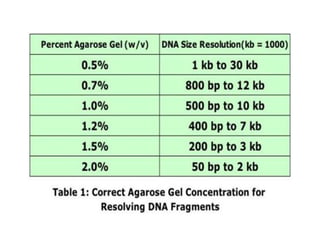
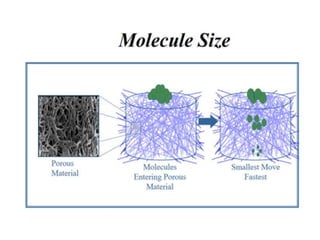
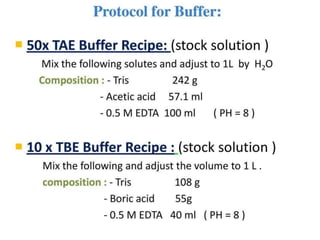
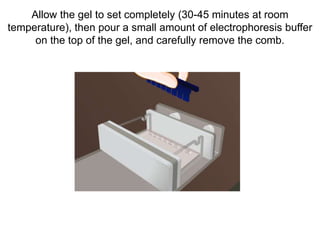
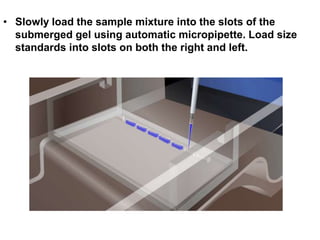
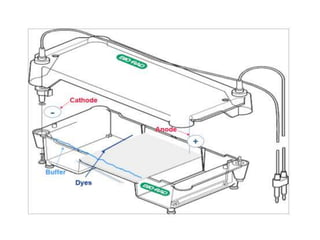
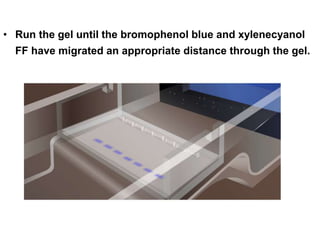
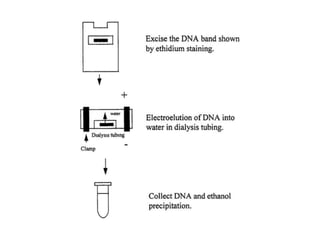
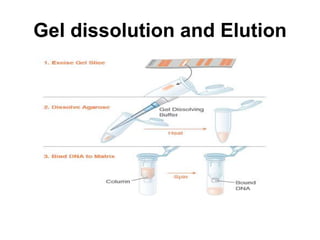
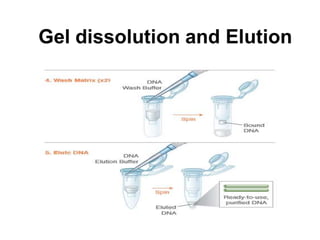
Electrophoresis is a technique used to separate molecules like proteins and nucleic acids based on their size and charge. It works by applying an electric current to move the molecules through a gel or liquid matrix. There are different types of gels like agarose and polyacrylamide that can be used depending on the size of molecules being separated. Agarose gels are commonly used to separate DNA fragments of different lengths. The process involves casting an agarose gel, loading samples mixed with a dye, running a current through the gel, and visualizing the separated DNA bands.