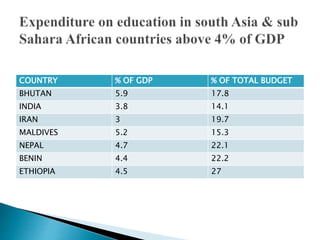
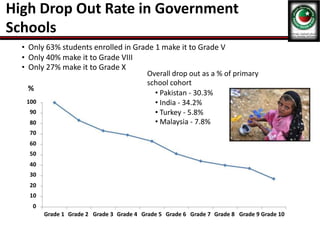
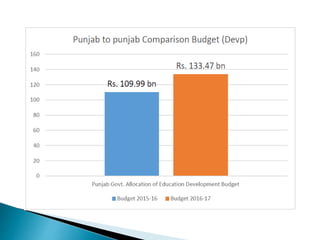
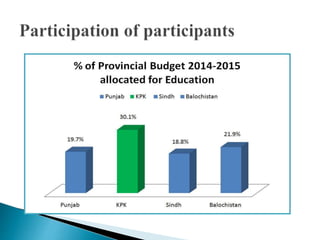
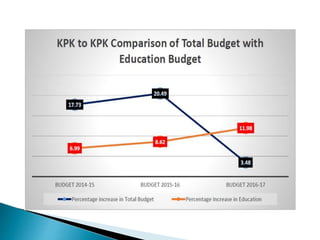
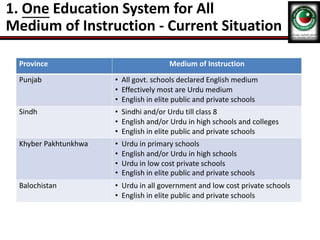
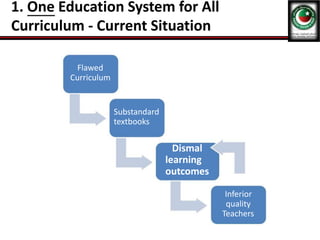
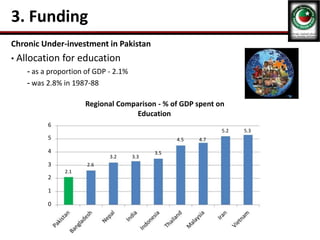
This document discusses the poor state of education in Pakistan and reasons for it. It notes low education spending, gender disparities, poor infrastructure, and high dropout rates. It also summarizes Pakistan's National Education Policy 2017 which aims to increase education funding, promote early childhood education and reforms, and improve teacher training. Key education initiatives by the Punjab and KP governments are also outlined, such as the KP government's 6-point education emergency plan to establish a single education system and increase funding to 5% of GDP. Overall the document analyzes challenges facing Pakistan's education system and policies aimed at addressing them.