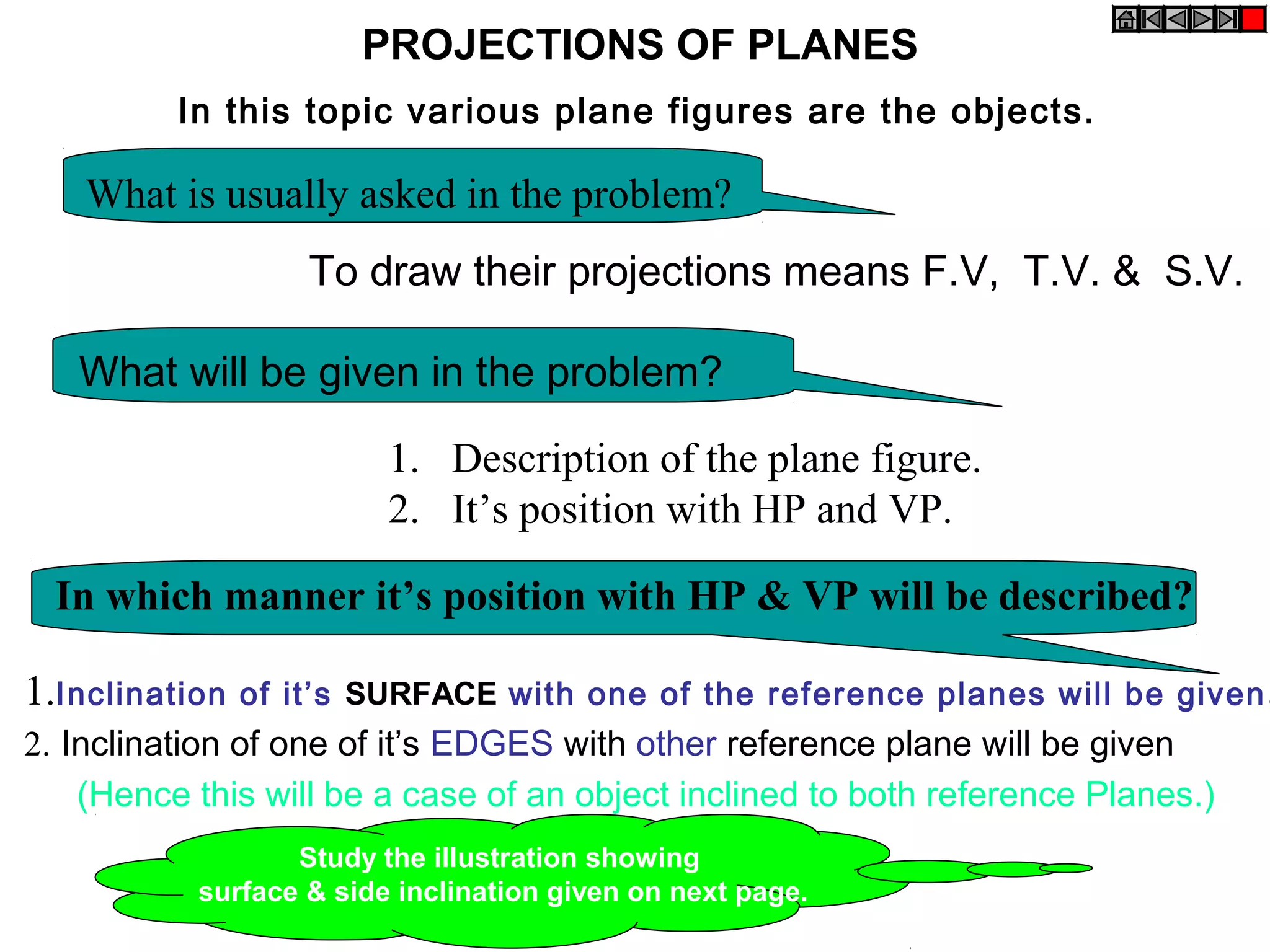
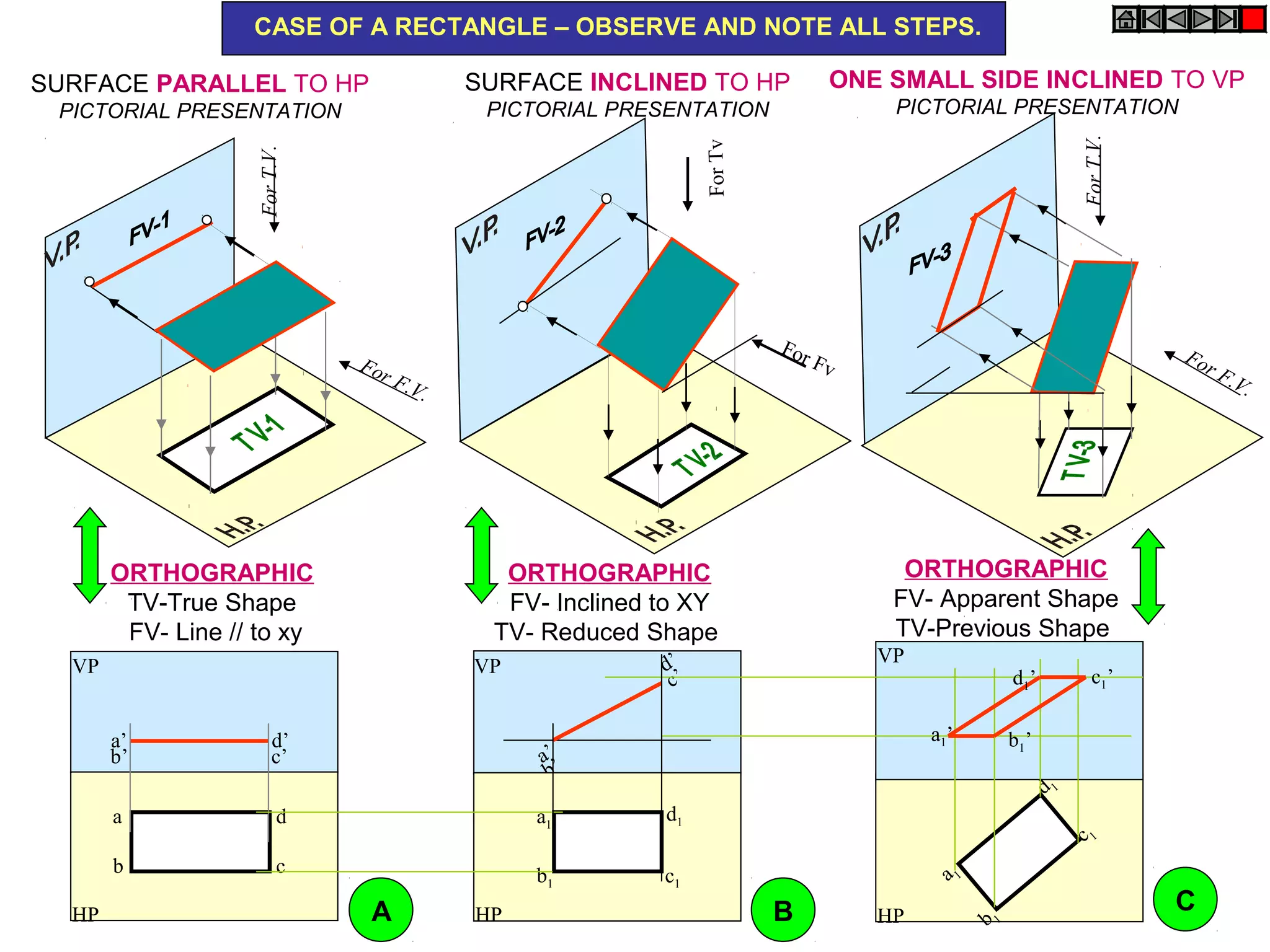
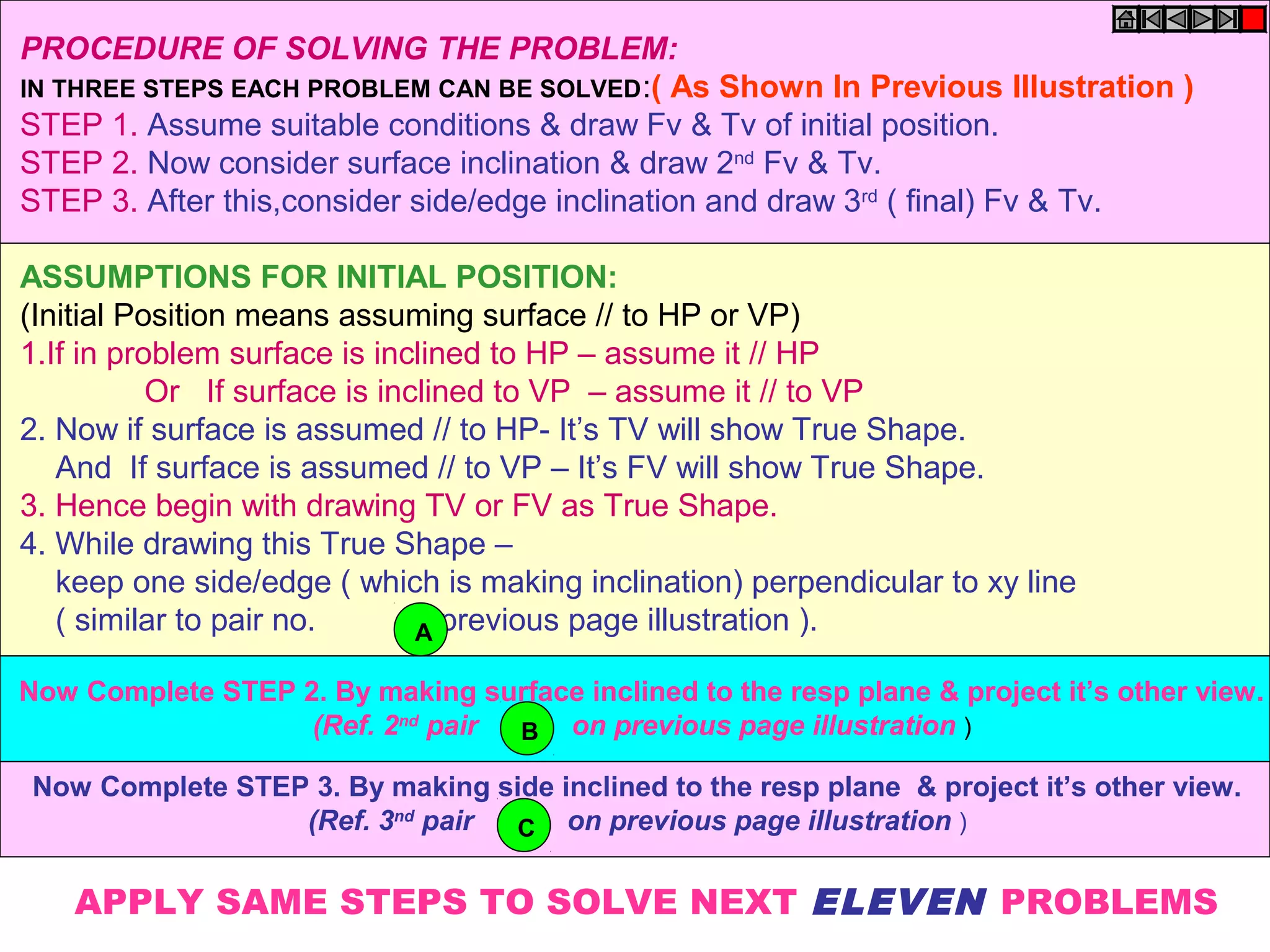
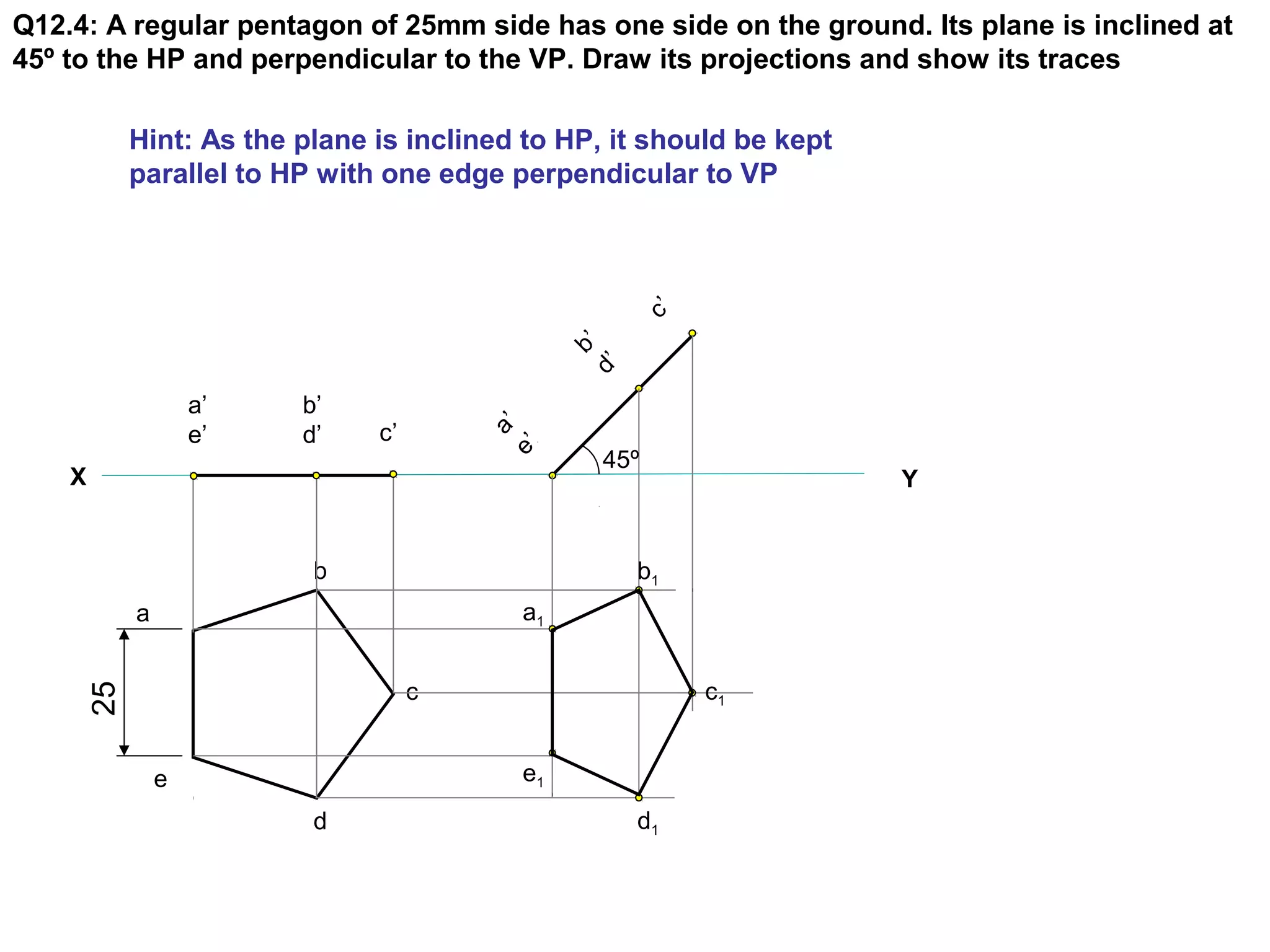
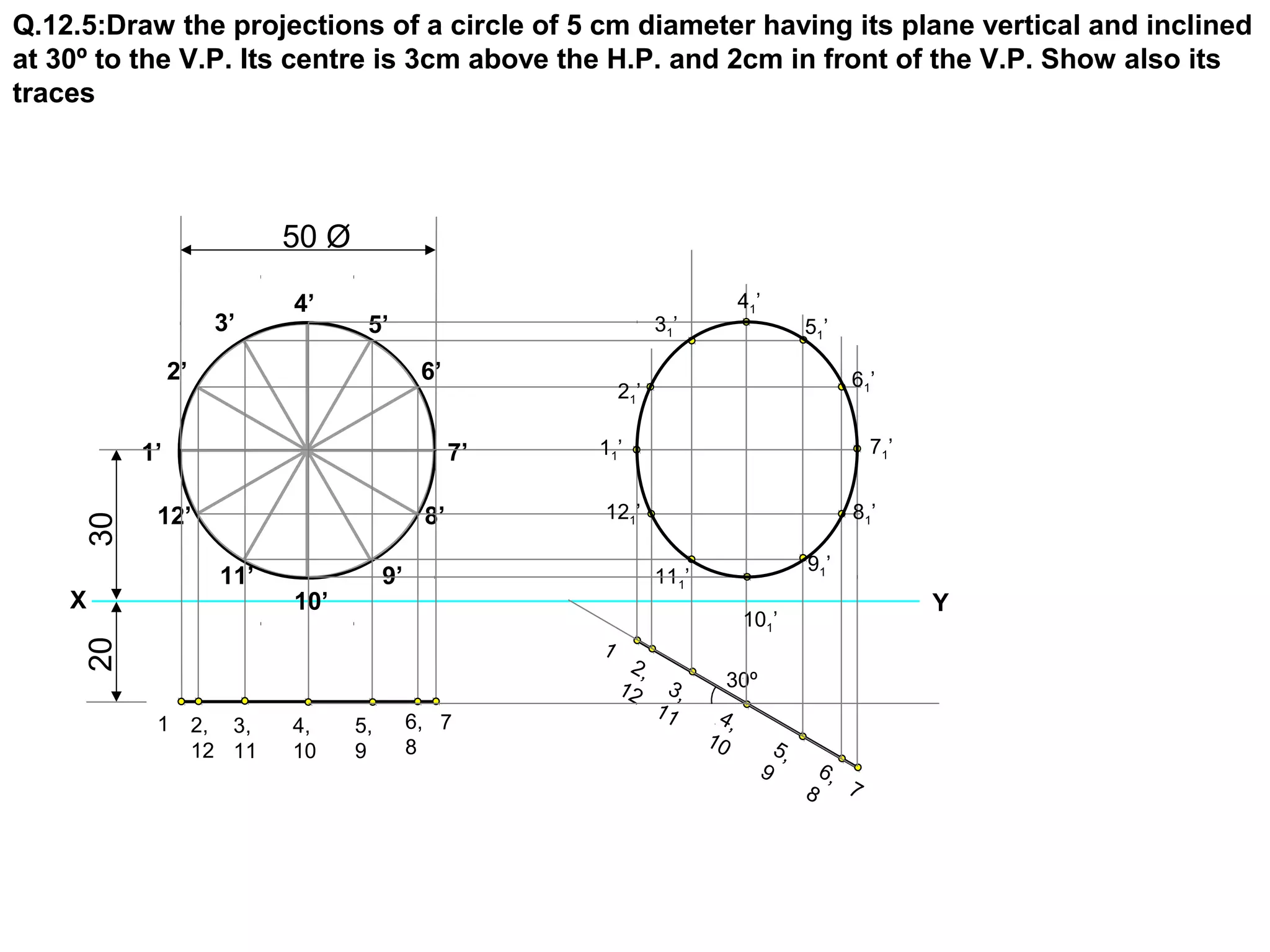
