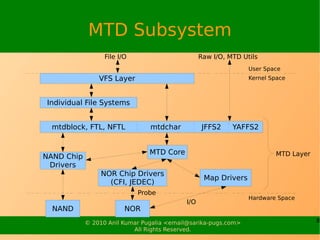
The document discusses embedded flash storage management. It provides an overview of memory technology devices (MTDs) such as NOR and NAND flash, the MTD subsystem and related drivers, flash file systems like JFFS2 and YAFFS2 that handle the constraints of flash storage, and useful flash tools. It also covers the history and timelines of storage technologies, characteristics of NOR and NAND flash, writing processes, and kernel configurations for MTD support.









![NAND Chip Drivers
Drivers for NAND Controller to access NAND
Sources: drivers/mtd/nand/
A NAND Drive should do the following
Add an entry to nand_flash_ids[] in drivers/mtd/nand/nand_ids.c
Entries being
Id Name, Device Id, Page Size, Erase Block Size, Chip Size, Options like
Bus Width, …
As, no automatic configuration support
Specify its out-of-band (OOB) spare area layout through the
“struct nand_ecclayout” (Header: <mtd/mtd-abi.h>)
For ECCs, to implement error correction & detection
Enable Error Management, in case NAND Controller doesn't do it
Software ECC is implemented in drivers/mtd/nand/nand_ecc.c
© 2010 Anil Kumar Pugalia <email@sarika-pugs.com> 11
All Rights Reserved.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embeddedstoragemgmt-100628224450-phpapp02/85/Embedded-Storage-Management-11-320.jpg)




