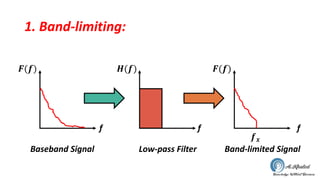
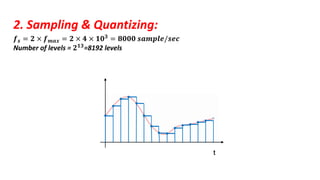
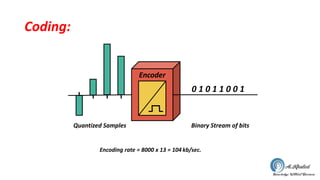
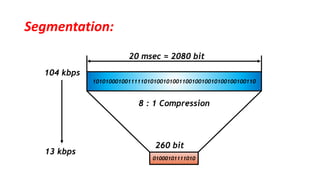
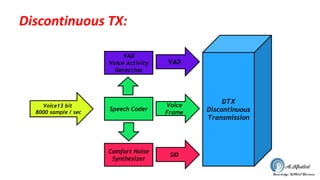
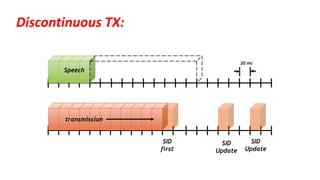
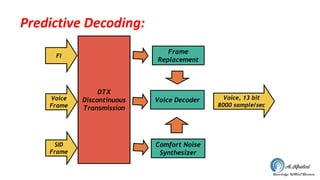
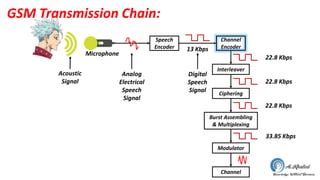
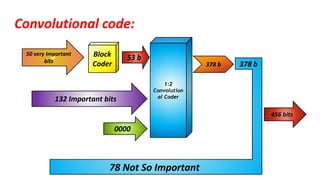
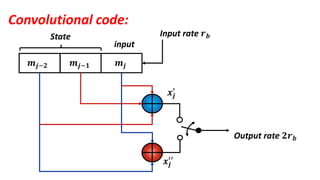
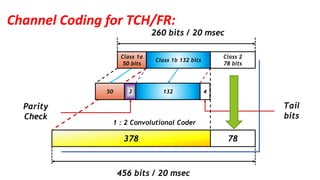
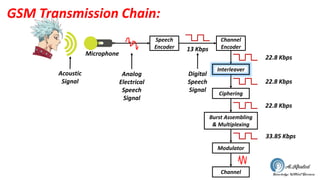
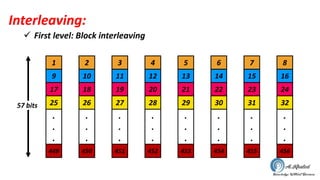
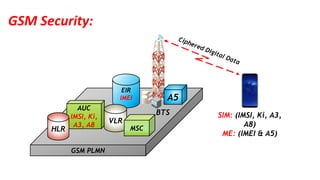
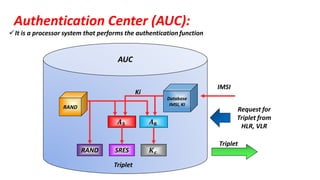
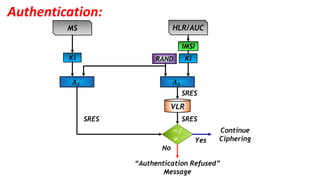
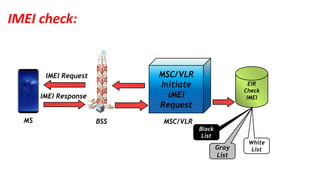
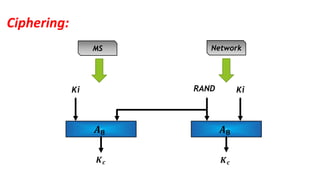
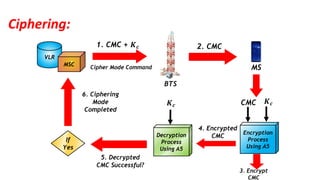
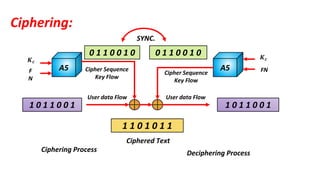
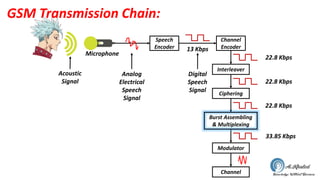
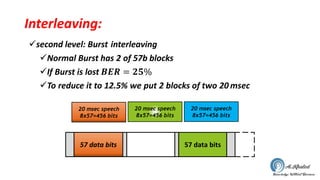
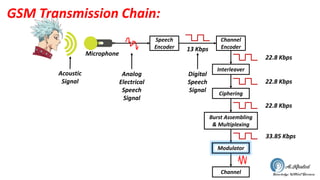
The document discusses the GSM transmission and reception chain, including processes such as speech encoding, error correction, and security measures. It explains the steps of digital signal processing, mobile channel coding, and the importance of modulation in ensuring effective communication. Additionally, it outlines GSM security protocols including authentication and ciphering techniques to protect user data.