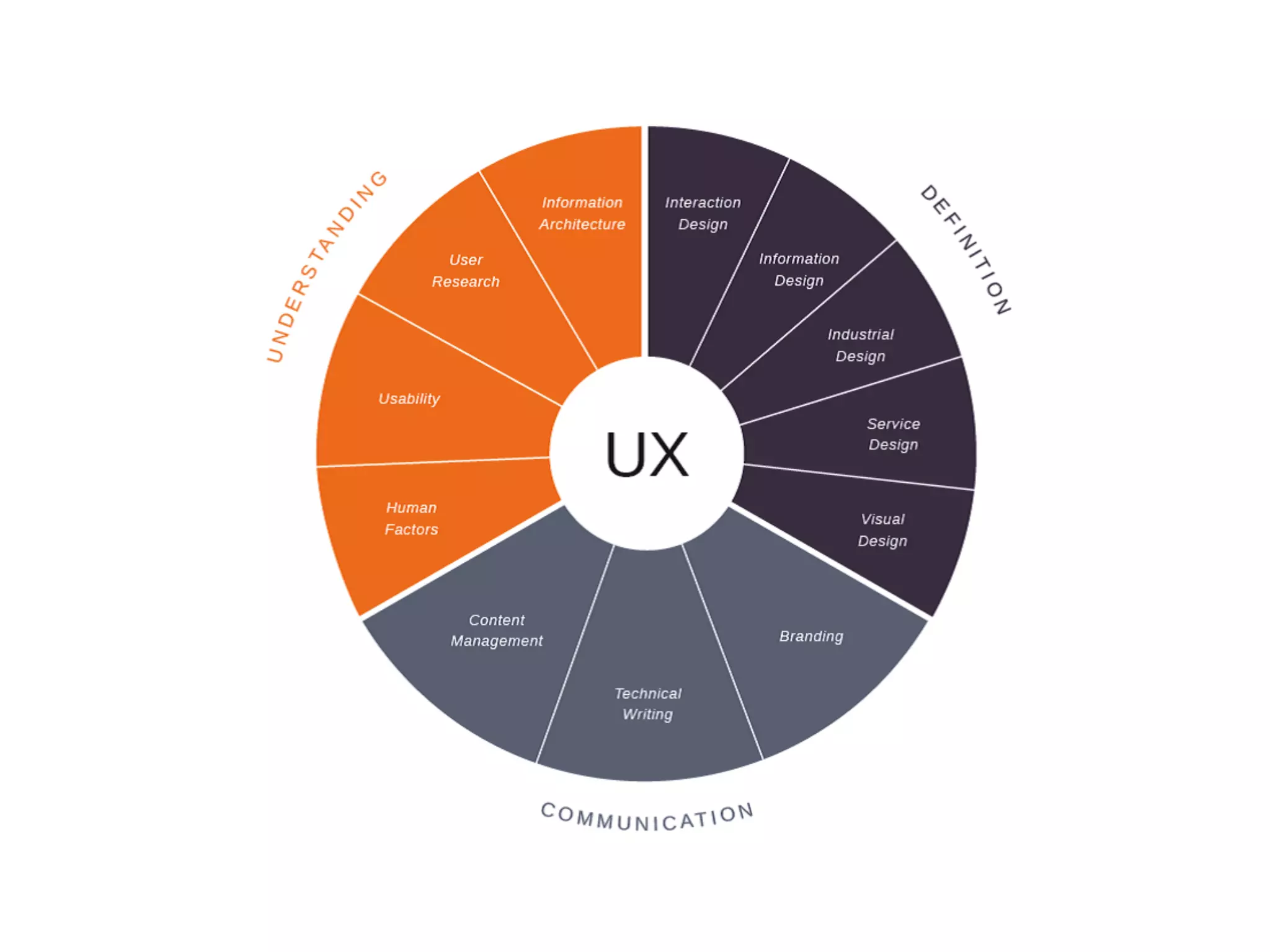
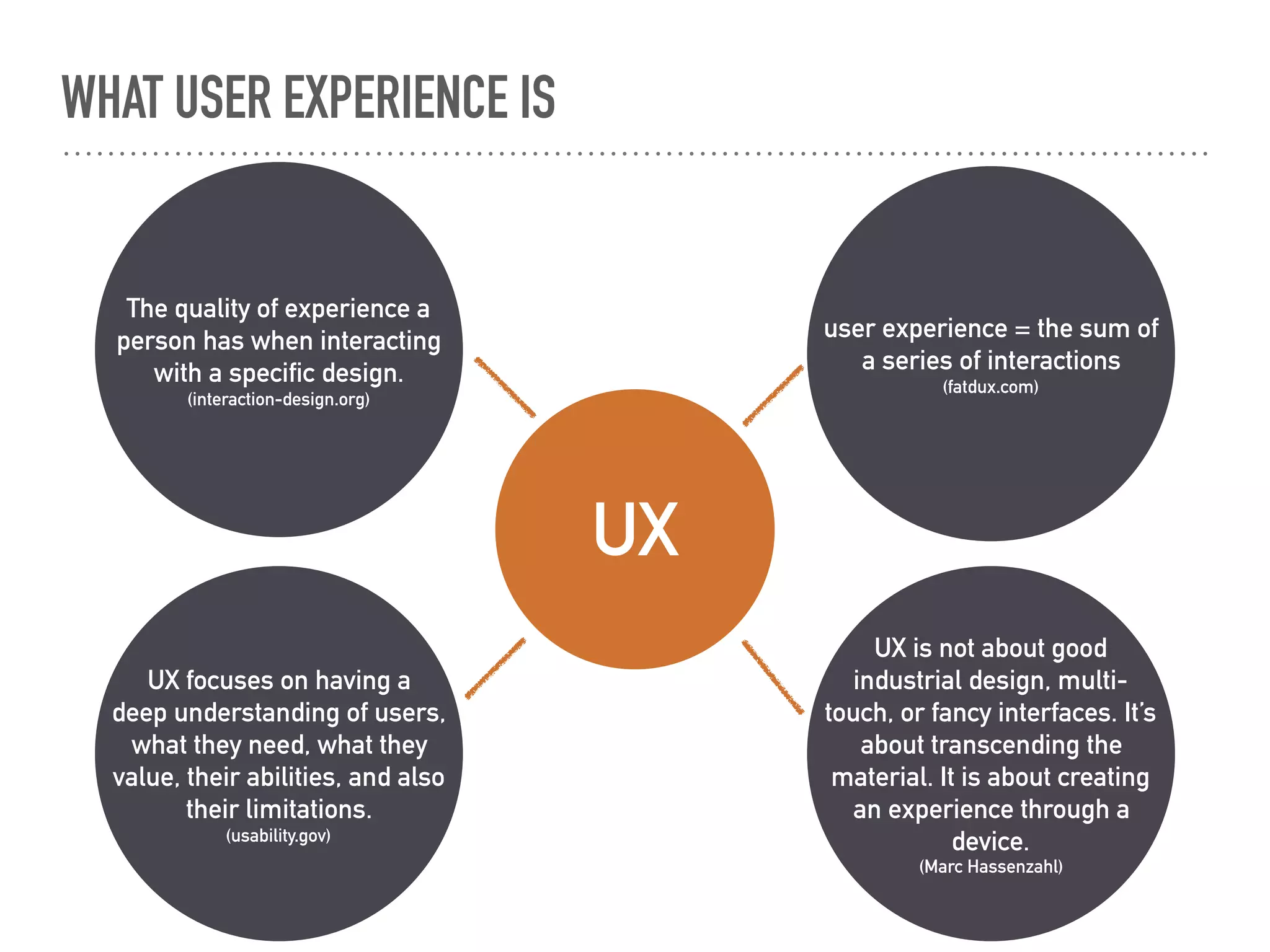
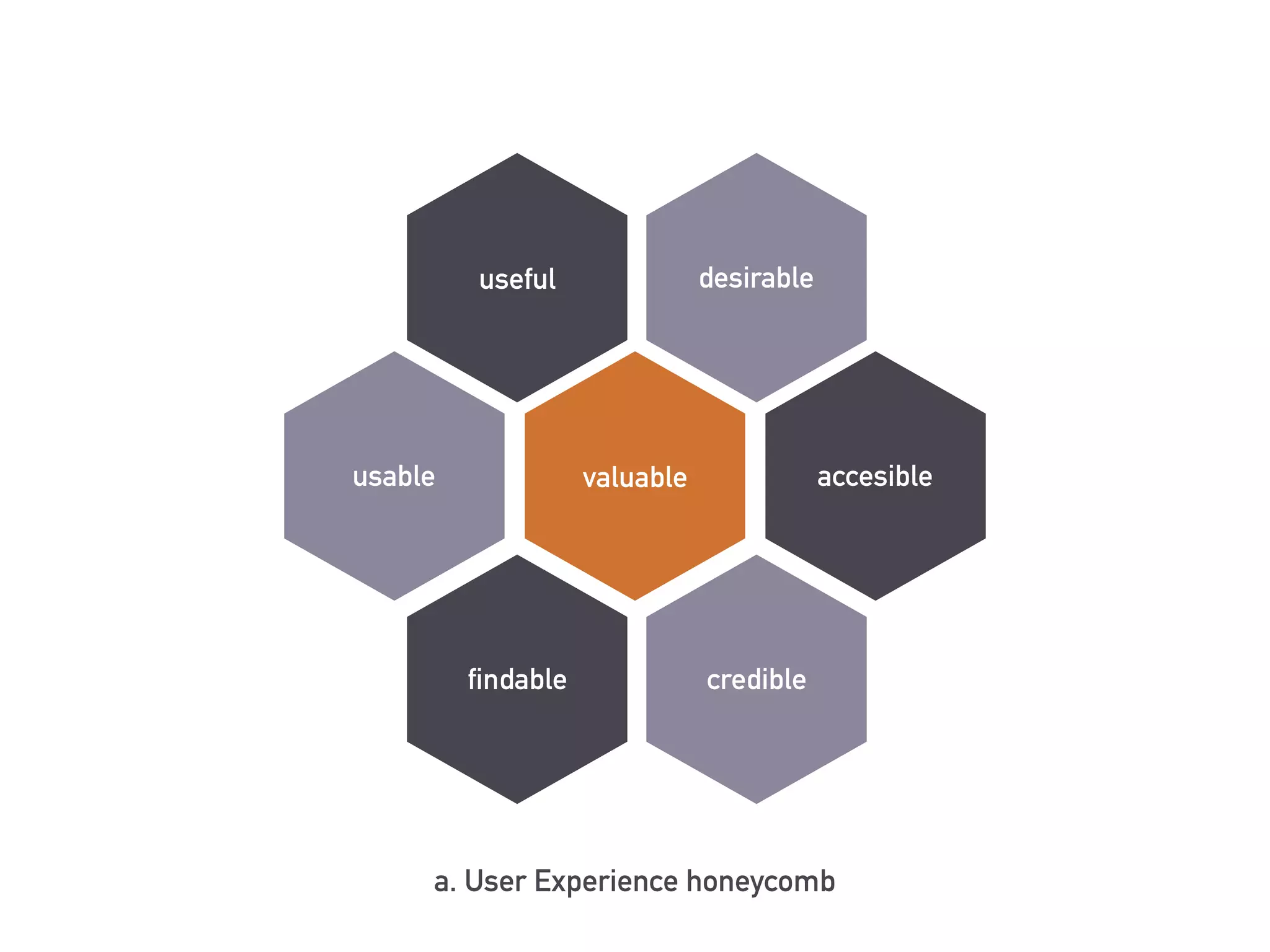
