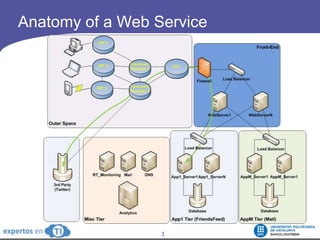
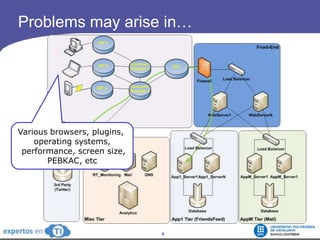
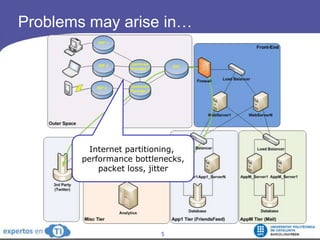
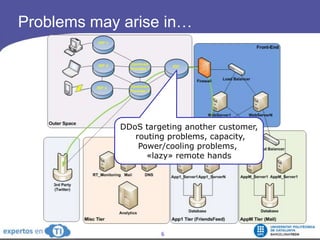
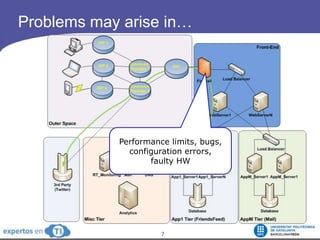
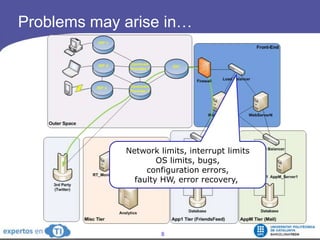
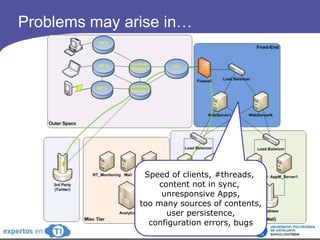
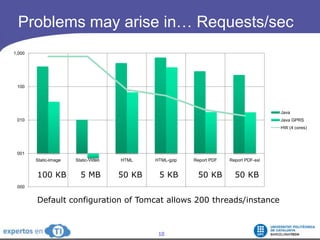
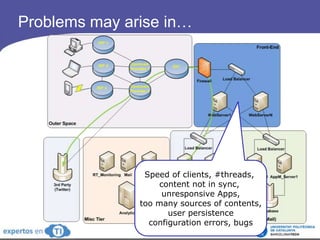
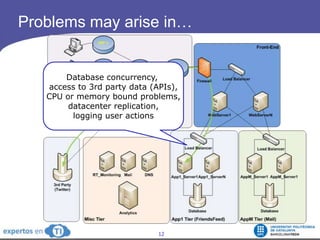
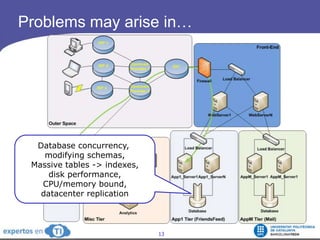
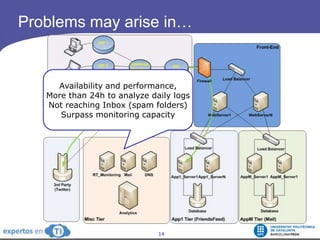
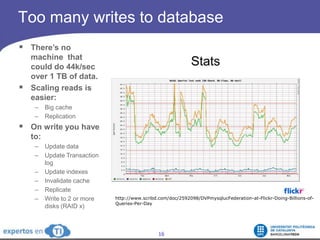
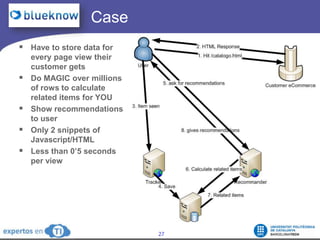
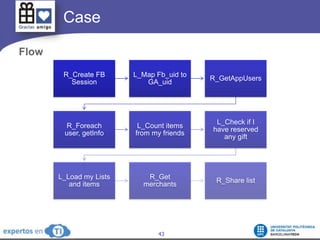
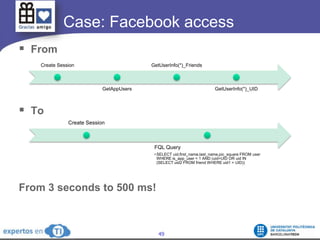
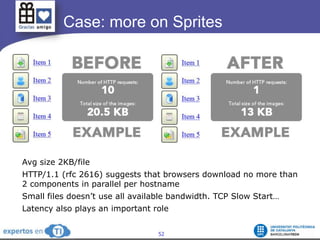
The document discusses the complexities and challenges of web-scale distributed computing, focusing on the anatomy of web services, database concurrency, and performance bottlenecks. It details various solutions for managing data writes, sharding, and addressing performance issues across large systems, often drawing on case studies from platforms like Flickr and Facebook. Additionally, it explores the benefits and drawbacks of different infrastructure strategies, such as using CDNs and asynchronous processing to enhance scalability and efficiency.