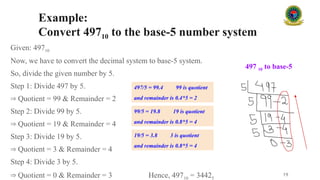
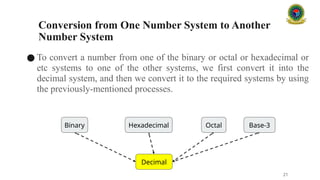
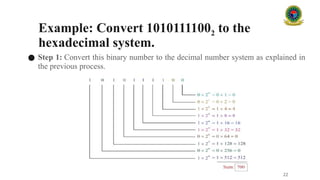
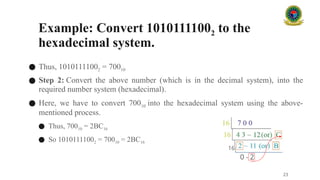
Certainly! Here's a comprehensive 40,000-character description on **Number Systems**, suitable for an in-depth lecture or detailed slide notes.
---
## 📘 Number Systems: Foundations, Types, Conversions, and Applications
### 1. Introduction to Number Systems
A **number system** is a structured way to represent numbers using a consistent set of symbols or digits. These systems are fundamental in mathematics, computing, and digital electronics, providing the foundation for counting, calculations, data representation, and algorithm design.
In everyday life, we predominantly use the **decimal system** (base 10), which employs ten digits: 0 through 9. However, in various scientific and technical fields, other number systems are utilized for their efficiency and suitability to specific applications.
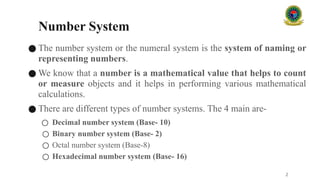
### 2. Types of Number Systems
#### 2.1 Decimal Number System (Base 10)
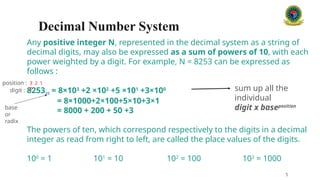
The **decimal system** is the standard system for denoting integer and non-integer numbers. It is also called the base 10 system because it is based on ten symbols: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9. Each position in a decimal number represents a power of 10, depending on its place from the decimal point.
**Example:**
* The number 345.67 in decimal can be expanded as:
* $3 \times 10^2 + 4 \times 10^1 + 5 \times 10^0 + 6 \times 10^{-1} + 7 \times 10^{-2}$
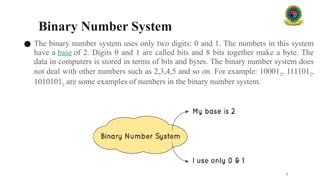
#### 2.2 Binary Number System (Base 2)
The **binary system** uses only two digits: 0 and 1. It is the foundation of digital systems and computing, as electronic circuits have two states: on (1) and off (0). Binary numbers are used in computer memory, logic circuits, and data storage.
**Example:**
* The binary number 1101 represents:
* $1 \times 2^3 + 1 \times 2^2 + 0 \times 2^1 + 1 \times 2^0 = 13$ in decimal.
#### 2.3 Octal Number System (Base 8)
The **octal system** uses eight digits: 0 through 7. It is often used in computing as a more compact representation of binary numbers. Each octal digit corresponds to three binary digits (bits), making it easier to convert between binary and octal.
**Example:**
* The octal number 17 represents:
* $1 \times 8^1 + 7 \times 8^0 = 15$ in decimal.
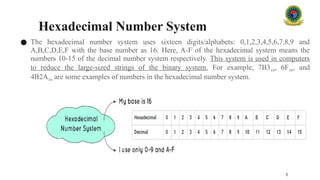
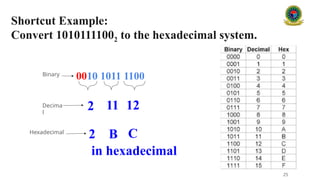
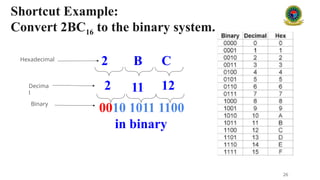
#### 2.4 Hexadecimal Number System (Base 16)
The **hexadecimal system** uses sixteen digits: 0 through 9 and A through F, where A represents 10, B represents 11, and so on up to F, which represents 15. Hexadecimal is widely used in computing as a more human-friendly representation of binary-coded values.
**Example:**
* The hexadecimal number 2F represents:
* $2 \times 16^1 + 15 \times 16^0 = 47$ in decimal.
#### 2.5 Other Number Systems
* **Binary-Coded Decimal (BCD):** Represents each decimal digit with its binary equivalent.
* **Gray Code:** A binary numeral system where two successive values differ in only one bit, used in error correction in digital communication.
* **Excess-K Notation:** A binary encoding system used to represent signed numbers.
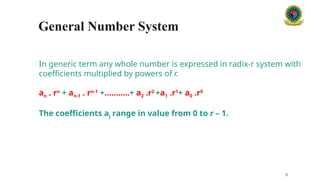
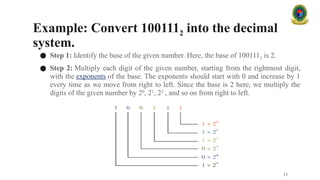
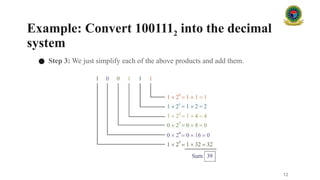
### 3. Conversion Between Number Systems
Converting numbers between di