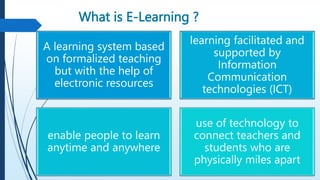
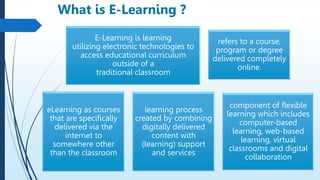
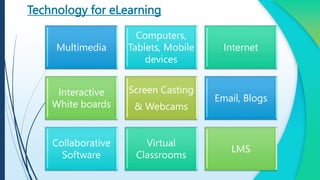
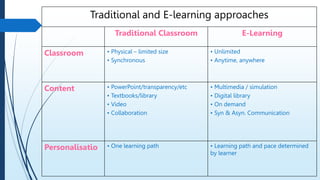
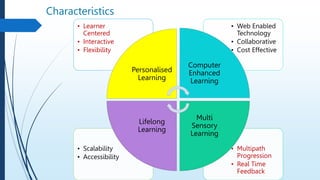
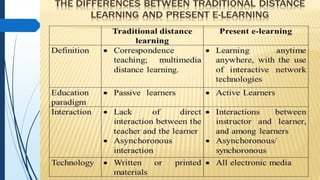
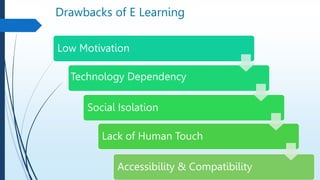
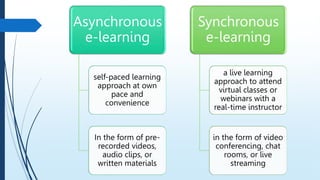
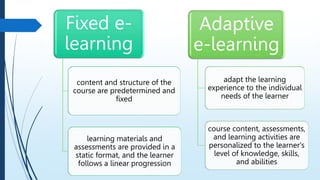
E-learning refers to online learning facilitated through information communication technologies. It allows learning to occur anytime and anywhere through electronic resources. E-learning has grown due to increased demand for flexible education opportunities and the need to reduce costs. It offers benefits like personalized learning, improved retention, and environmental sustainability. While e-learning has drawbacks like low motivation and isolation, it comes in asynchronous, synchronous, fixed, and adaptive formats and can be used for teaching, online courses, training, and more.