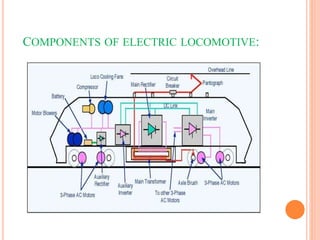
An electric locomotive uses electricity to power its motors instead of an onboard fuel source. It collects power through overhead lines or a third rail. Early electric locomotives used DC current, but modern ones use AC current with three-phase induction motors powered by rectifiers and inverters. Key components include pantographs, circuit breakers, transformers, and regenerative braking systems which convert kinetic energy to electricity during braking. Electric locomotives have advantages over diesel such as higher energy efficiency and lower emissions.