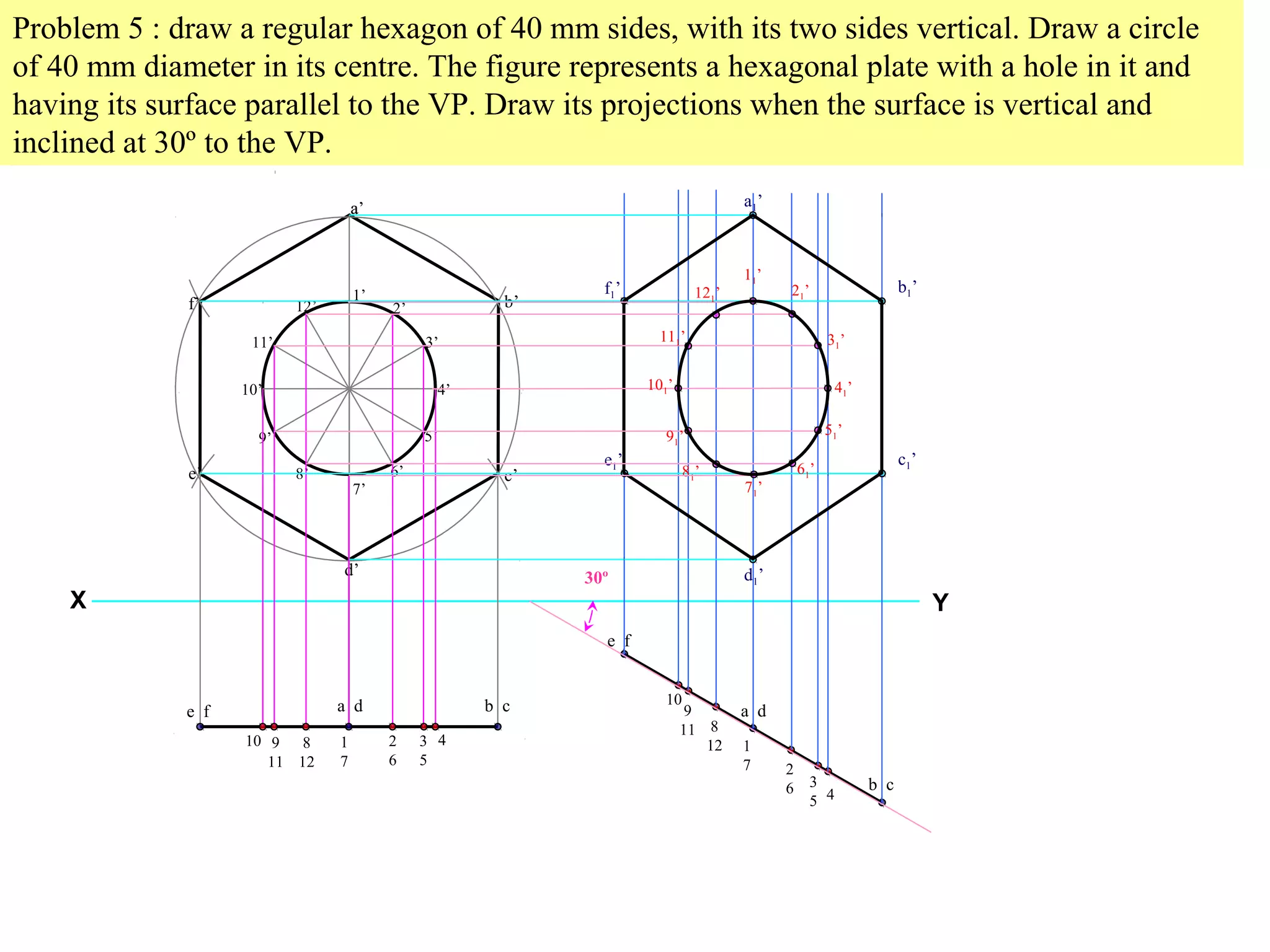
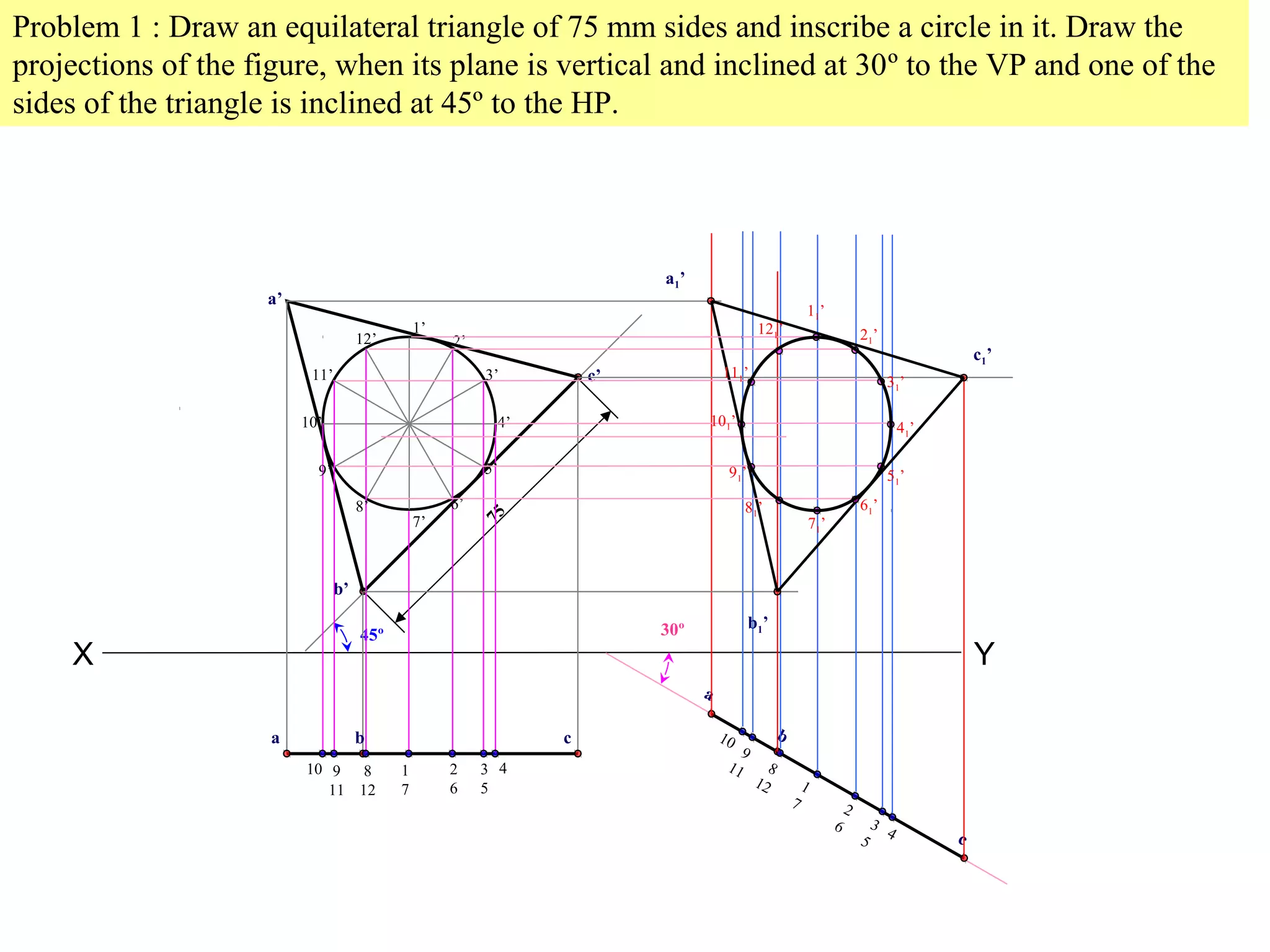
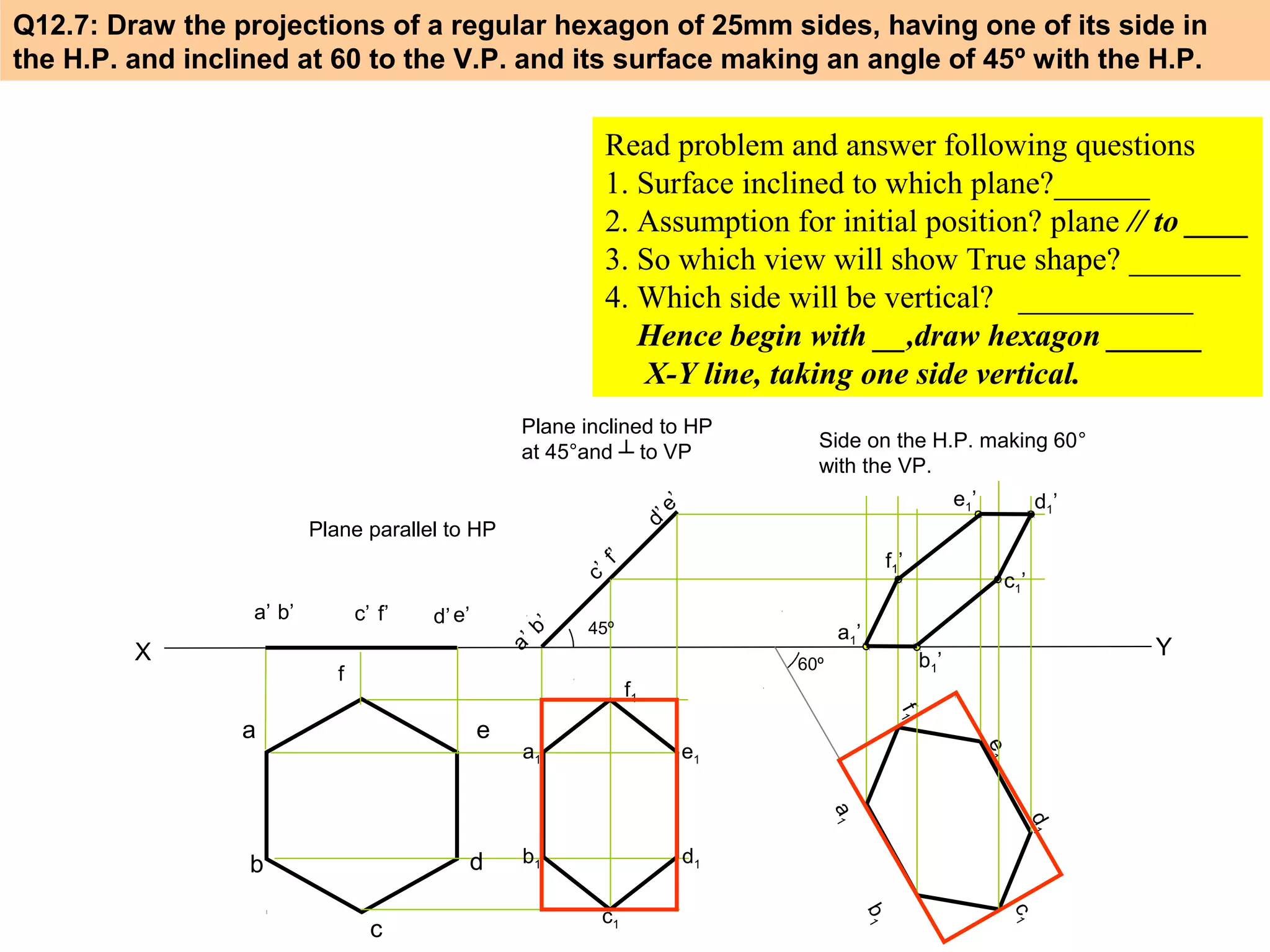
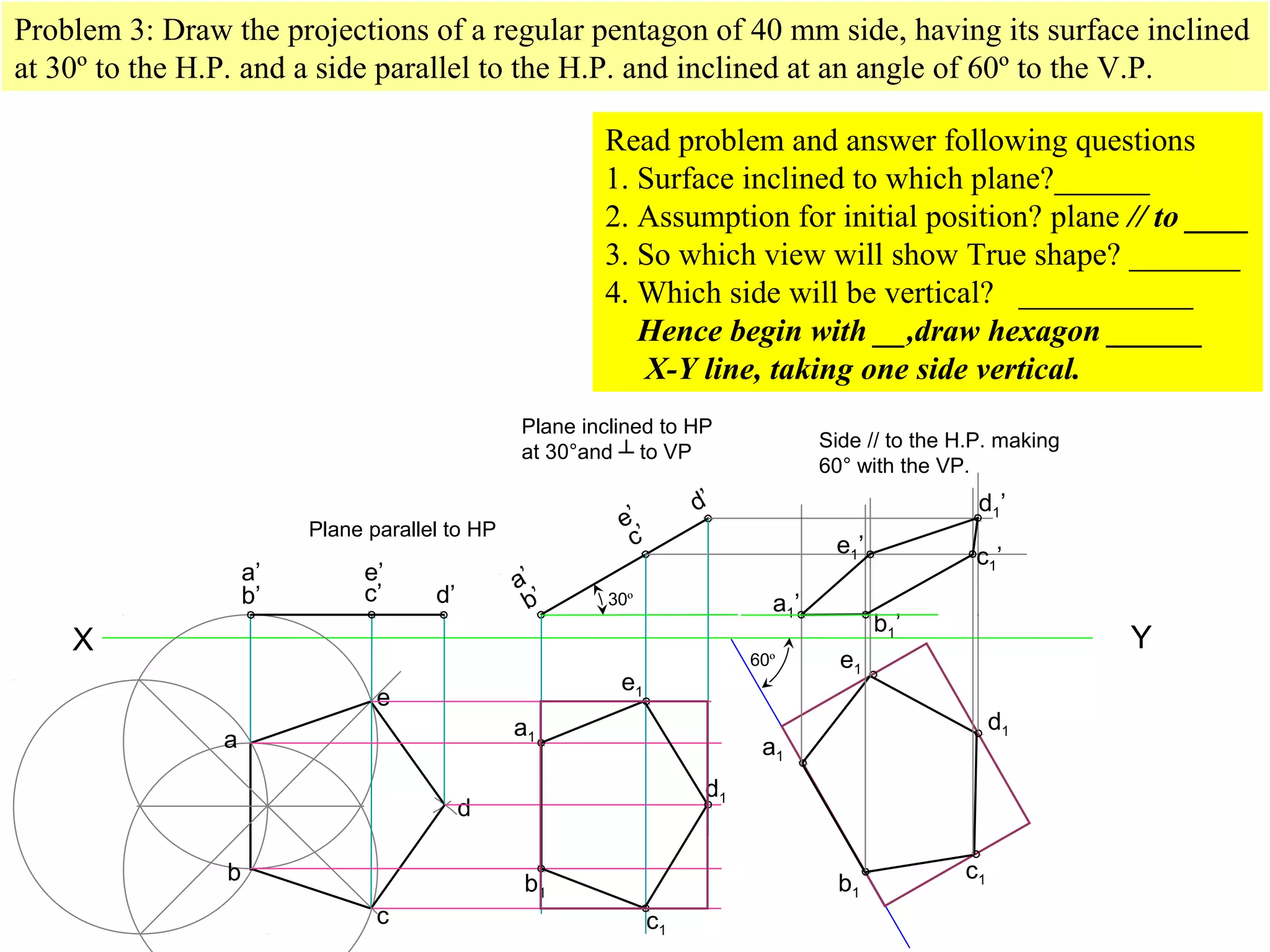
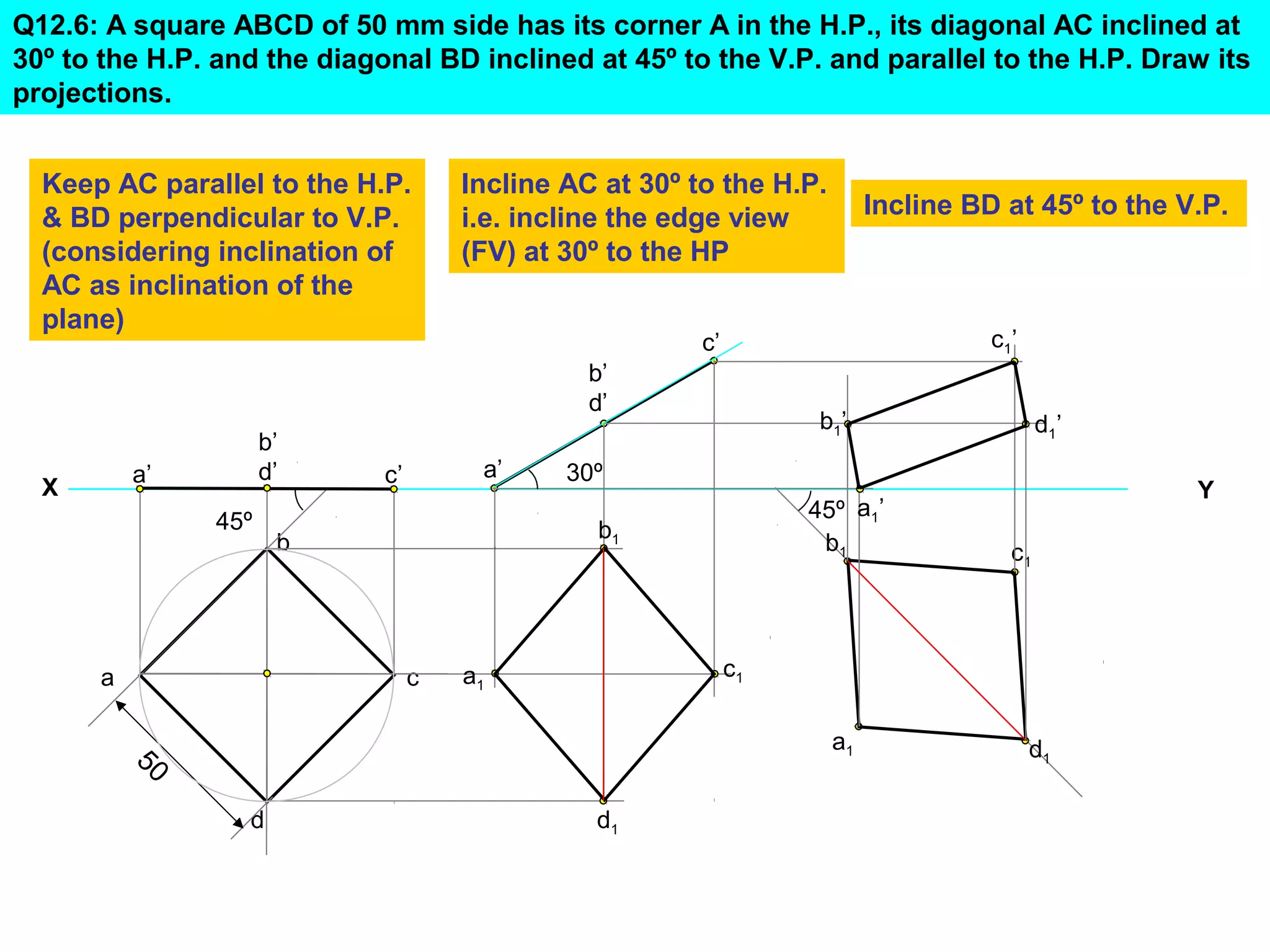
