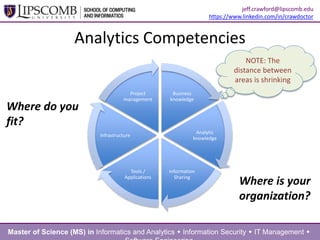
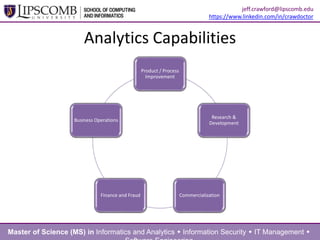
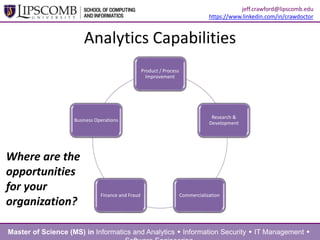
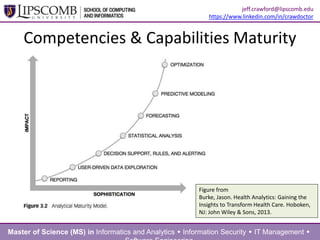
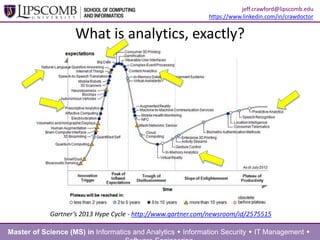
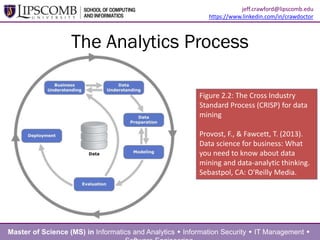
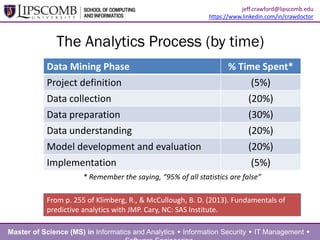
This document summarizes a presentation about building an effective organizational analytics capability. It discusses taking a holistic, long-term view of analytics by focusing on developing competencies and capabilities. It also advocates for intentionally implementing analytics by learning from how IT projects are implemented. Key competencies for analytics include business knowledge, analytic knowledge, information sharing abilities, tools/applications expertise, infrastructure management skills, and project management. Critical capabilities areas include product/process improvement, research and development, commercialization, finance/fraud analysis, and business operations analytics.





![Organizational Analytics?
Prahalad, C. K., & Hamel, G. (1990). The
Core Competence of the Corporation.
Harvard Business Review, 68(3), 79-91.
Ulrich, D., & Smallwood, N. (2004).
Capitalizing on Capabilities. Harvard
Business Review, 82(6), 119-127.
“the diversified
corporation is a large
tree…the root system that
provides
nourishment, sustenance,
and stability is the core
competence” (Prahalad &
Hamel, 1990, p. 81)
“*capabilities are] the
collective skills, abilities
and expertise of an
organization” (Ulrich &
Smallwood, 2004, p. 119)
Facilitating Conditions
• Corporate culture
• Executive support
• Trends and “hype”
• Degree of competition
• Law, policy, ethics
• Others?
Master of Science (MS) in Informatics and Analytics Information Security IT Management
jeff.crawford@lipscomb.edu
https://www.linkedin.com/in/crawdoctor
competencies
aka
who you are
capabilities
aka
what you do](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/crawfordjeff-analyticsforthemasses-140410214123-phpapp01/85/Building-an-Effective-Organizational-Analytics-Capability-9-320.jpg)