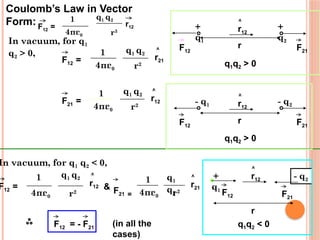
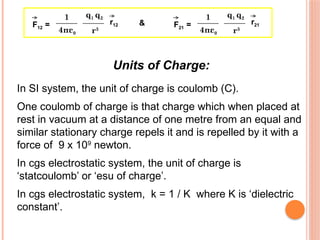
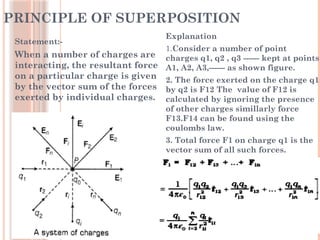
The document discusses electrostatics, focusing on Coulomb's law in vector form and the quantization of charge. It explains units of charge in both the SI and CGS systems, including coulombs, statcoulombs, and abcoloumbs, as well as the concept of dielectric constant. Additionally, it addresses the principle of superposition and poses several questions related to charge and electrical neutrality.