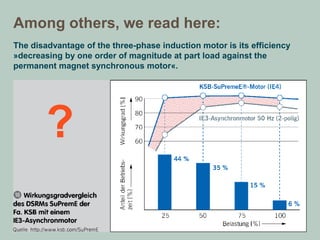
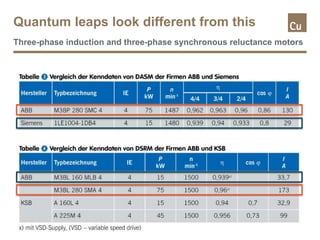
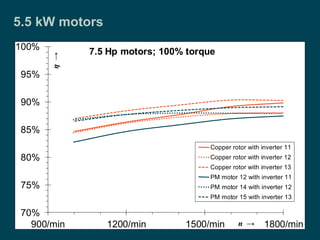
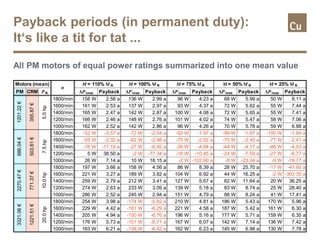
The document compares the efficiency of permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSMs) with cast copper cage induction motors, highlighting the efficiency drop of induction motors at part load versus PMSMs. It details the measurements conducted on various motor types, the challenges in acquiring the motors, and the differences in costs and lead times. Overall, it critiques the methodology of comparing high-performance PMSMs with average induction motors, emphasizing the nuances in efficiency across different operating conditions.