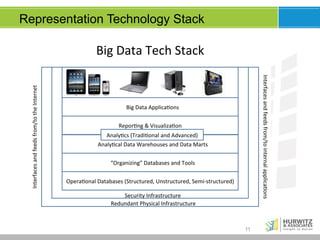
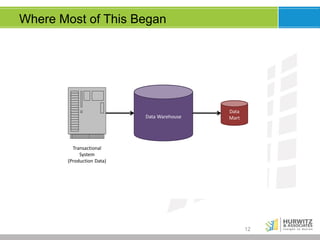
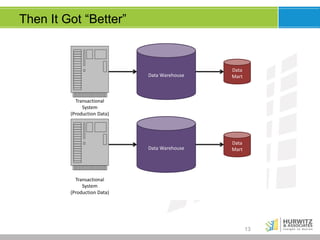
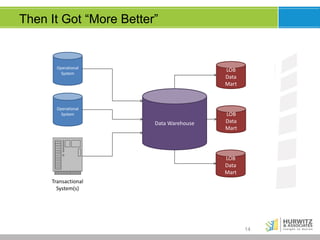
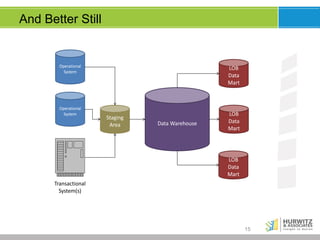
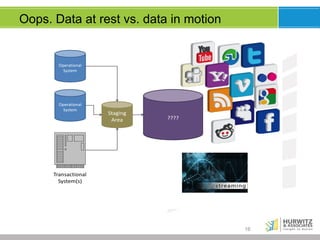
The document discusses the significance of big data, emphasizing that while it involves large volumes of data, its real value is in distilling this data into actionable insights. It defines big data through its key characteristics (volume, variety, velocity, veracity) and highlights the importance of data scientists in navigating complex analyses. Furthermore, it explores the evolving data landscape, the necessity for real-time analytics, and the shift from traditional data models to accommodating varied and increasingly unstructured data.