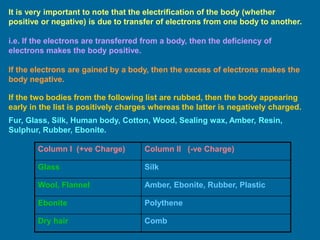
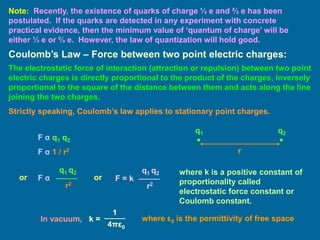
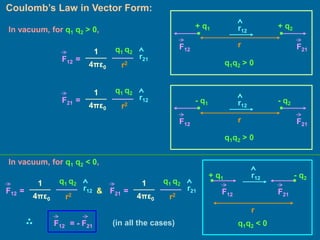
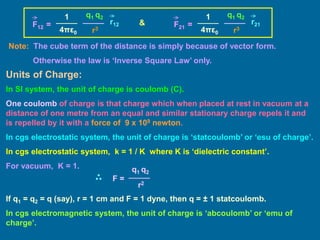
This document discusses the basics of electrostatics including frictional electricity, properties of electric charges, Coulomb's law, units of charge, and continuous charge distribution. It explains that rubbing two materials like glass and silk can cause the transfer of electrons leaving one material positively charged and the other negatively charged. Coulomb's law states that the electrostatic force between two point charges is directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. Continuous charge distributions can be characterized by linear, surface, and volume charge densities which describe the charge per unit length, area, or volume, respectively.