This document discusses the synthesis of analogue circuits to realize a given network function. It begins by reviewing the properties and characteristics required for network functions to correspond to realizable passive circuits. It then examines four canonical forms - Foster and Cauer forms - for realizing LC, RC, and RL network functions as either impedance or admittance driving point functions through partial fraction or continued fraction expansions. Specific examples are worked through to illustrate the realization of LC network functions using the different forms. Finally, it notes the properties of RC driving point functions before discussing their realization.



![Chapter 3 – Synthesis of analogue circuits 135
.
1
2/3
2
1/4
.
.
1
1
1
2
1/2
2
1/6
4
1/8
8/3
3/32
8/3
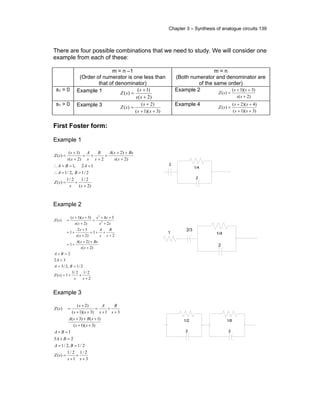
Example 1 Example 2
Example 3 Example 4
We can obtain a general realisation for the admittance function Y(s) as follows:
0,0,,)( 0
,...3,1
22
0
>≥
+
++= ∞
=
∞ ∑ p
m
p p
p
kkk
s
sk
s
k
sksY
ω
1/k1
K1/w1
2
1/k3
K3/w3
2kinf
1/k0
1/km
Km/wm
2
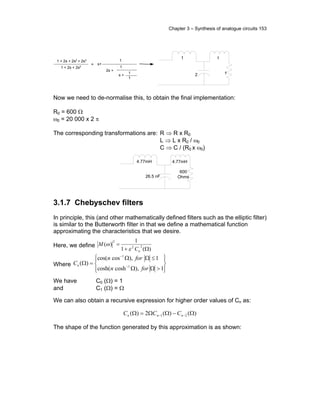
Realisation of LC network functions using First Cauer form
The first Cauer form is generated by the continued fraction expansion of a
reactance function about the point at infinity.
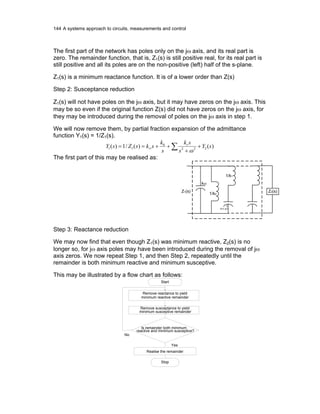
Consider a ladder network as shown [Note that the series arms are impedances
while the shunt arms are admittances]
:
z1 z3 z5
y2
y4
y6
1 I1
1'
2
2'
E1
E2
I2
To compute the driving point impedance
1
1
I
E
Z = , we start at the other end:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ee321s3-150519124809-lva1-app6891/85/Ee321s3-1-5-320.jpg)










![Chapter 3 – Synthesis of analogue circuits 149
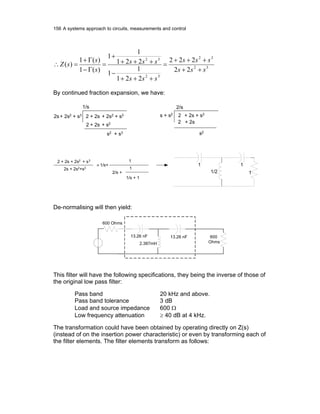
3.1.5 Insertion power function
and the refection coefficient
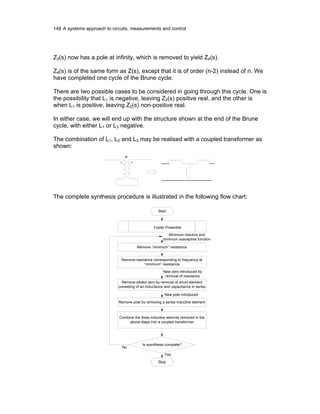
Let us consider an LC filter. As there are no resistance elements, there will be no
filter loss in such a filter. Let us see what happens when we connect such a
lossless LC filter between a source and a load.
.
R1
E1
R2E2
P2
..
.
.
Lossless
LC filter
Z1
R1
E1
R2
E20
P20
..
.
The figure shows the voltage and power distribution before and after the insertion
of a lossless LC filter.
Voltage insertion function α
e
E
E
=
2
20
Power insertion function α2
2
2
2
2
2 00
e
E
E
P
P
==
We also have: 22
21
2
1
2
)(
][ 0
R
RR
E
P
+
=
For [P20] to be a maximum,
1
2
1
max2
12
212
2
21
3
212
2
2
4
][
)(2
0)()(2
0
0
0
R
E
P
RR
RRR
RRRRR
R
P
=
=
+=
=+++−
=
∂
∂
−−
The maximum value that P2 can take is only the maximum value of P20
1
)(
44
)(][
][ 2
21
21
1
2
1
2
21
2
2
1
.max2
2
.min
2
9
0
≤
+
=
+
==∴
RR
RR
E
R
RR
RE
P
P
e α
It is of course obvious that this has to be less than or equal to unity, for the
transmitted power cannot be more than the available power. This is also known
as the transmission ratio.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ee321s3-150519124809-lva1-app6891/85/Ee321s3-1-19-320.jpg)

![152 A systems approach to circuits, measurements and control
n
M 22
2
1
1
)(
Ω+
=
ε
ω
1
)1(log103
:1
2
10
=∴
+=
=Ω
ε
ε
At
For an attenuation of 40 dB at 100 kHz.,
386.2
210.9609.12
9999ln5ln2
99995
1000051
)51(log10)1(log1040
:5
20
100
2
2
2
10
2
10
⇒=
=∗
=
=
=+
+=Ω+=
==Ω
n
n
n
At
n
n
nn
62
21
21
622
2
1
1
)(
4
1)()(
:
,
1
1
1
1
)(
sRR
RR
ss
jsngSubstituti
M n
−+
−=−ΓΓ
Ω=
Ω+
=
Ω+
=
ε
ω
As R1 and R2 are given as 600 Ω,
)1)(1()1(11
1
1
1
1
)(
4
1)()( 33
6
3
6
6
6
662
21
21
2
ss
s
s
s
s
s
ssRR
RR
ss
+−
−
=
−
−
=
−
−
=
−
−=
−+
−=−ΓΓ
impedancenormalisedtheissZwhere
sZ
sZ
sBut
sss
s
schoseusLet
sss
s
sss
s
ssssss
s
)(
,
1)(
1)(
)(
)1)(1(
)(
)1)(1(
)(
)1)(1(
)(
)1)(1)(1)(1(
2
3
2
3
2
3
22
6
+
−
=Γ
+++
=Γ
+−−
−
+++
=
+−+++−
−
=
[ ] [ ]
2
32
32
32
3
221
2221
221
1
221
1
)(1
)(1
)(
1)(1)()(
1)()()()(
ss
sss
sss
s
sss
s
s
s
sZ
sssZ
sZssZs
++
+++
=
+++
−
+++
+
=
Γ−
Γ+
=
+Γ−=−Γ
−=Γ+Γ
This may now be synthesised. Using continued fraction expansion:
2s3
+ 2s2
+ 2s + 12s2
+ 2s + 1
s
2s3
+ 2s2
+ s
s + 1
2s
1
2s2 + 2s
2s2
+ 2s + 1s + 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ee321s3-150519124809-lva1-app6891/85/Ee321s3-1-22-320.jpg)