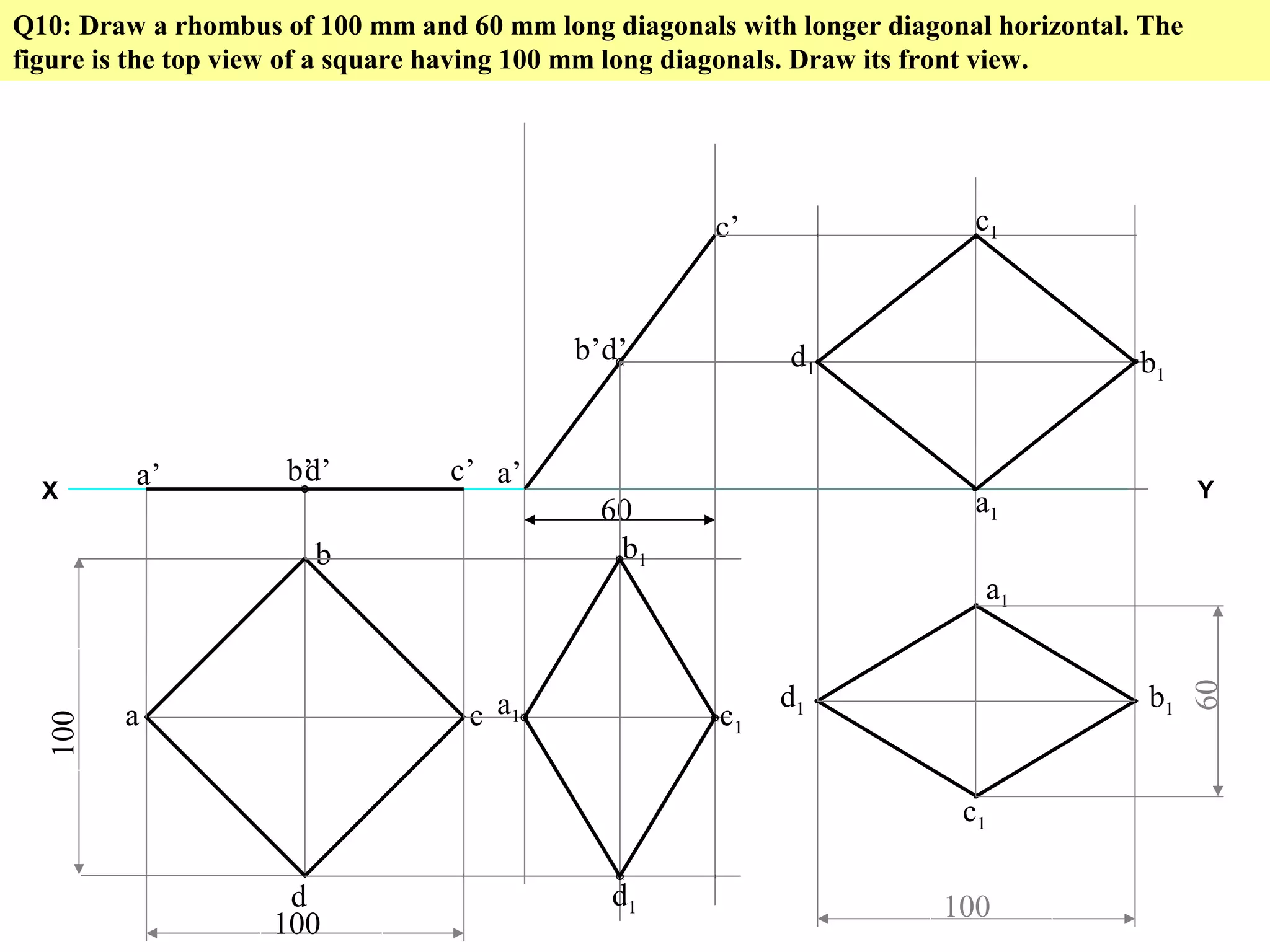
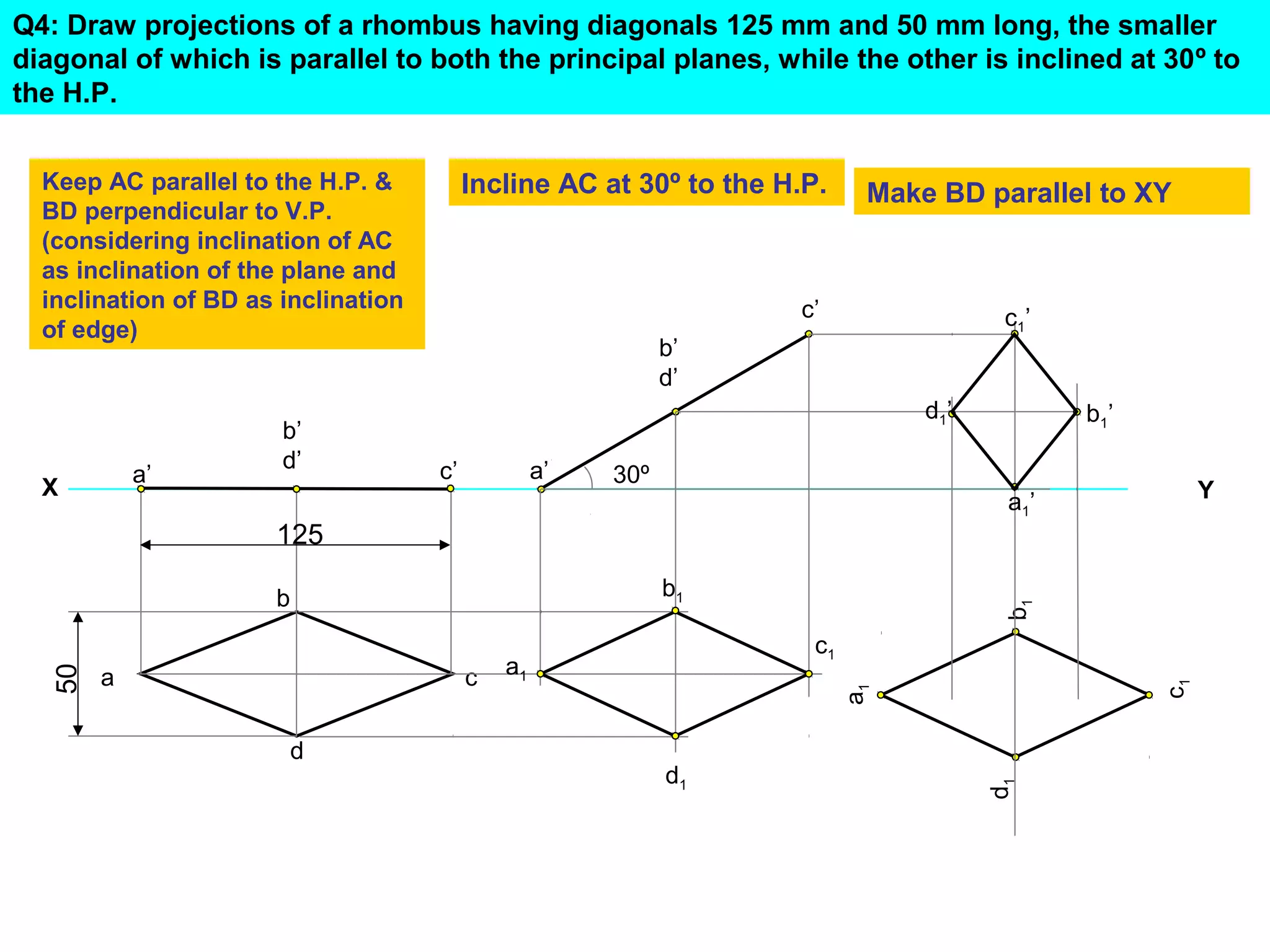
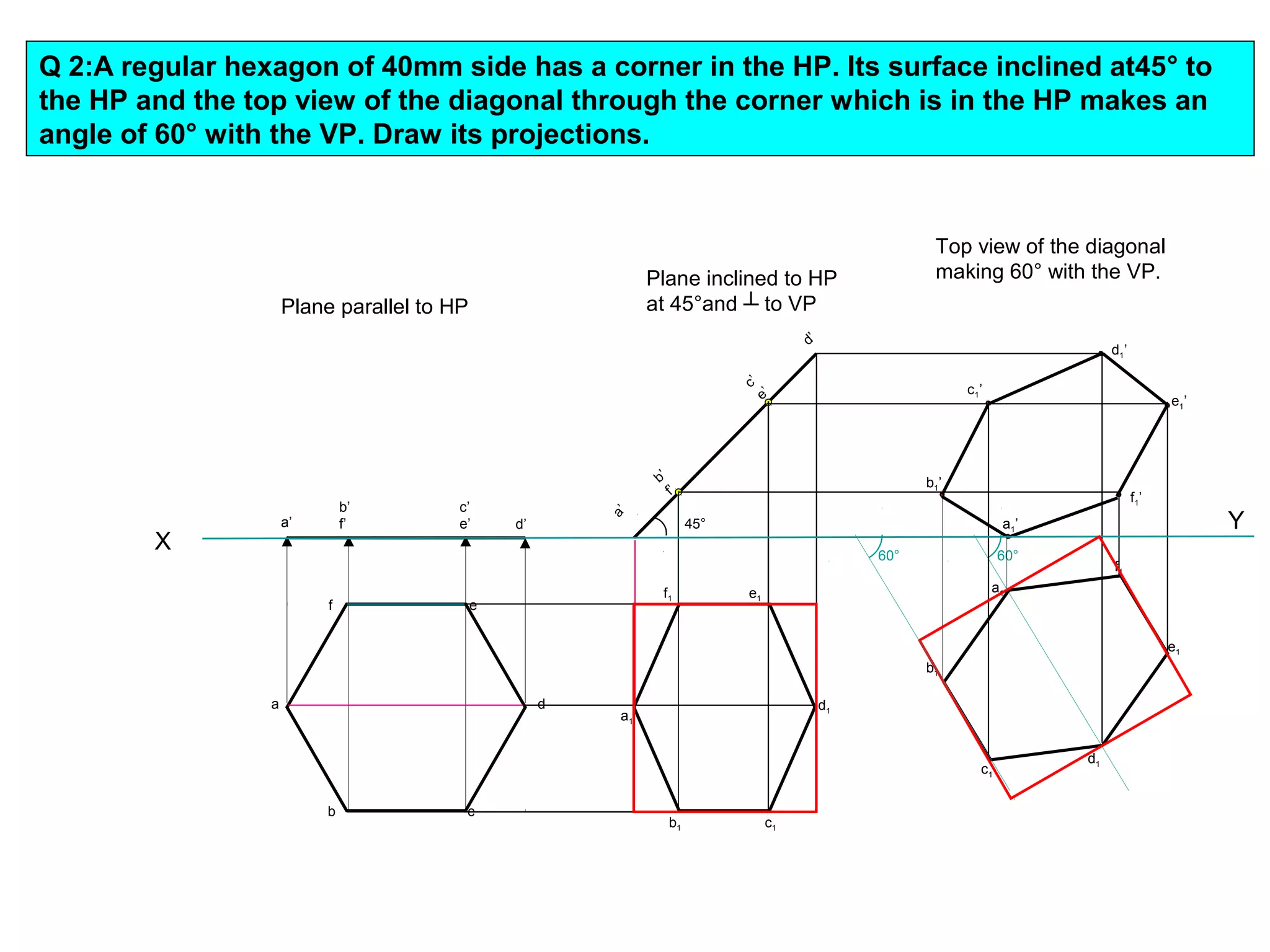
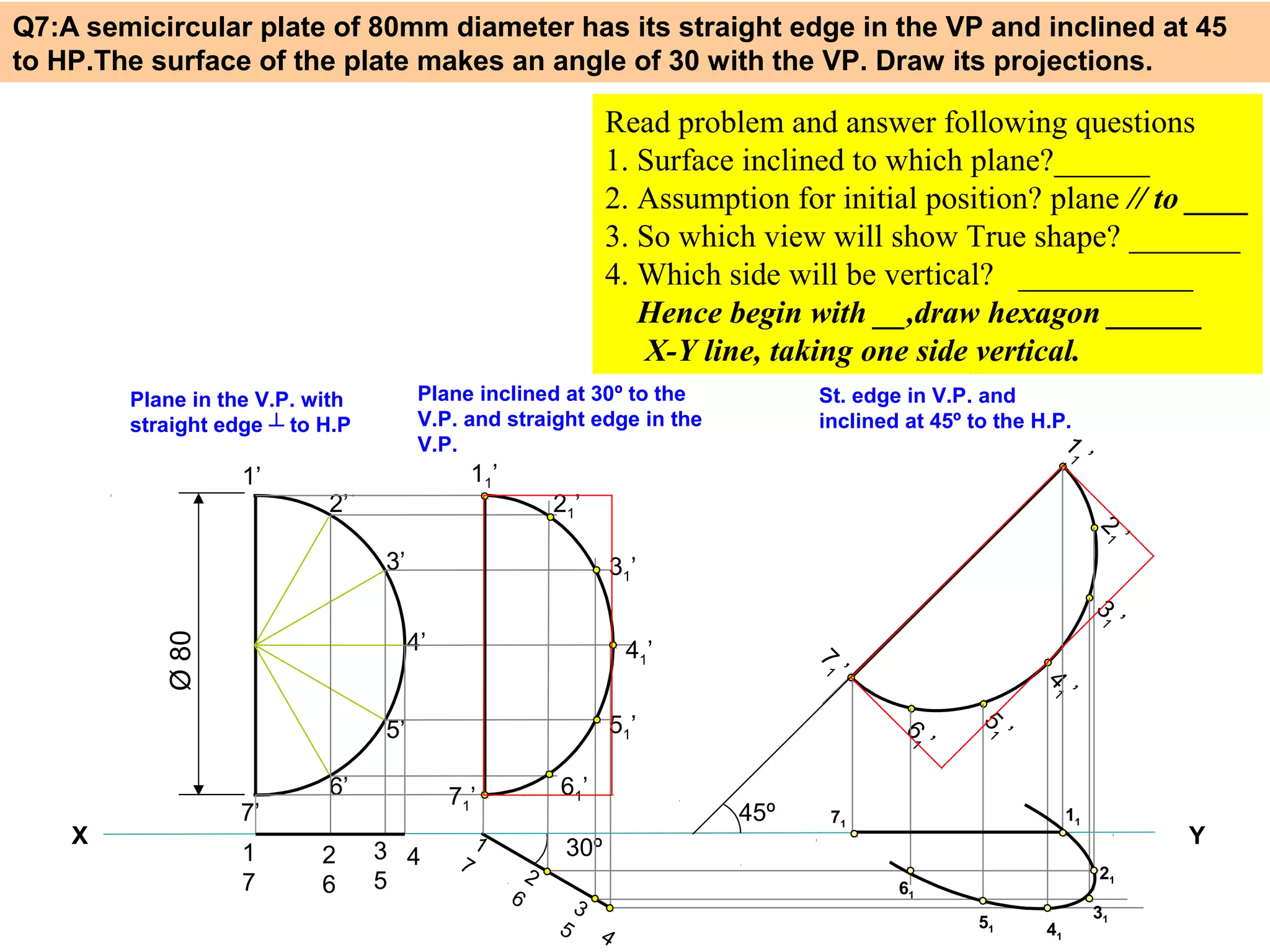
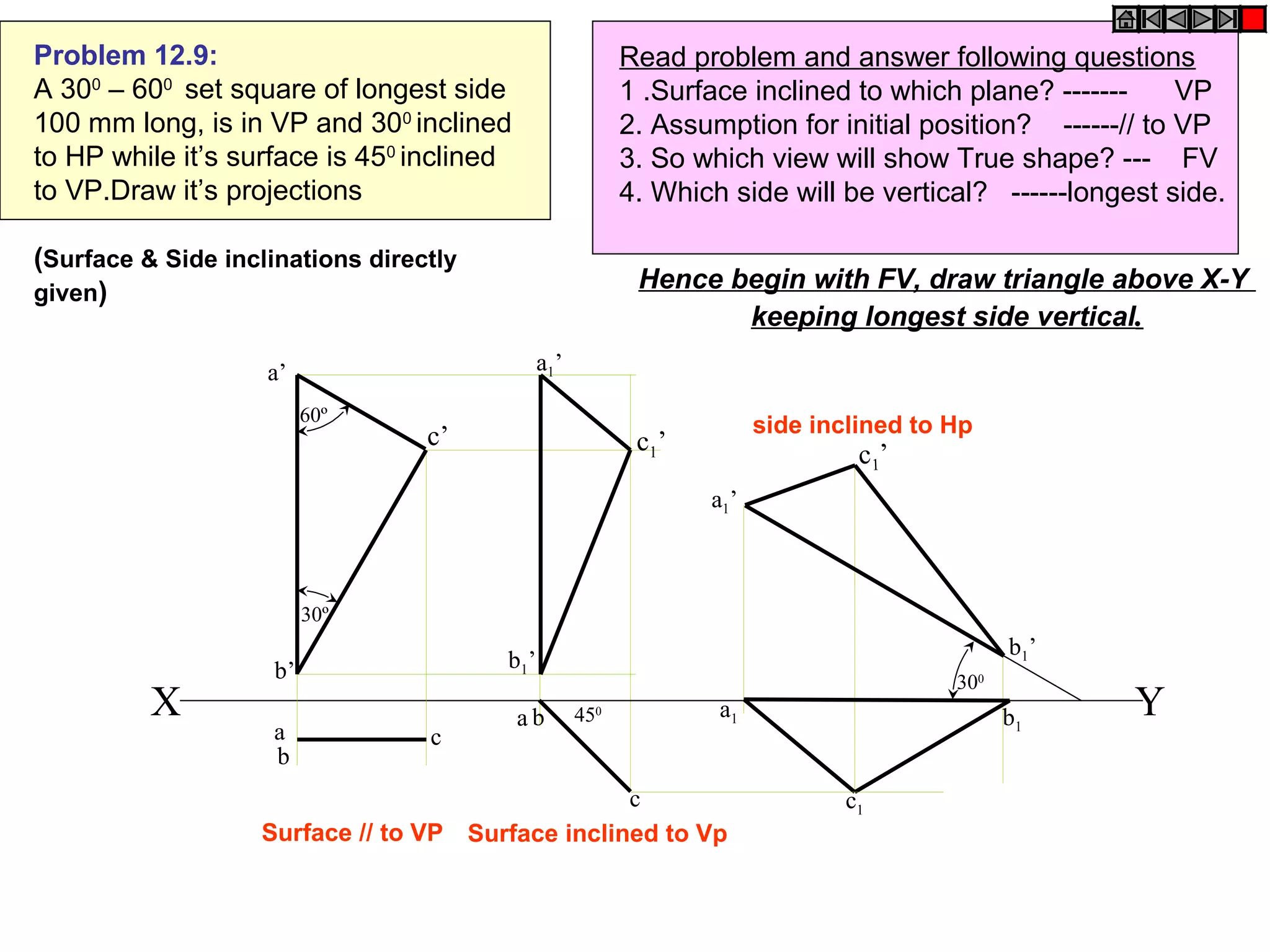