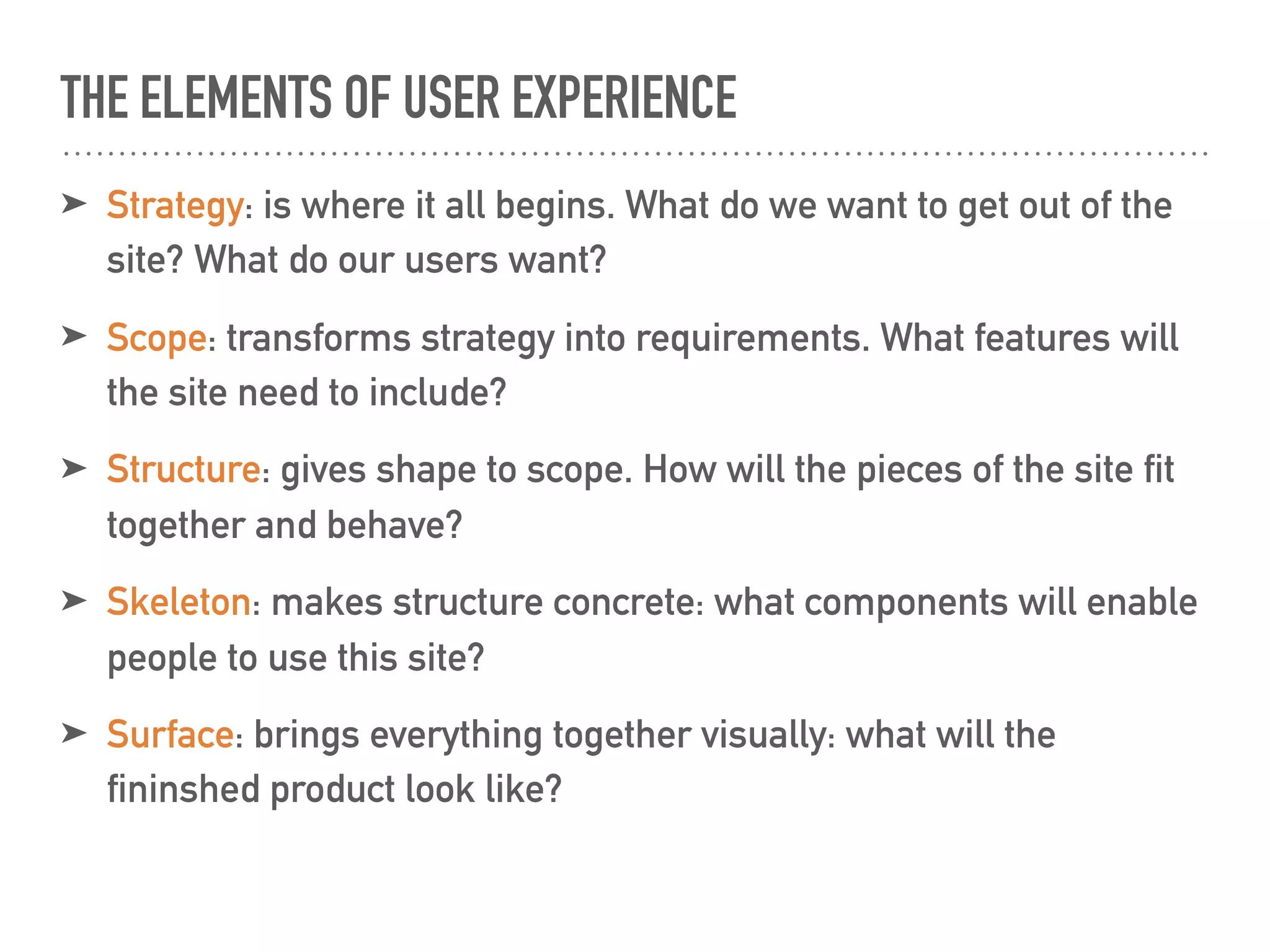
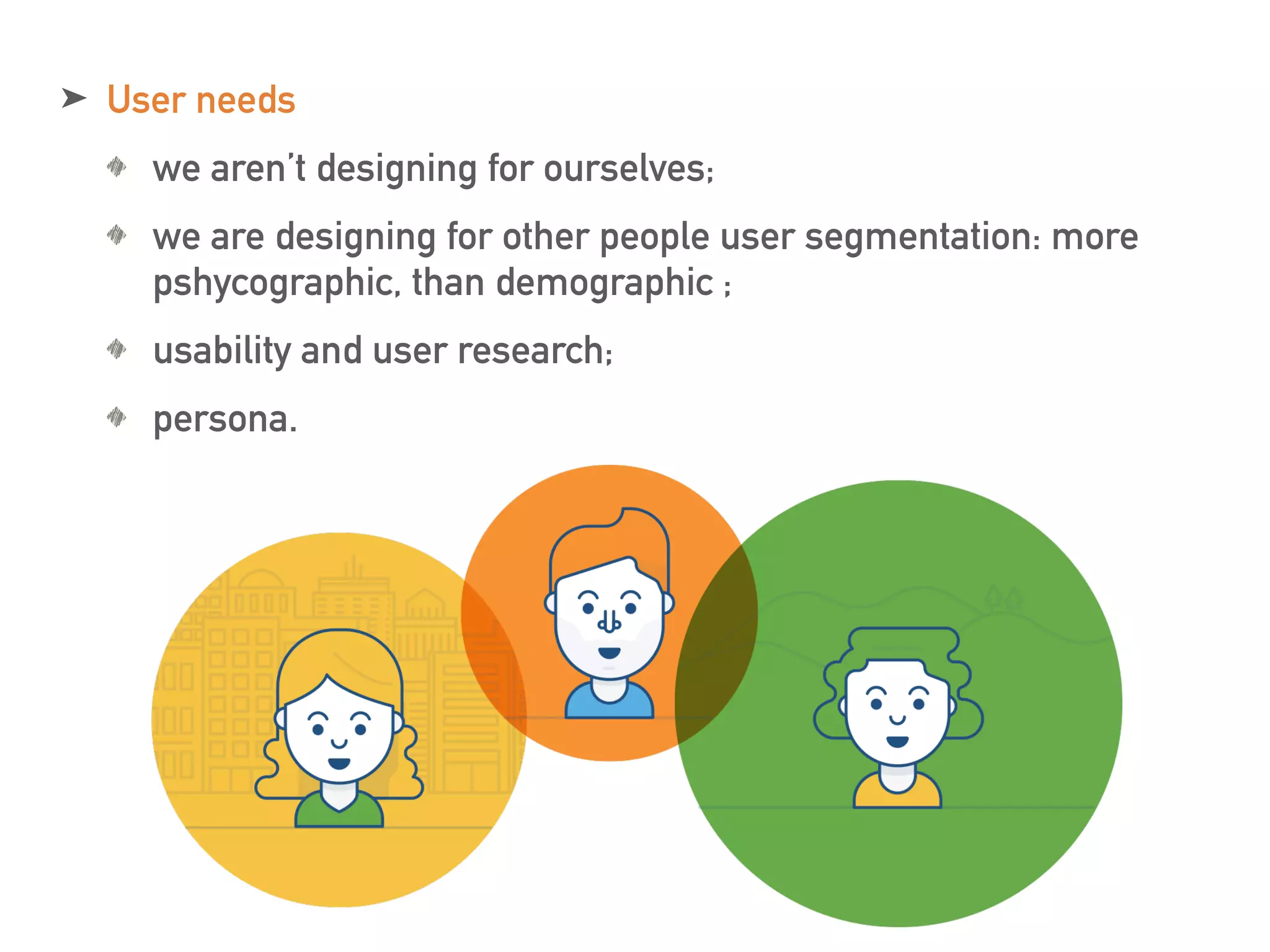
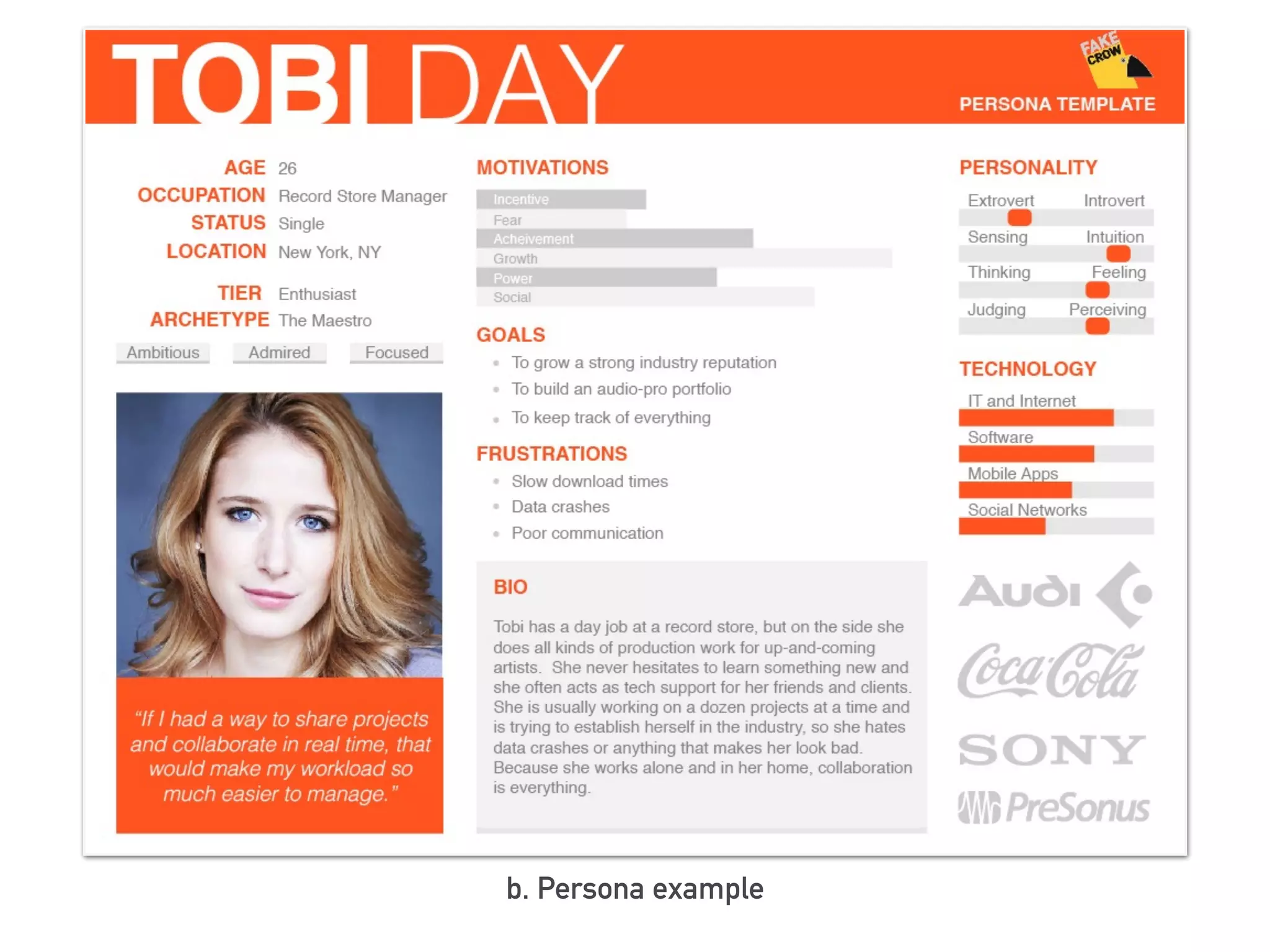
