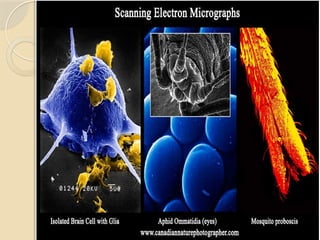
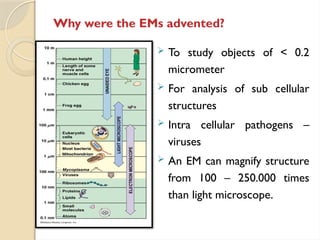
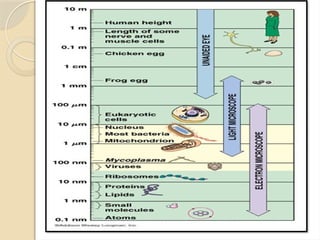
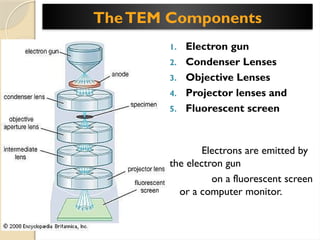
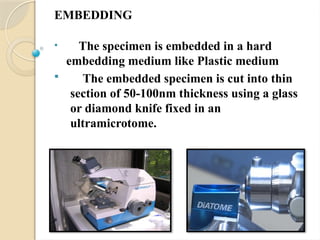
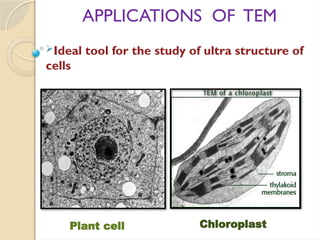
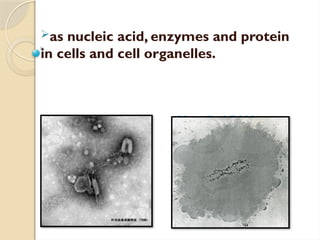
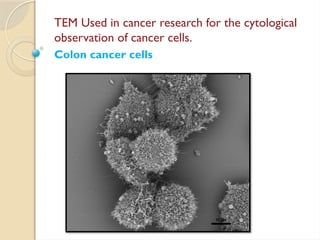
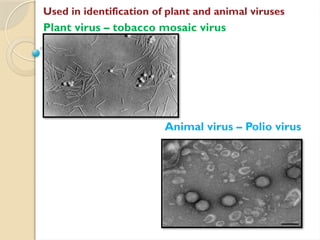
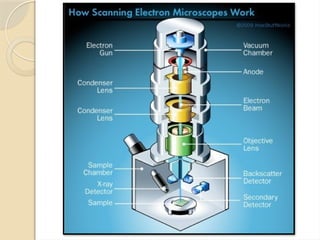
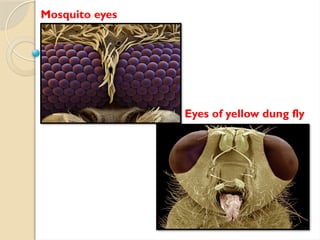
Electron microscopes utilize high-energy electrons to provide detailed information about objects at a scale below 0.2 micrometers, revealing topography, morphology, composition, and crystallographic data. The two main types are Transmission Electron Microscopes (TEM), which study inner components, and Scanning Electron Microscopes (SEM), which visualize surfaces. TEM is particularly powerful for magnifying up to one million times and is applied in various fields, including cancer research and virology, while SEM provides 3D structural analysis of surfaces.