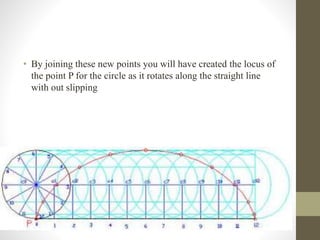
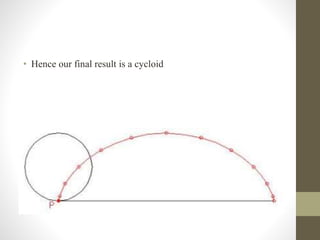
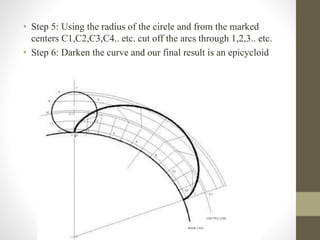
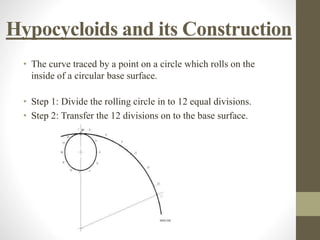
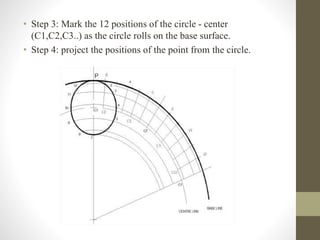
This document provides information about cycloidal curves. It defines different types of cycloidal curves that are generated when a circle rolls along a straight line or another circle without slipping. These include cycloids, epicycloids, and hypocycloids. The document outlines the classification of these curves and provides step-by-step instructions for constructing cycloids, epicycloids, and hypocycloids using compasses. It concludes with some applications of cycloidal curves in gear design, conveyors, and mechanical mechanisms.