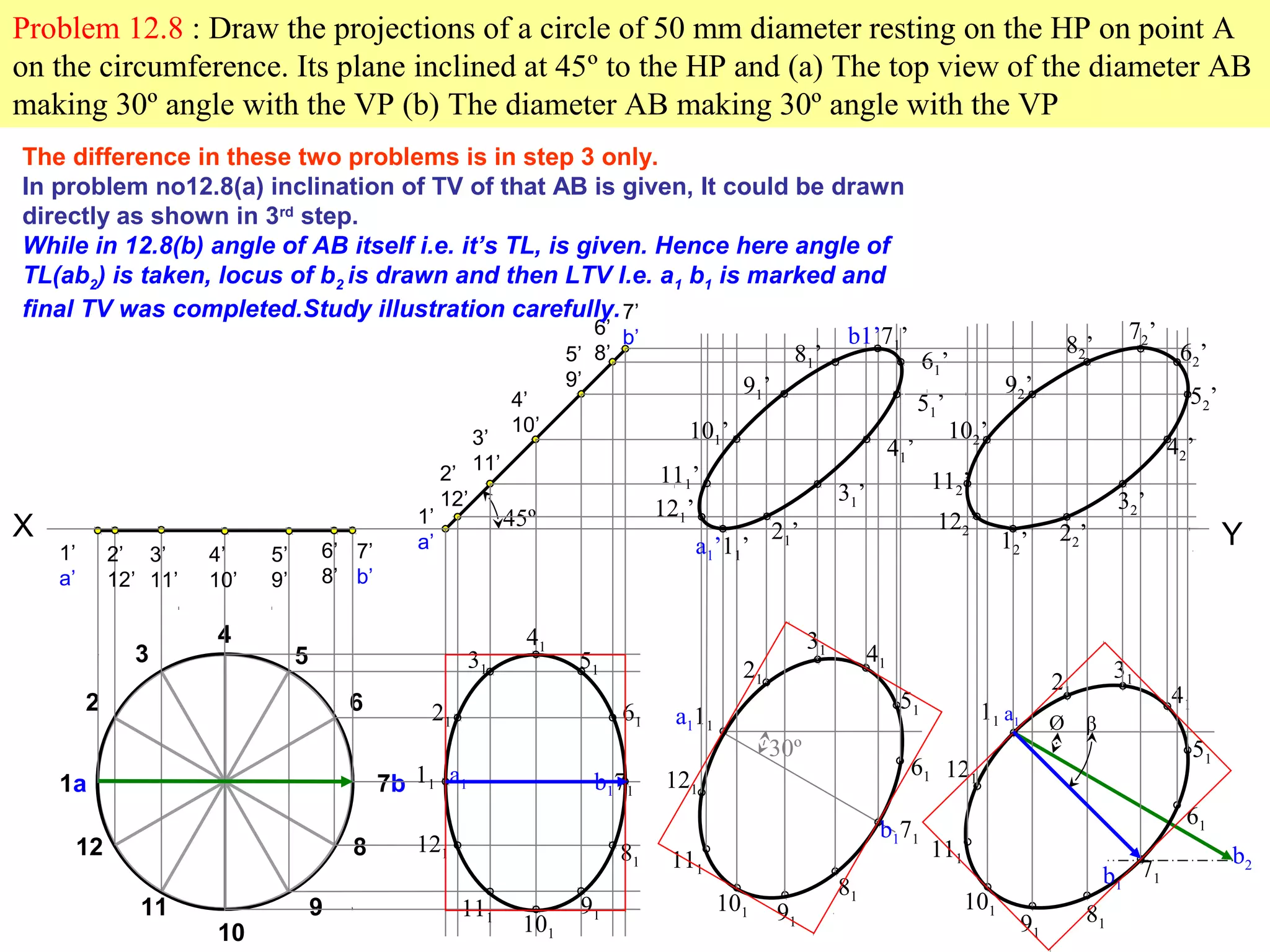
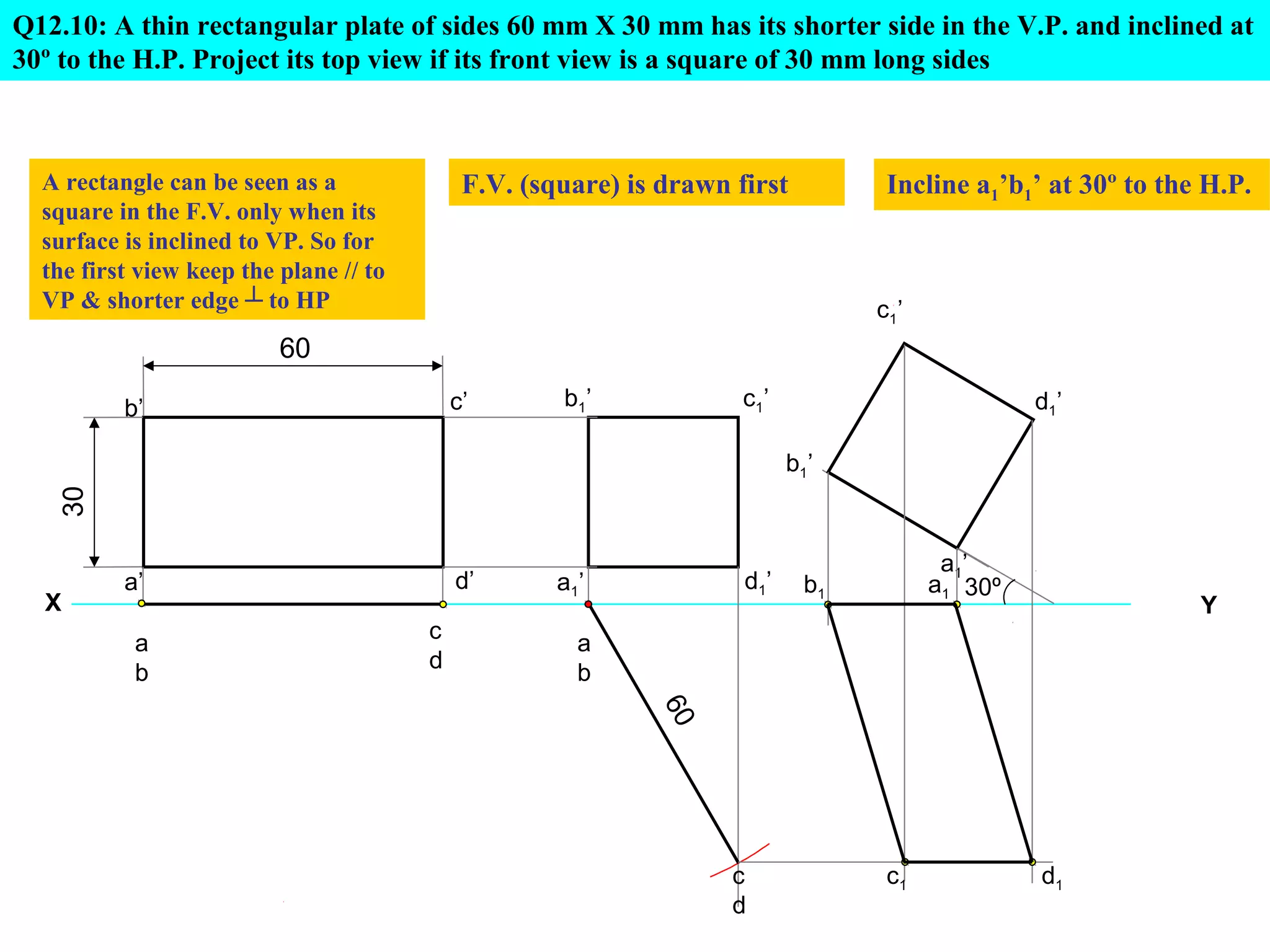
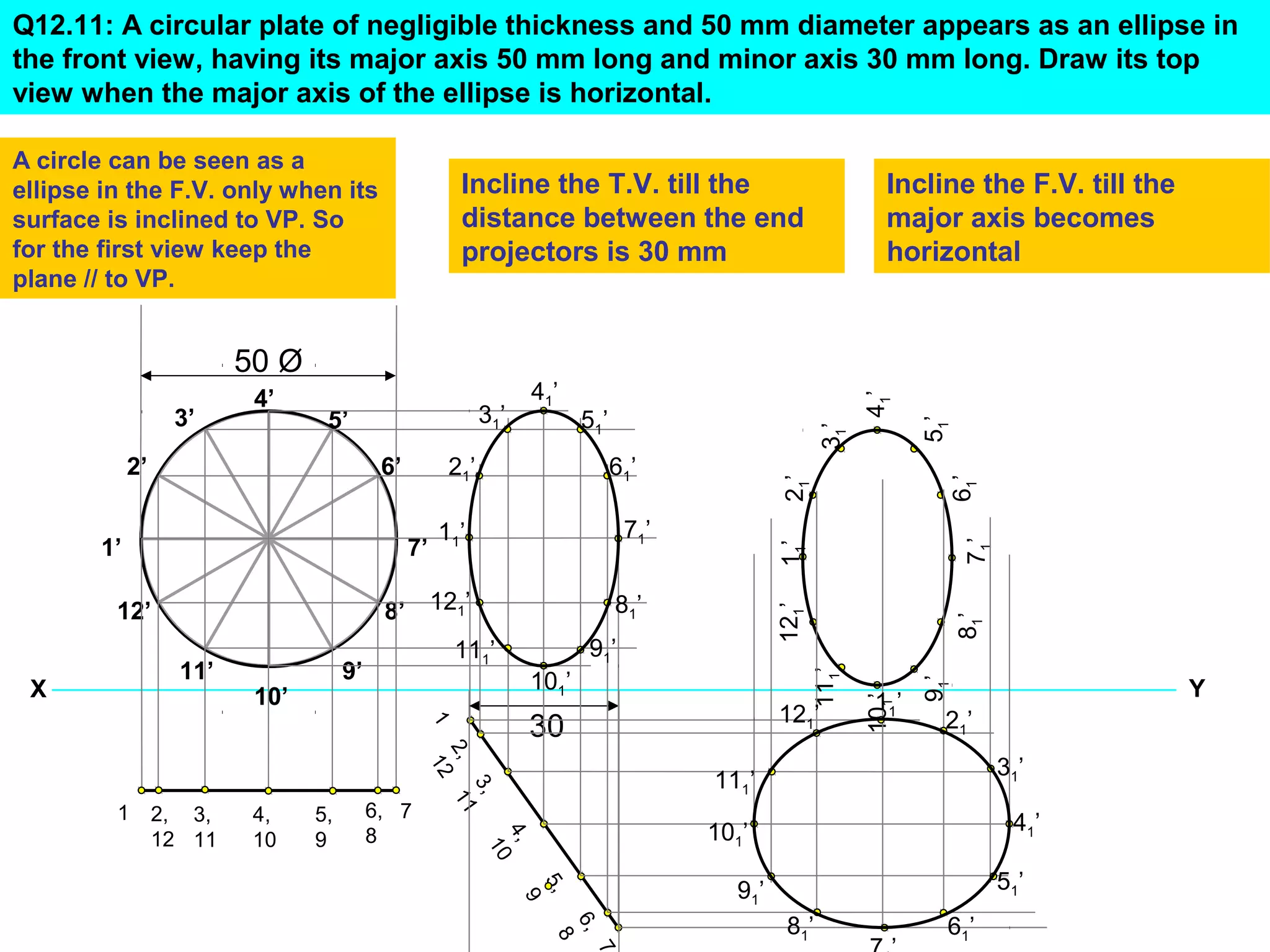
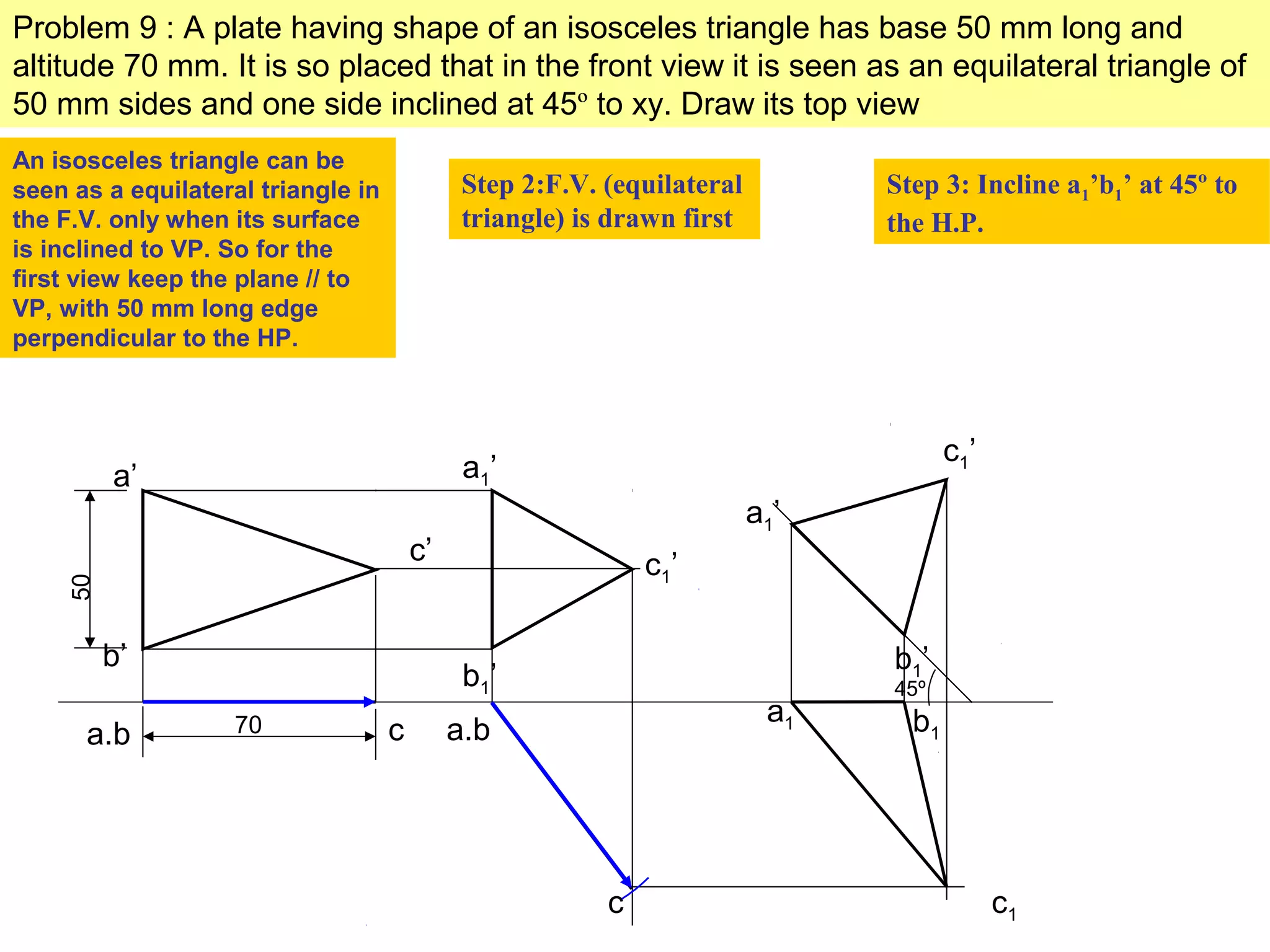
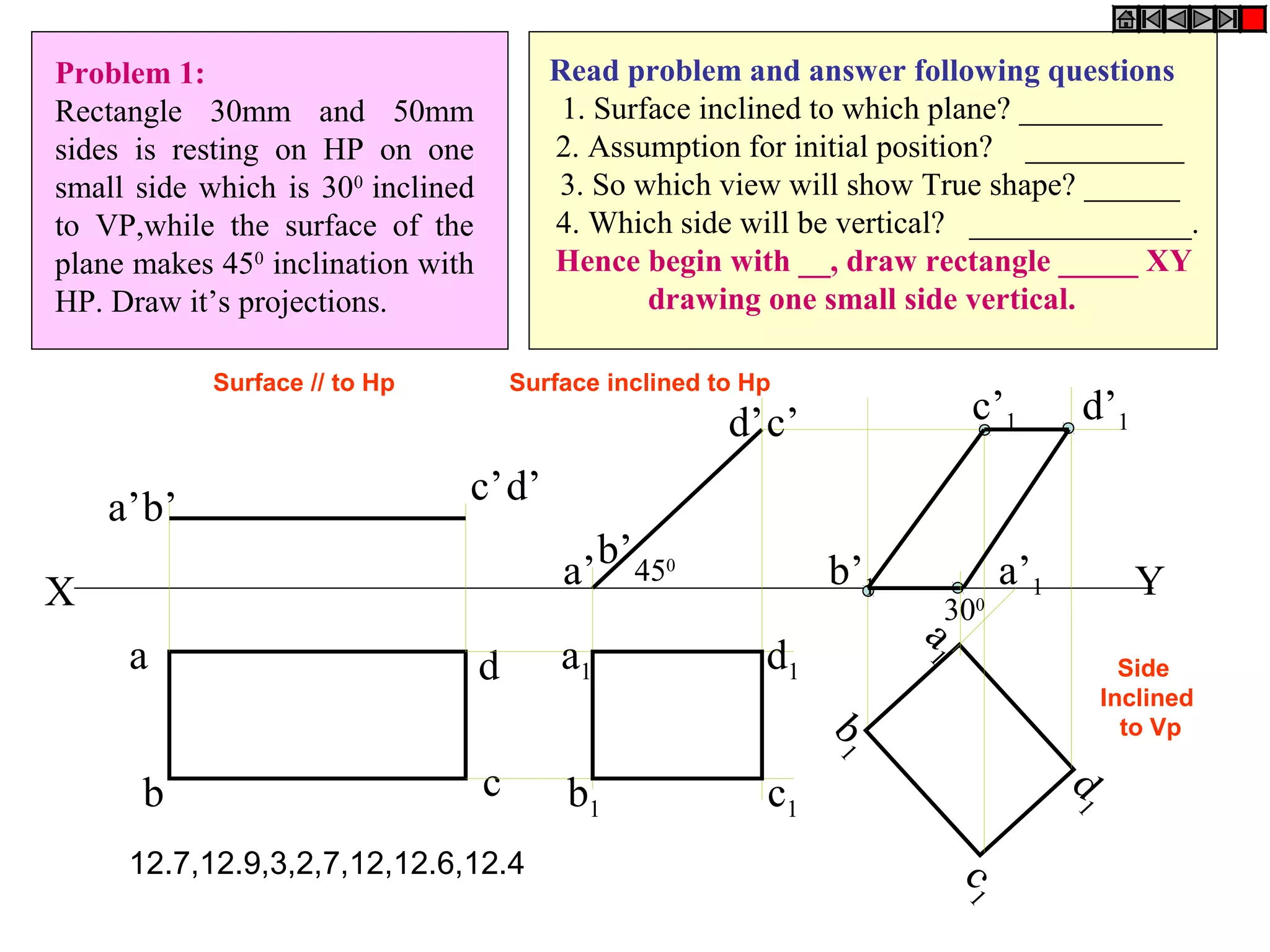
