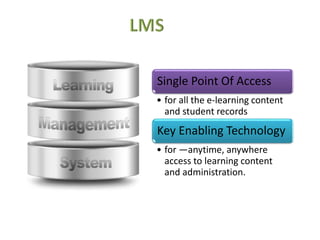
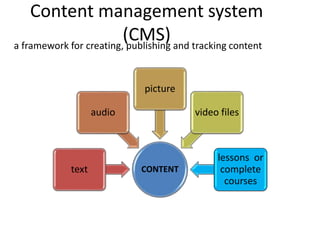
This document discusses learning management systems (LMS), content management systems (CMS), and learning content management systems (LCMS). It defines each term and outlines their key differences. An LMS is focused on managing how individuals participate in e-learning programs, tracking learner data. A CMS is concerned with how content for e-learning is created, published, and tracked. An LCMS is an integrated solution that provides a multi-user environment for developing, storing, reusing, delivering, and managing digital learning content from a central repository.