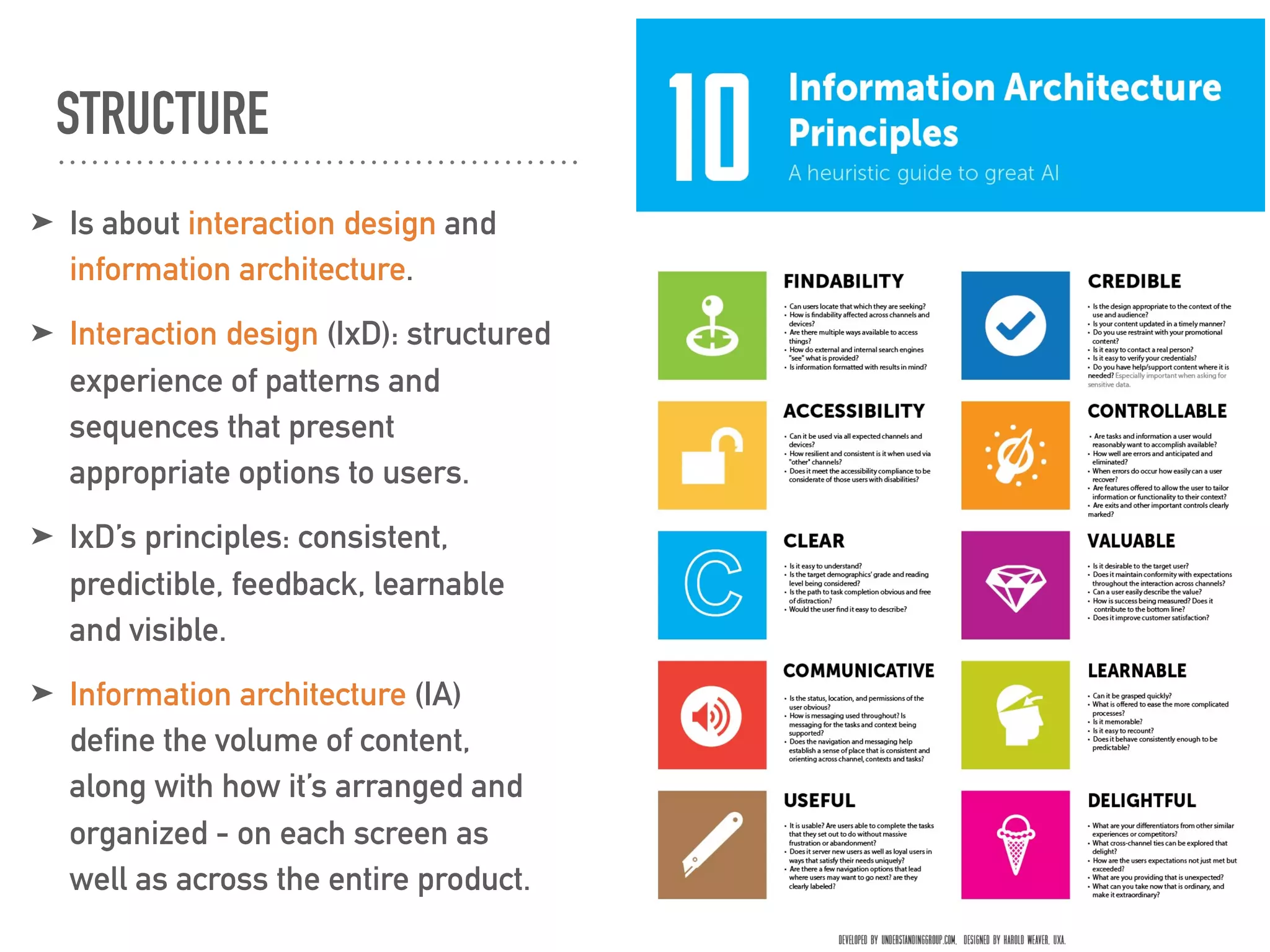
This document discusses the elements of user experience (UX) design. It explains that UX focuses on understanding users and their needs. The key elements of UX design are identified as strategy, scope, structure, skeleton, and surface. Strategy involves understanding user needs and objectives. Scope defines functional requirements and content. Structure determines interaction design and information architecture. Skeleton comprises interface and navigation design. Surface involves visual design elements. The goal of UX design is to create a positive experience that meets both user and business goals.