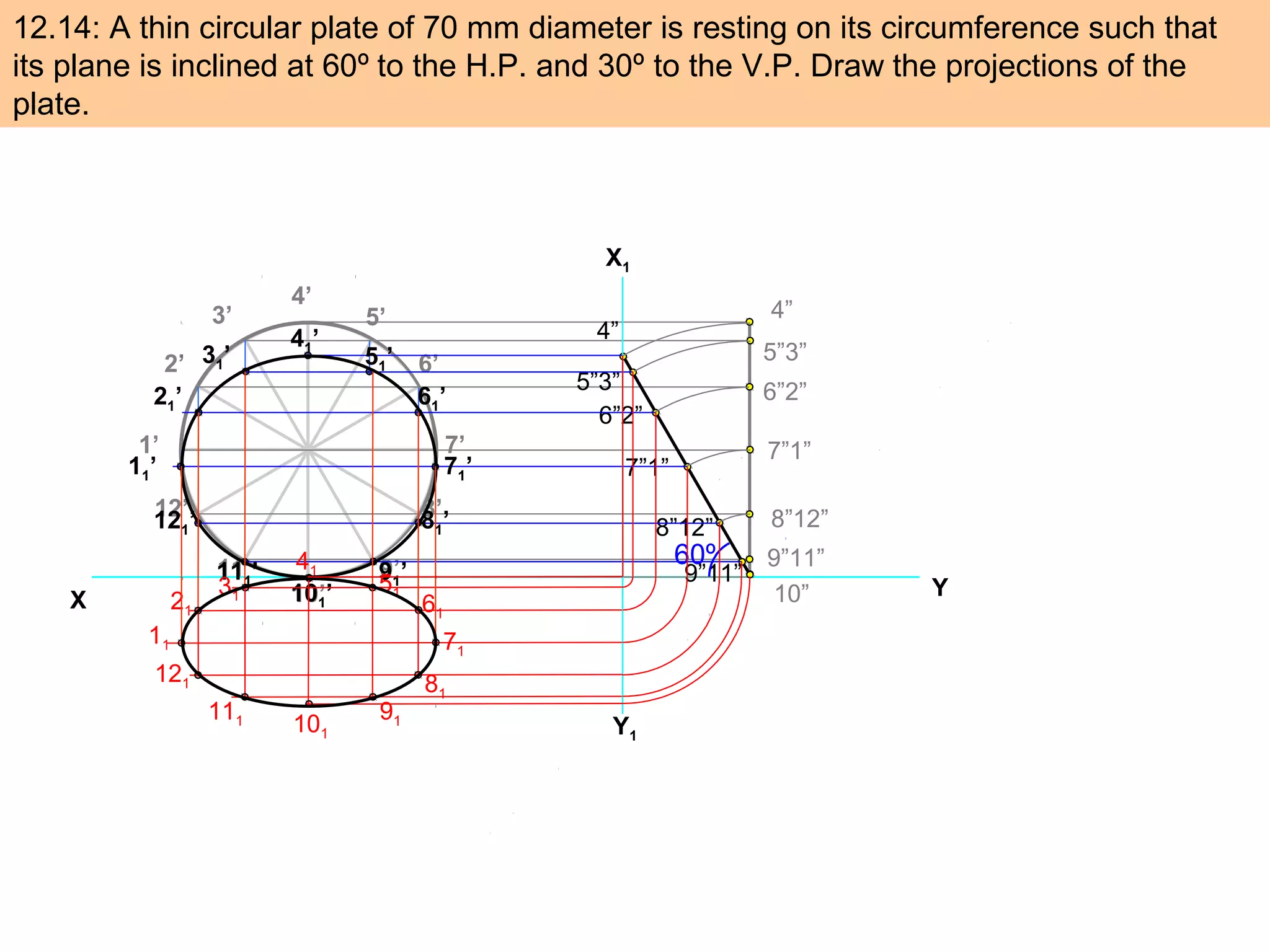
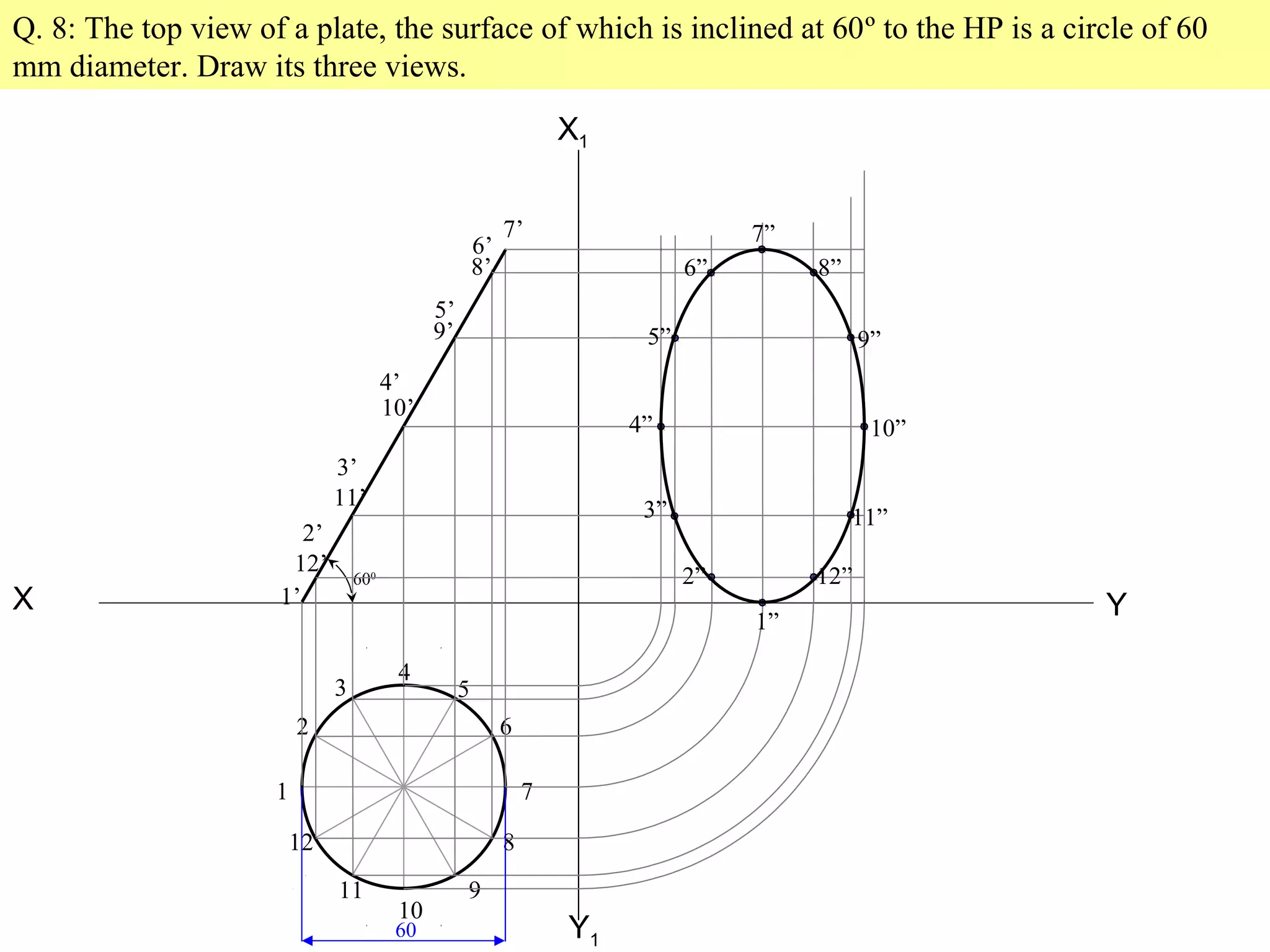
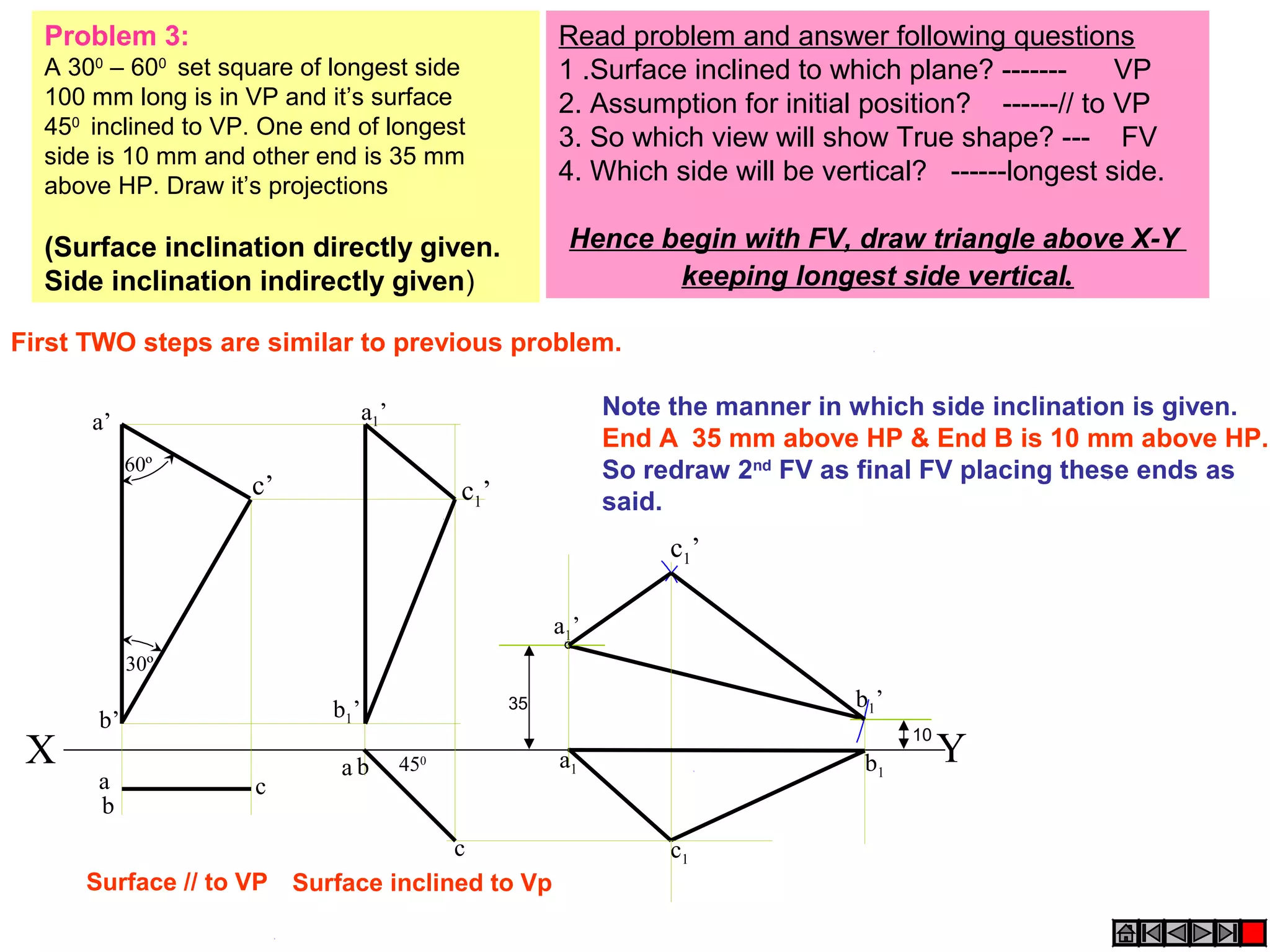
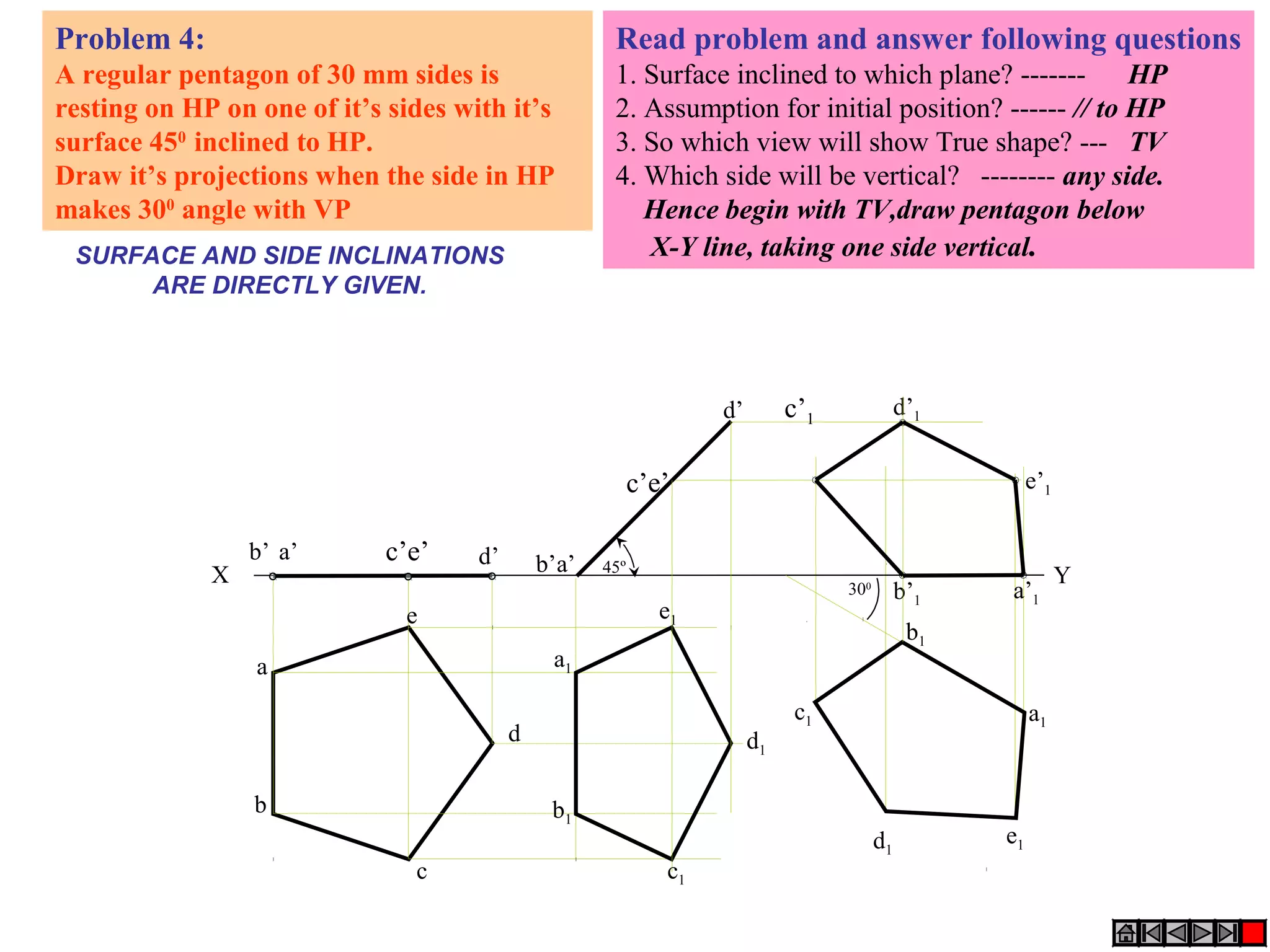
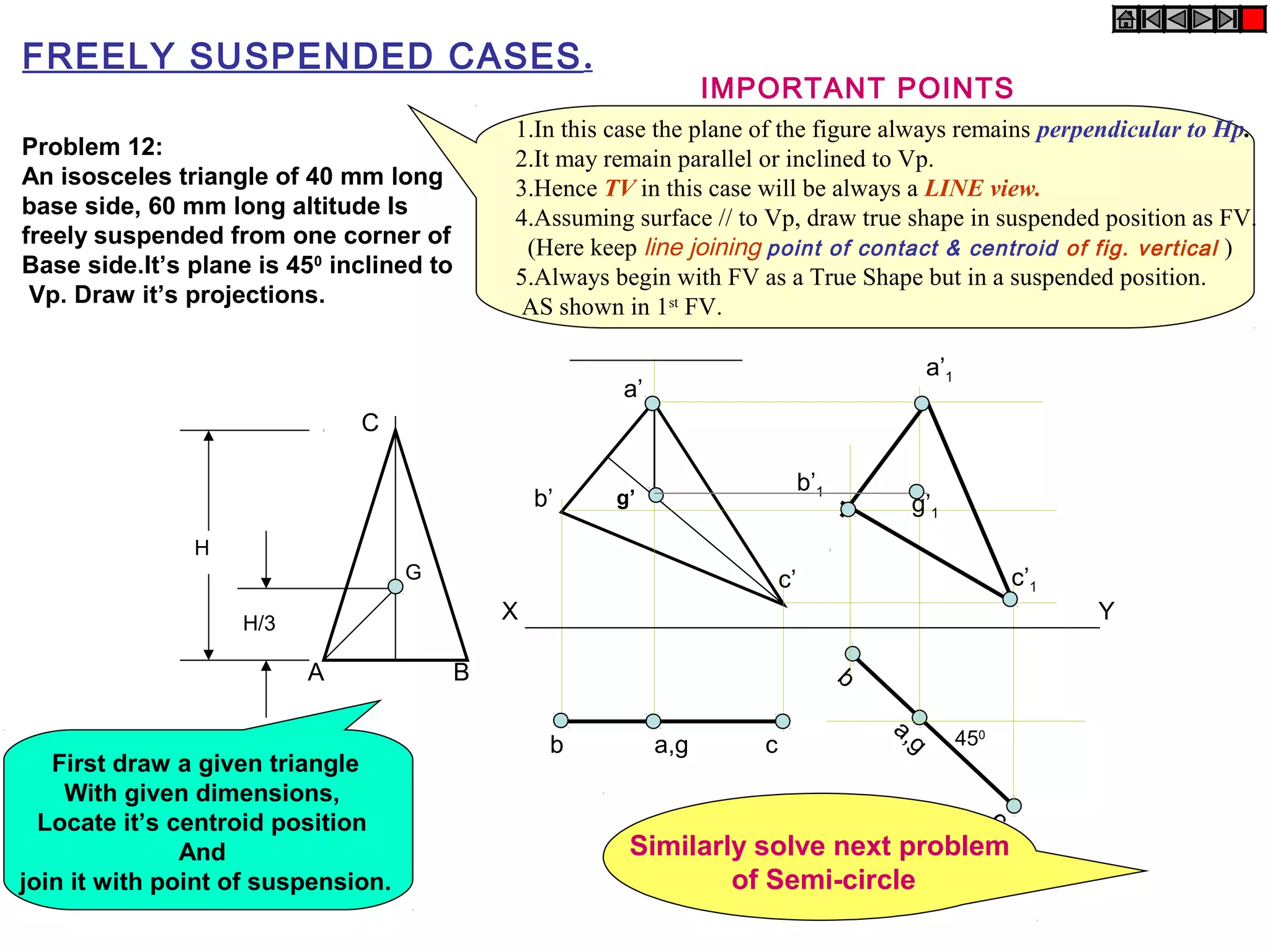
