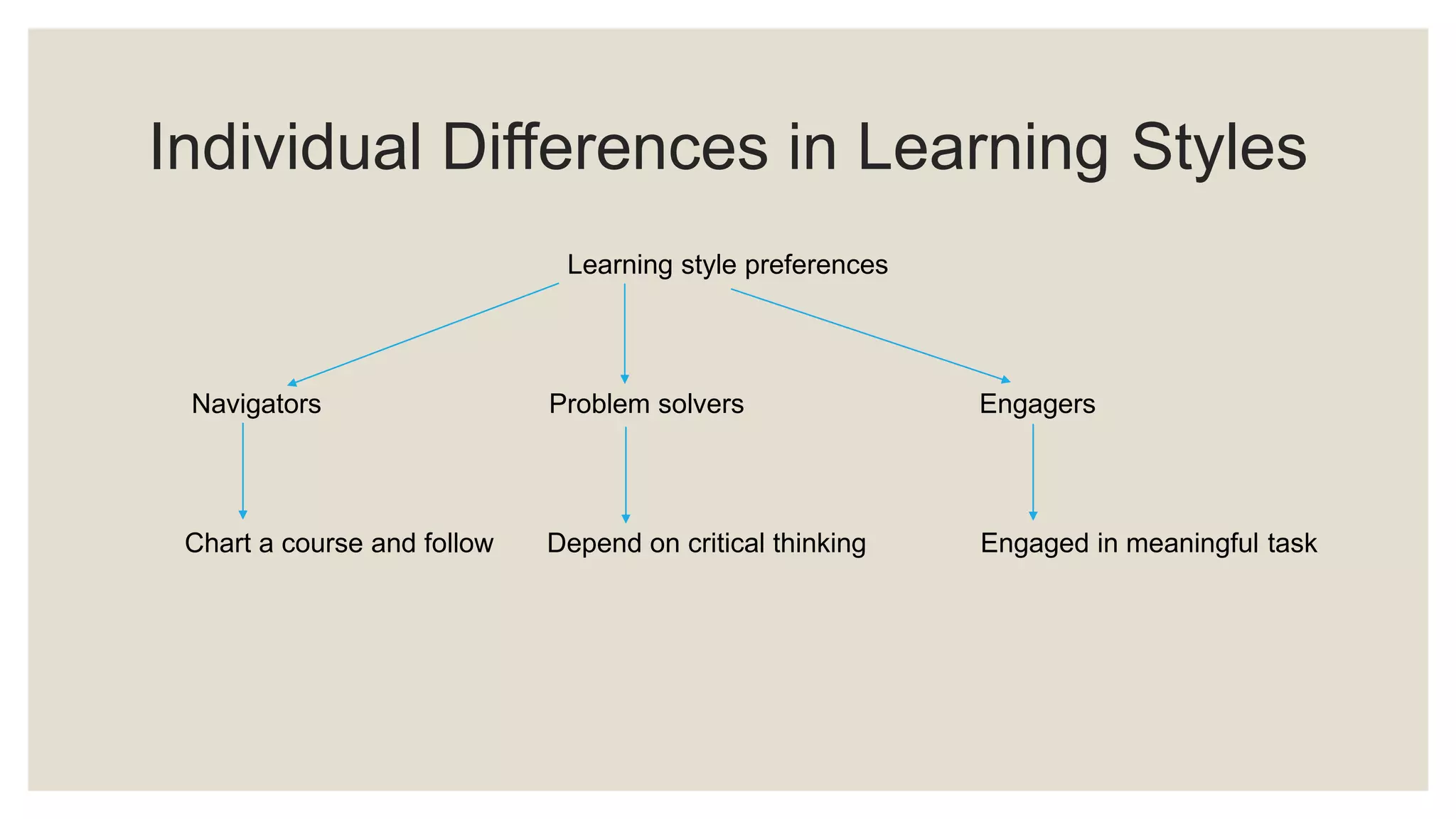
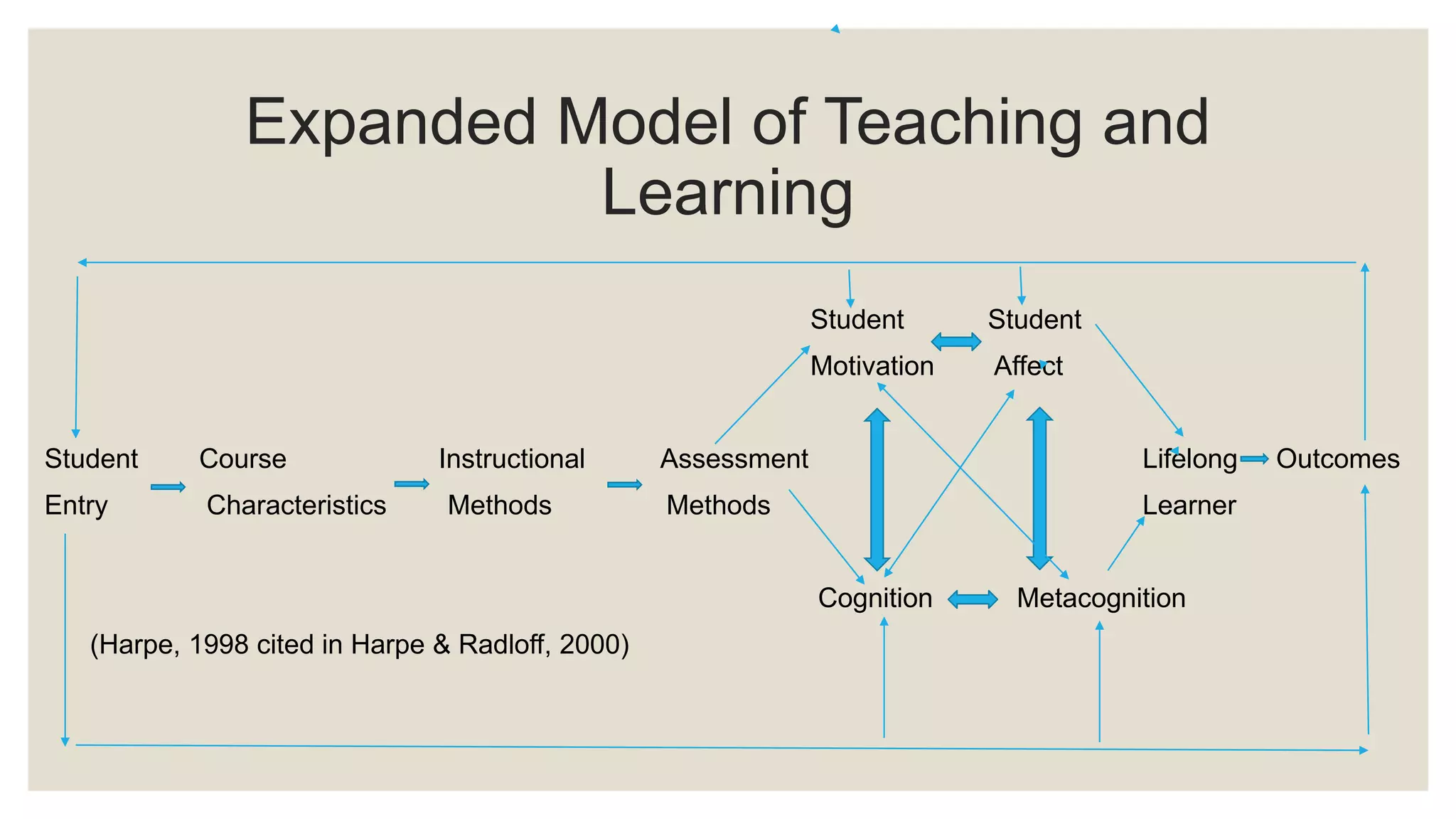
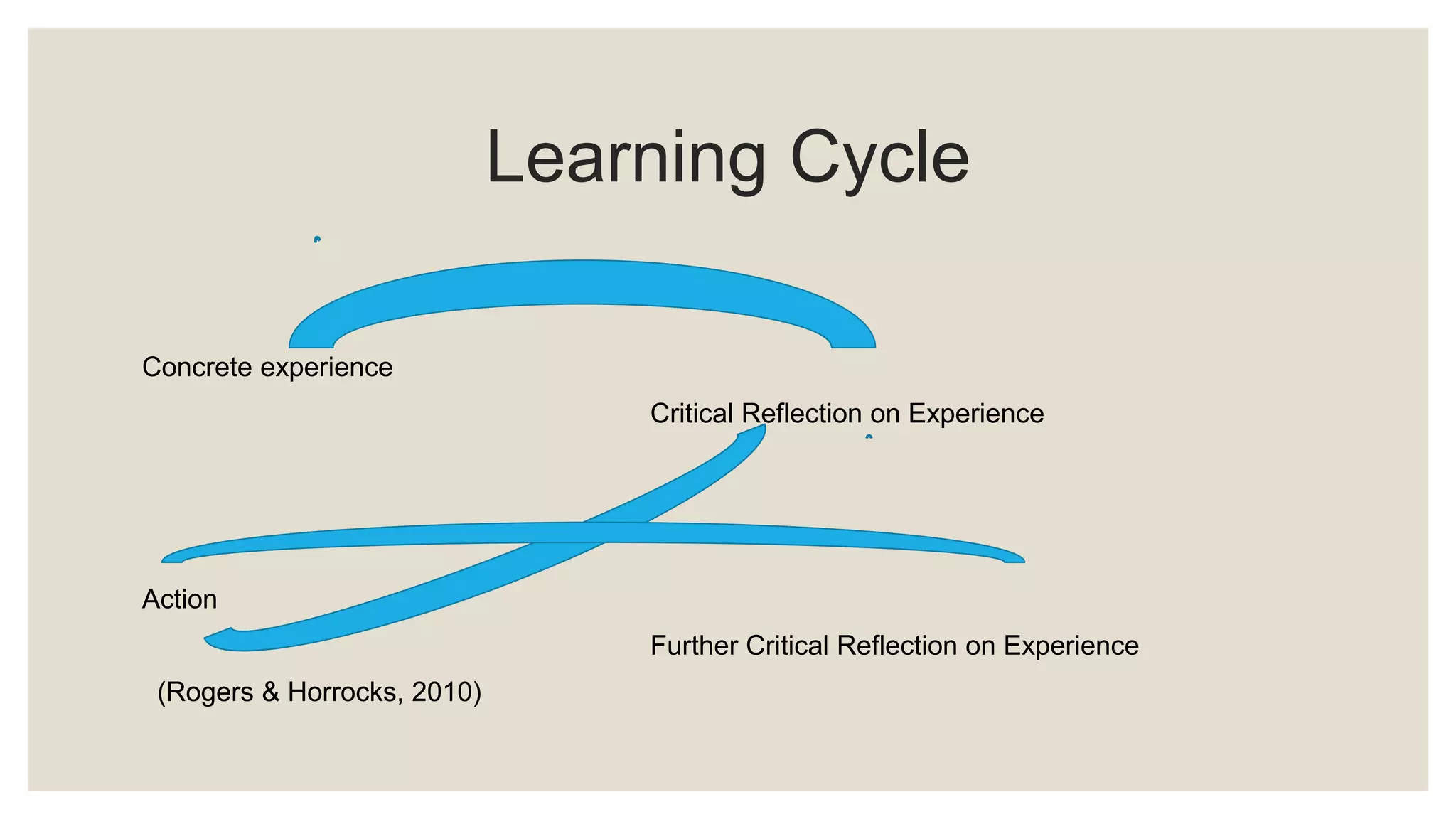
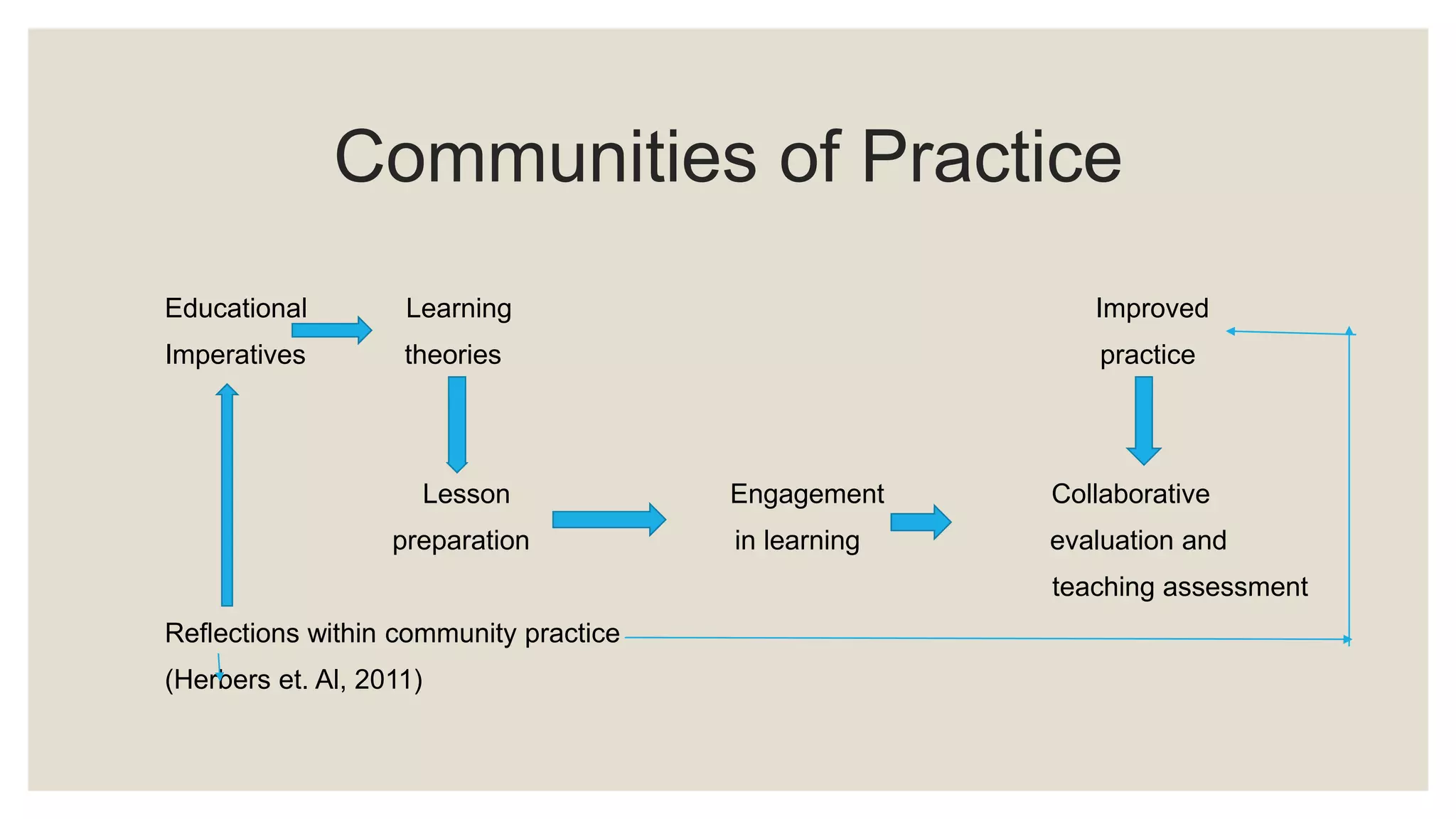
The document discusses characteristics of quality teaching in adult education. It covers topics such as the difference between pedagogy and andragogy, challenges in teaching adults, learning styles, lifelong learning, professional development for teachers and students, and communities of practice. Quality teaching involves specifying learning goals, utilizing skills and knowledge, conducting observations, developing hypotheses, and creating long term societal benefits. Teaching adults requires addressing diverse groups, motivation, and teaching 21st century skills.