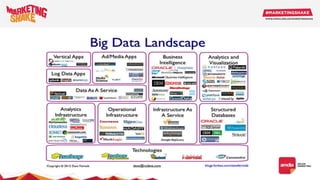
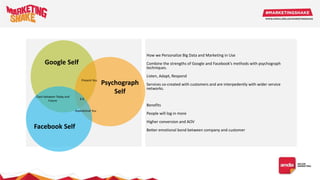
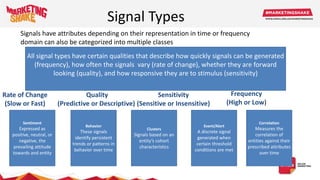
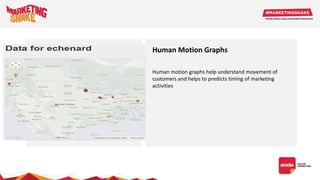
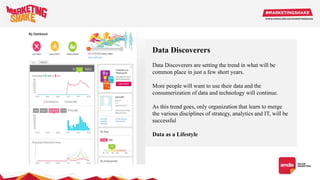
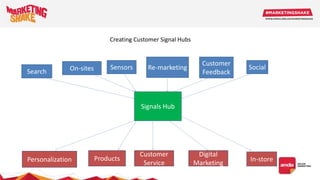
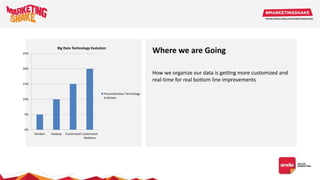
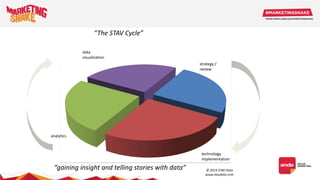
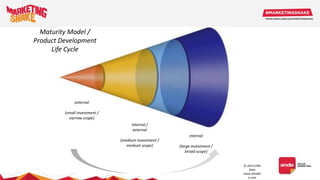
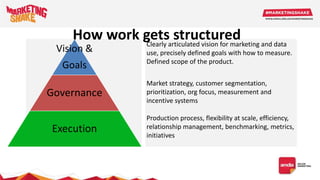
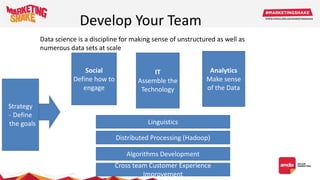
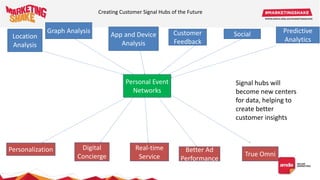
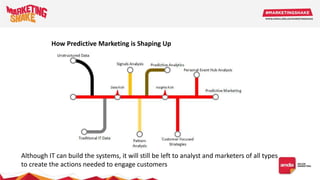
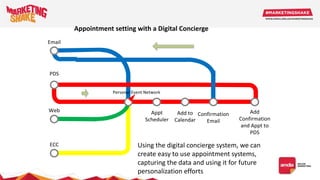
Big data and marketing is becoming an important tool for companies. The document discusses how big data can be used for personalization, listening to customers, and responding to better serve their needs. It outlines the key steps in the process from data collection and analysis to insights and actions. Various big data tools and techniques are mentioned to understand customer behavior and trends in order to tailor marketing and customer experiences. The importance of data visualization to tell the story of patterns and create useful insights for businesses is also highlighted.