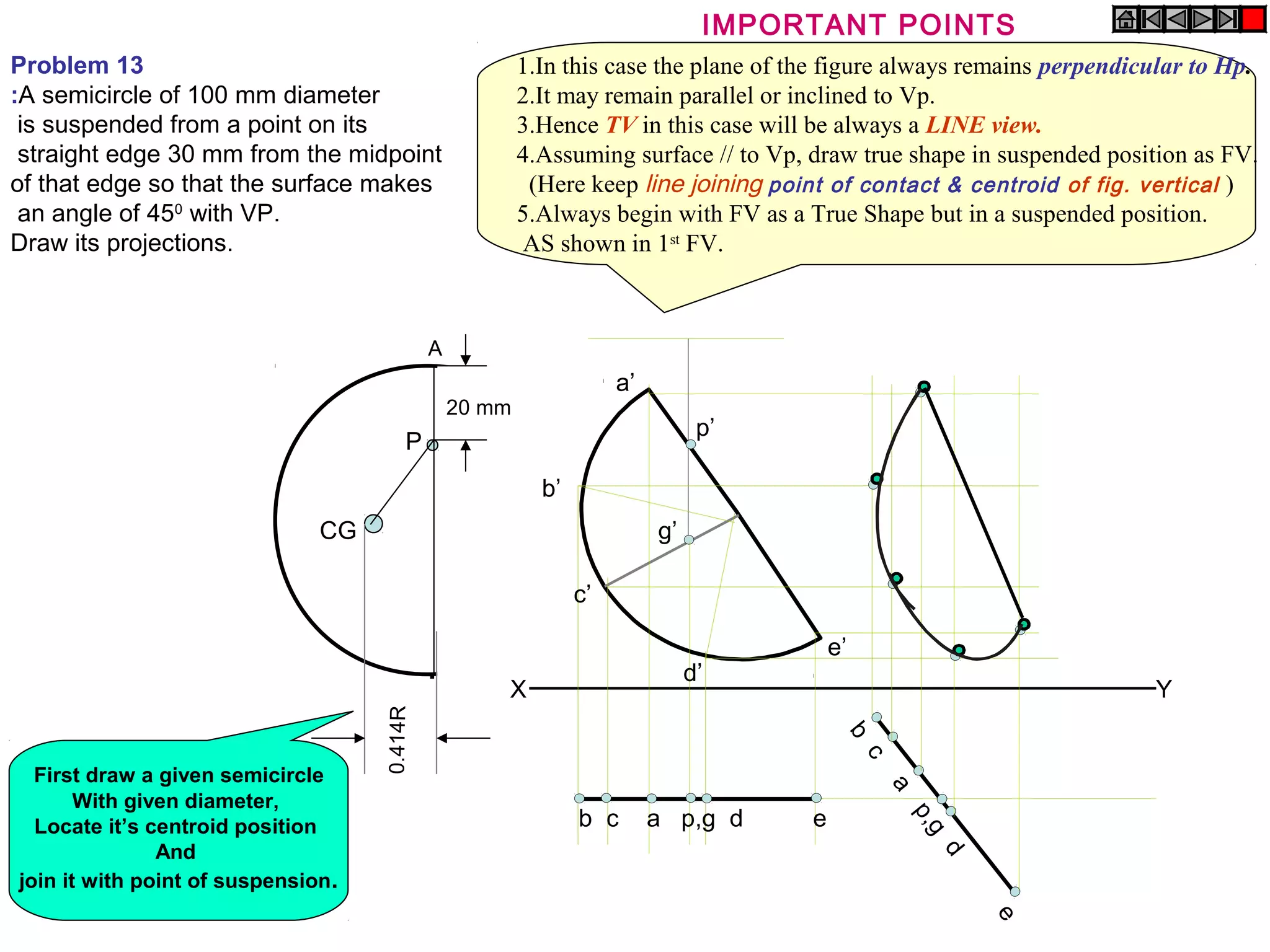
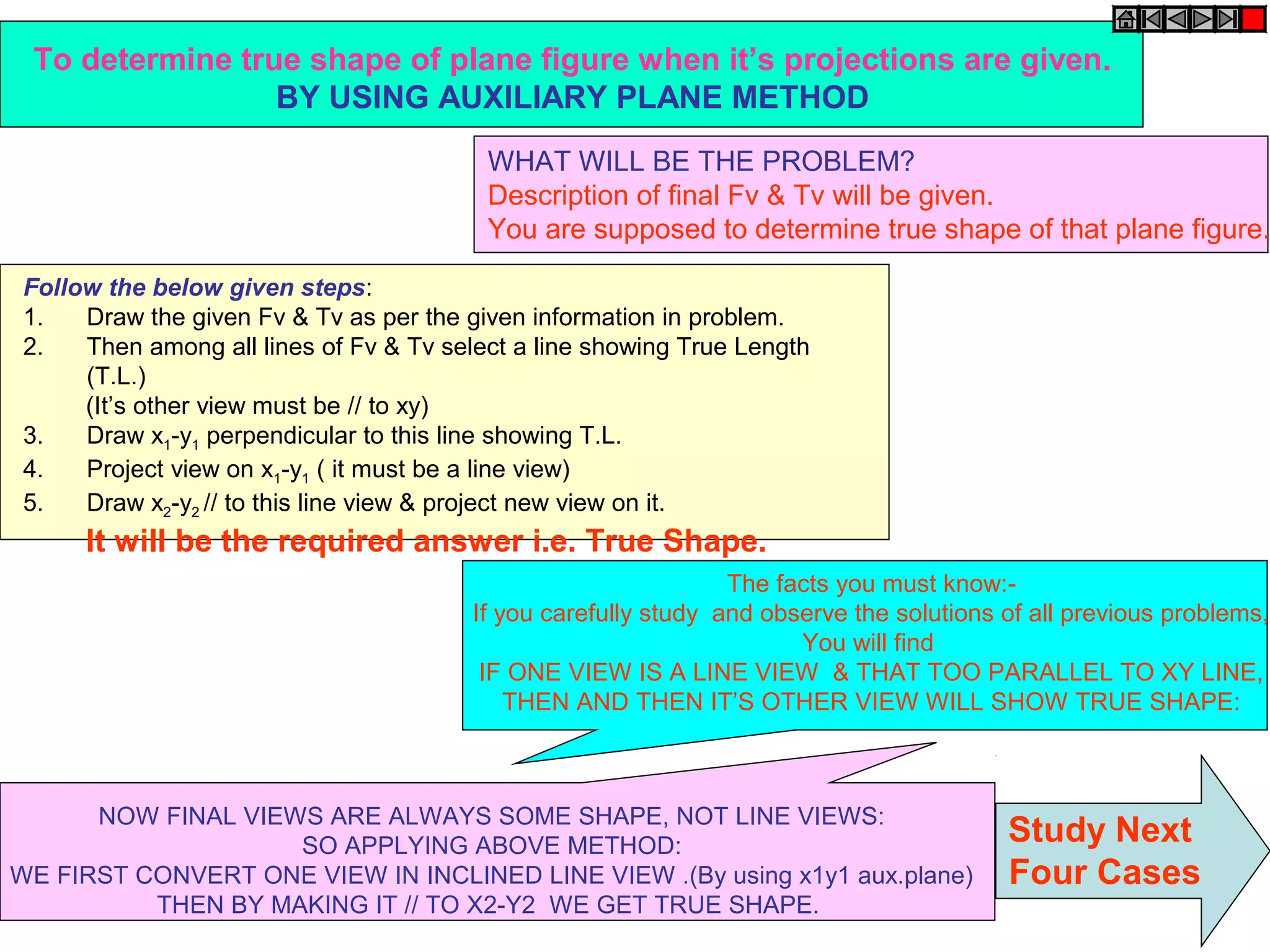
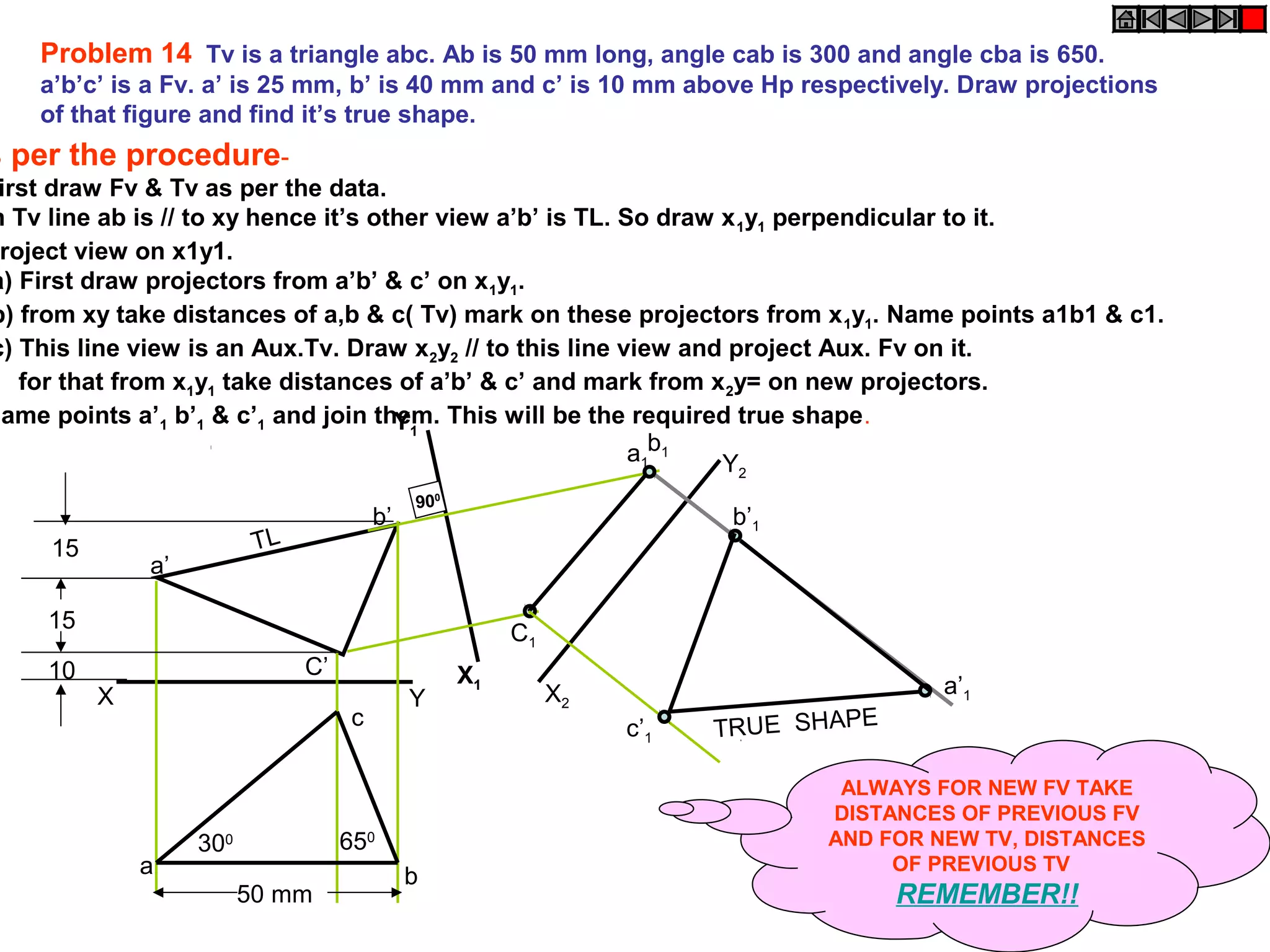
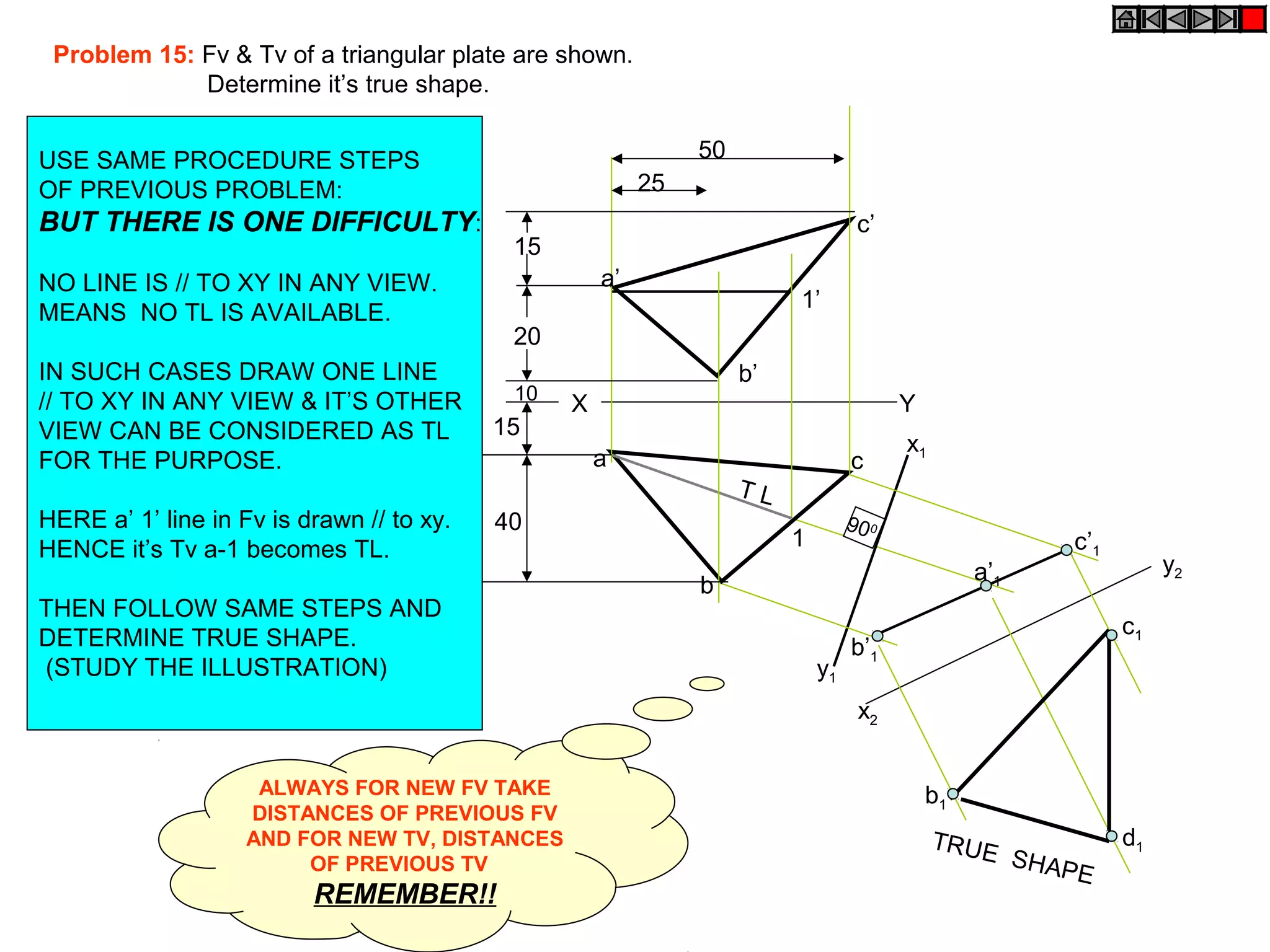
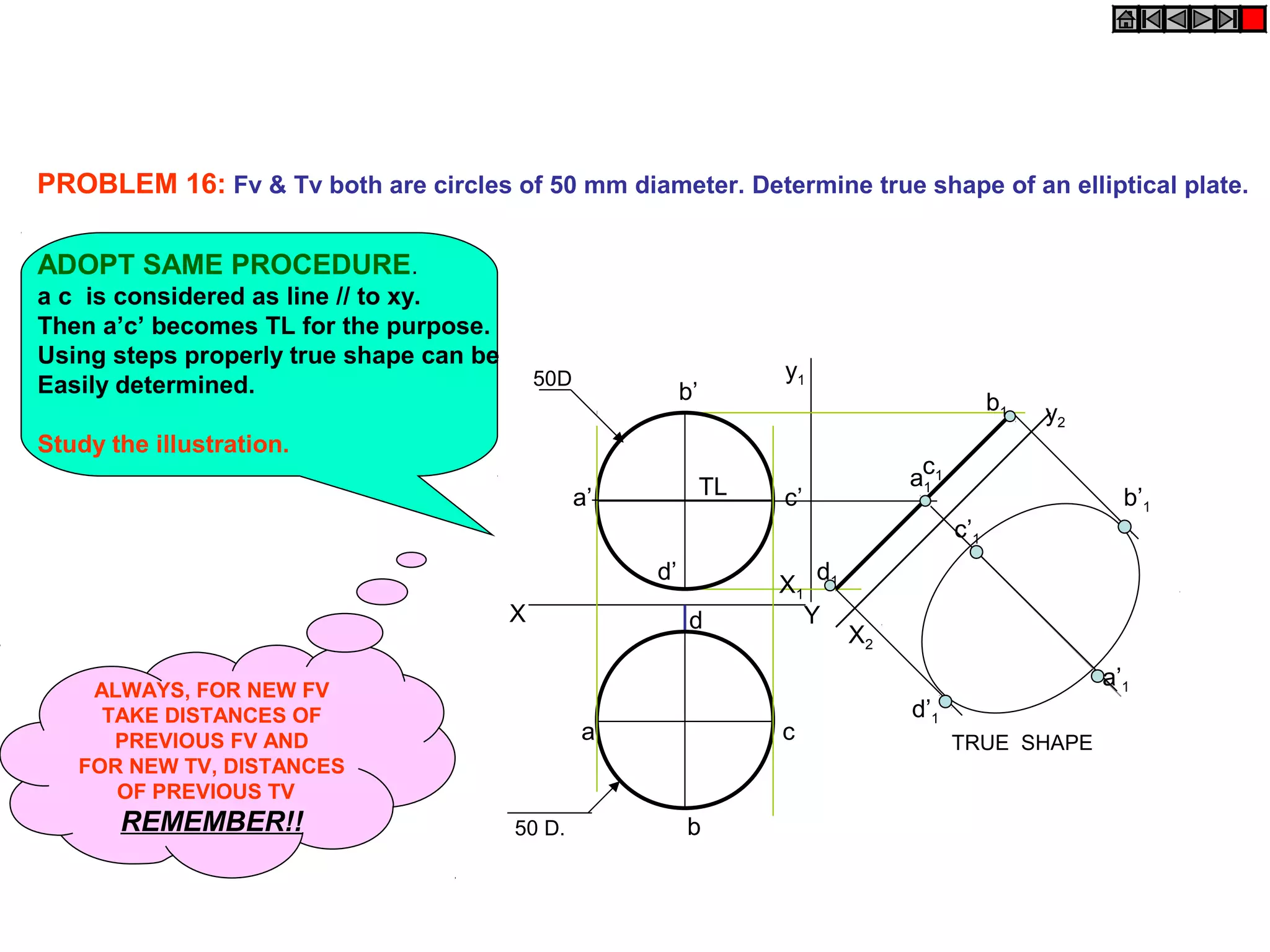
