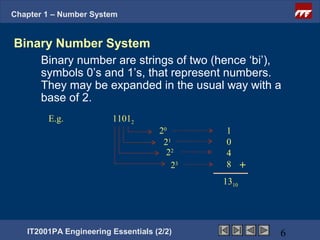
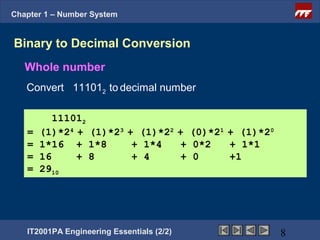
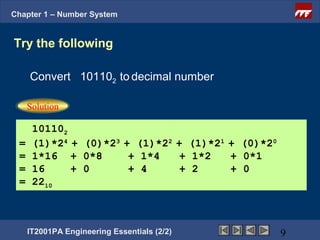
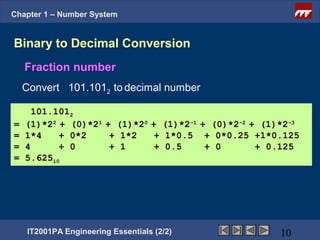
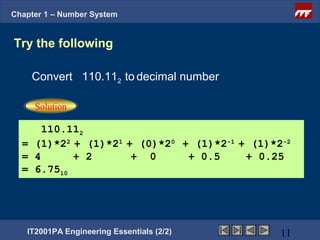
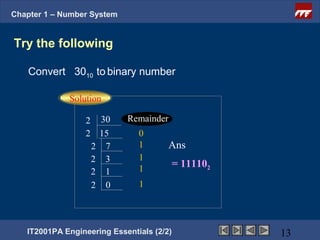
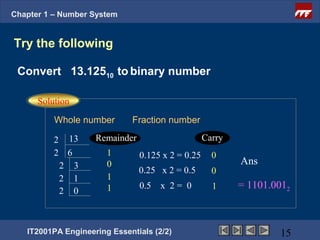
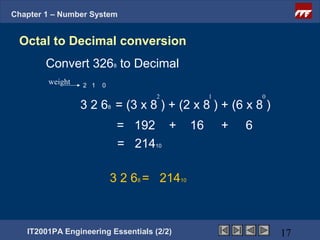
The document is a chapter from an engineering course on number systems. It discusses converting between binary, decimal, octal, hexadecimal and binary-coded decimal number systems. The objectives are to be able to convert numbers between these systems and explain their applications in digital electronics which uses binary to represent high and low voltage levels. It provides examples of converting specific numbers between the different number bases.