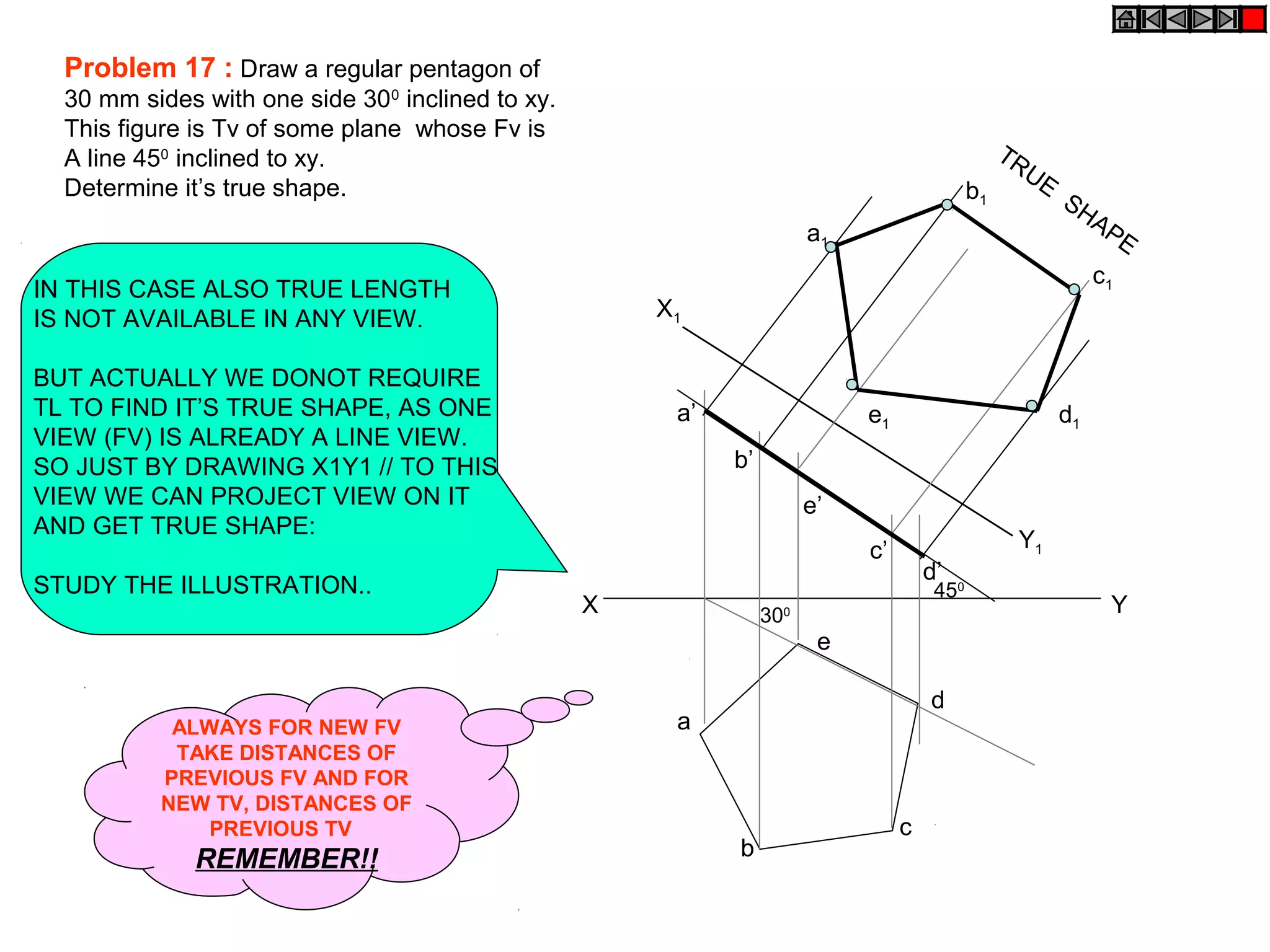
1. The document discusses the procedure for projecting plane figures by considering their position and orientation relative to the horizontal and vertical planes.
2. It explains that the position of a plane figure will be defined by specifying the inclination of its surface to one reference plane and the inclination of one of its edges to the other plane.
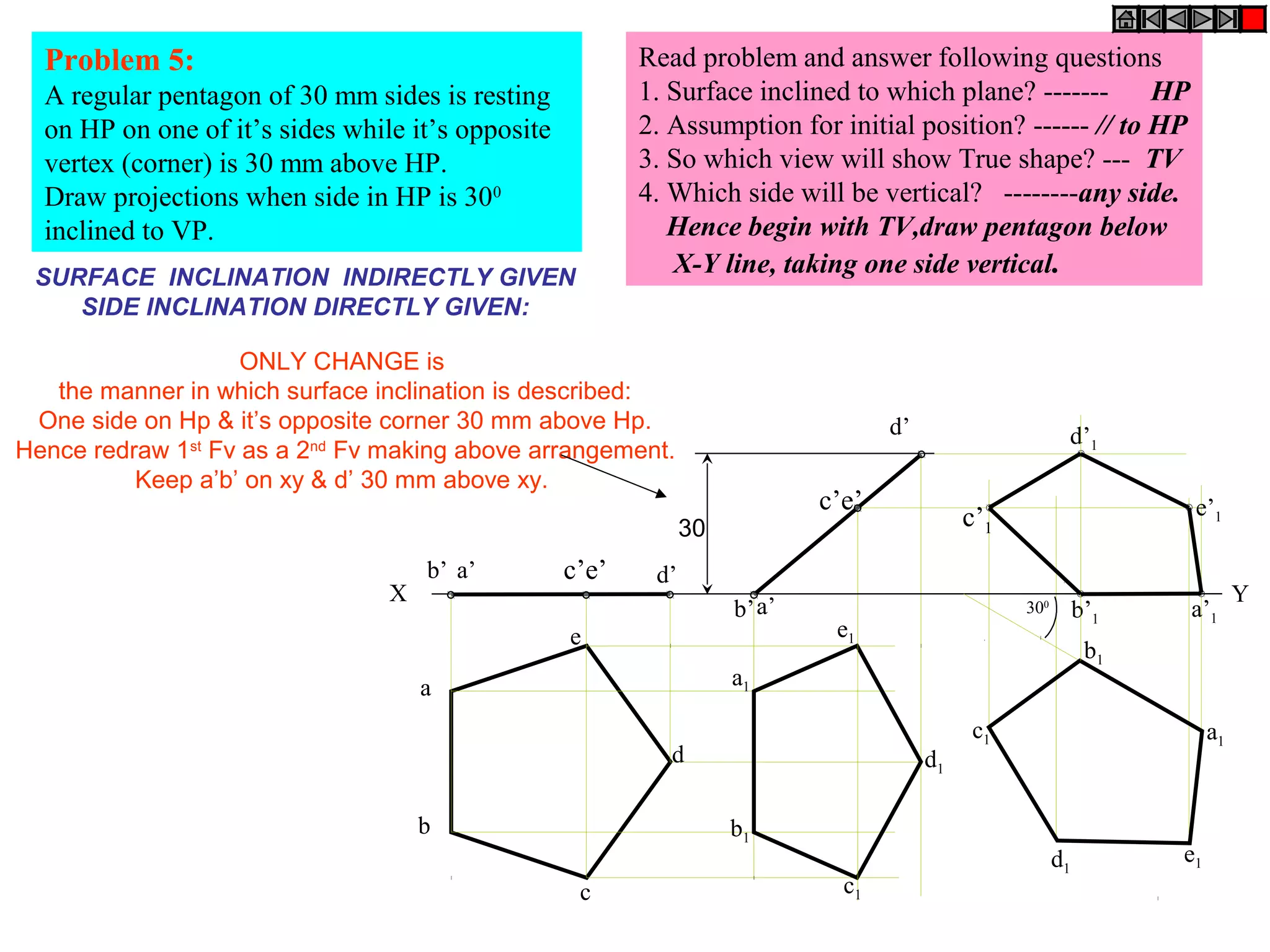
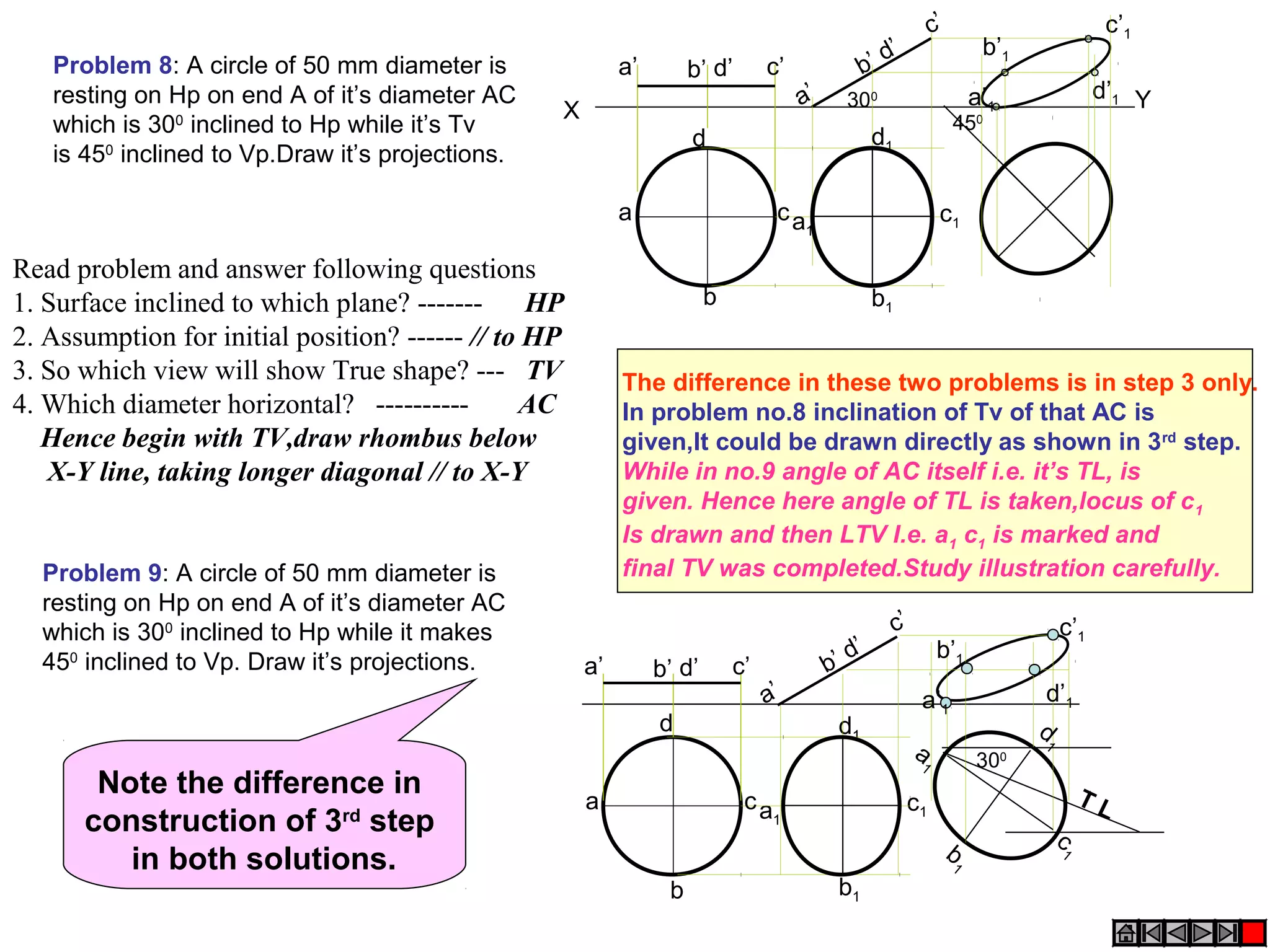
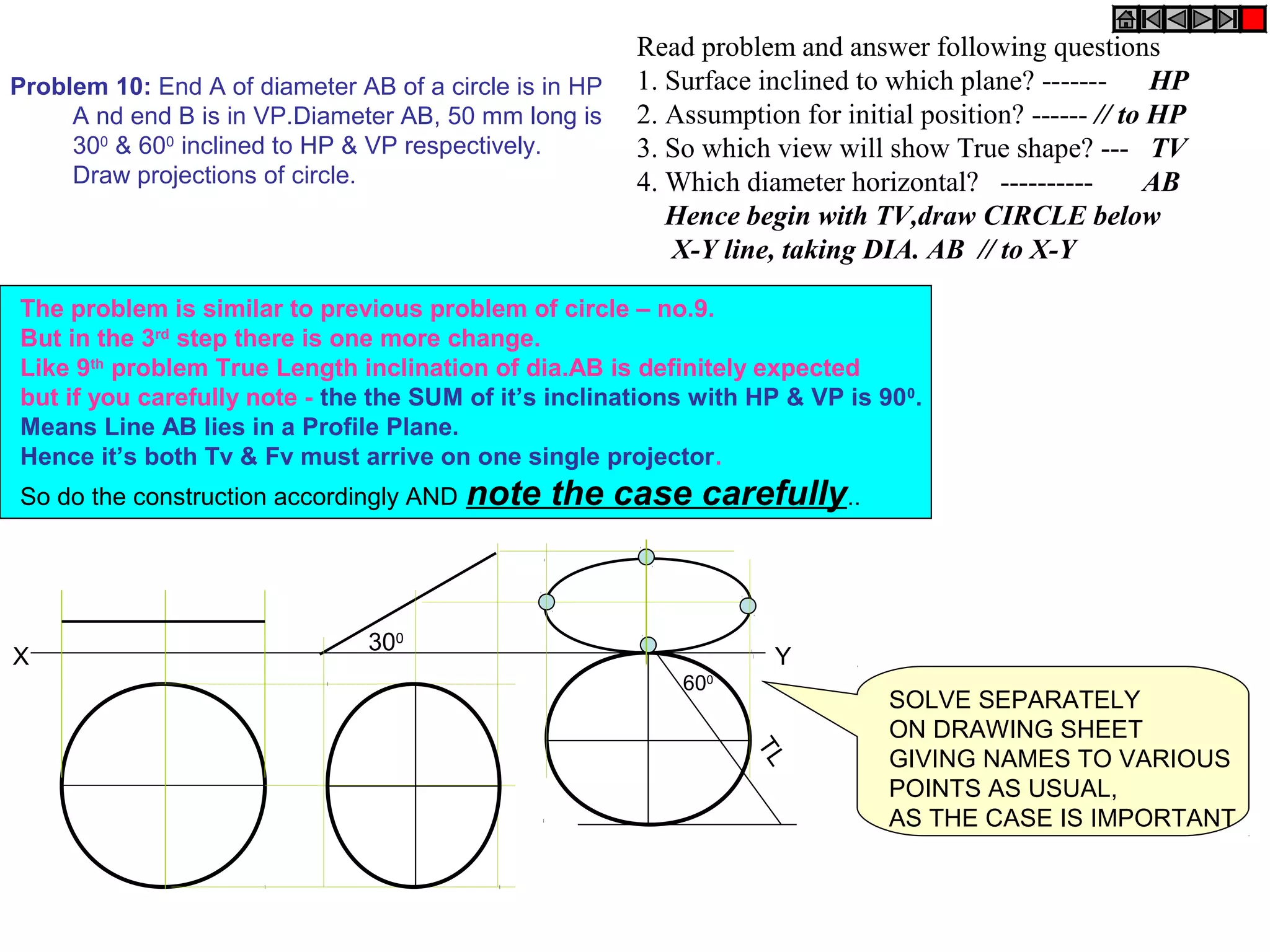
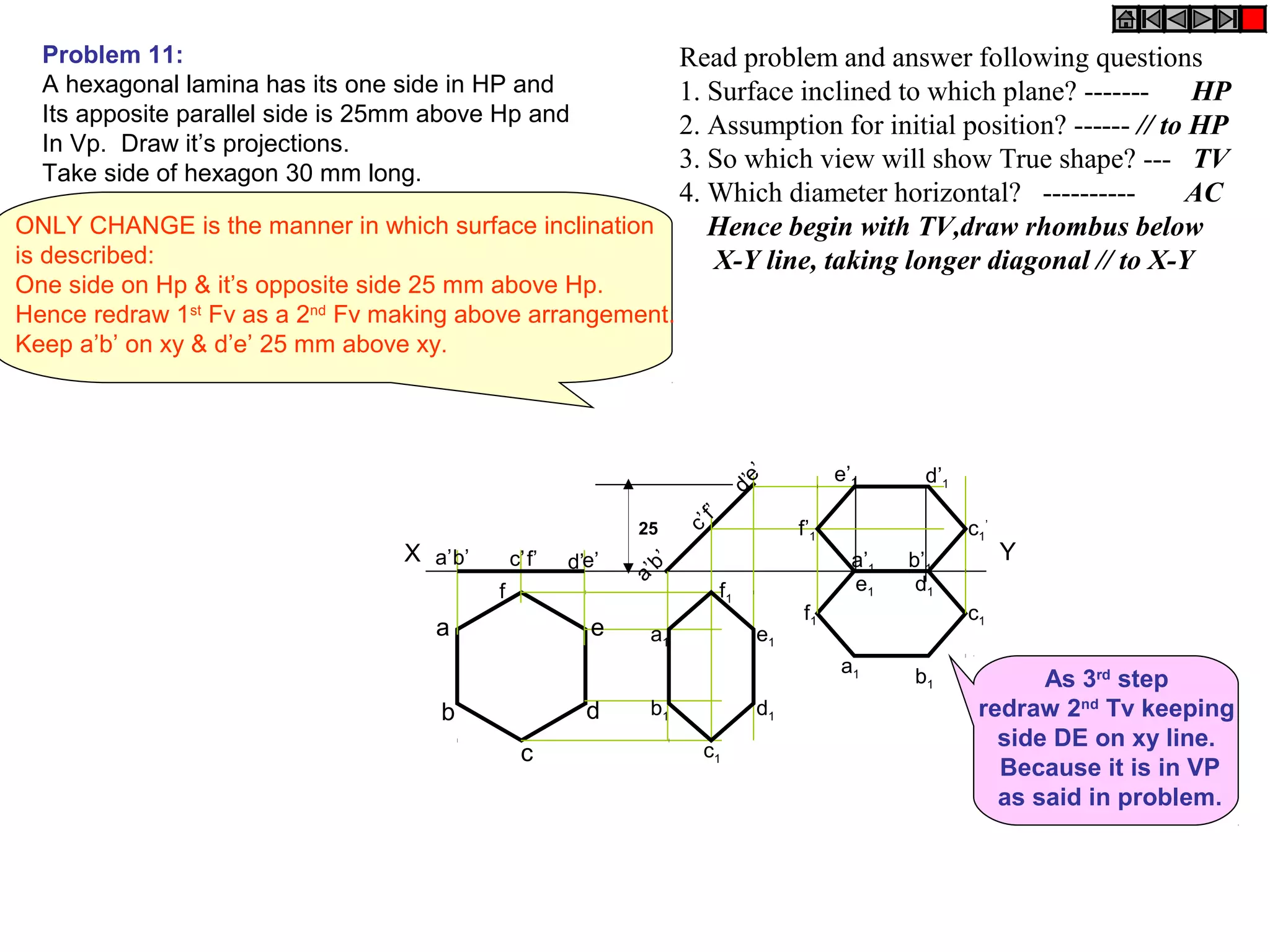
3. The document provides examples of applying the three step procedure to solve projection problems: 1) assume initial position and draw front and top views, 2) consider surface inclination and redraw views, 3) consider edge inclination and draw final views.