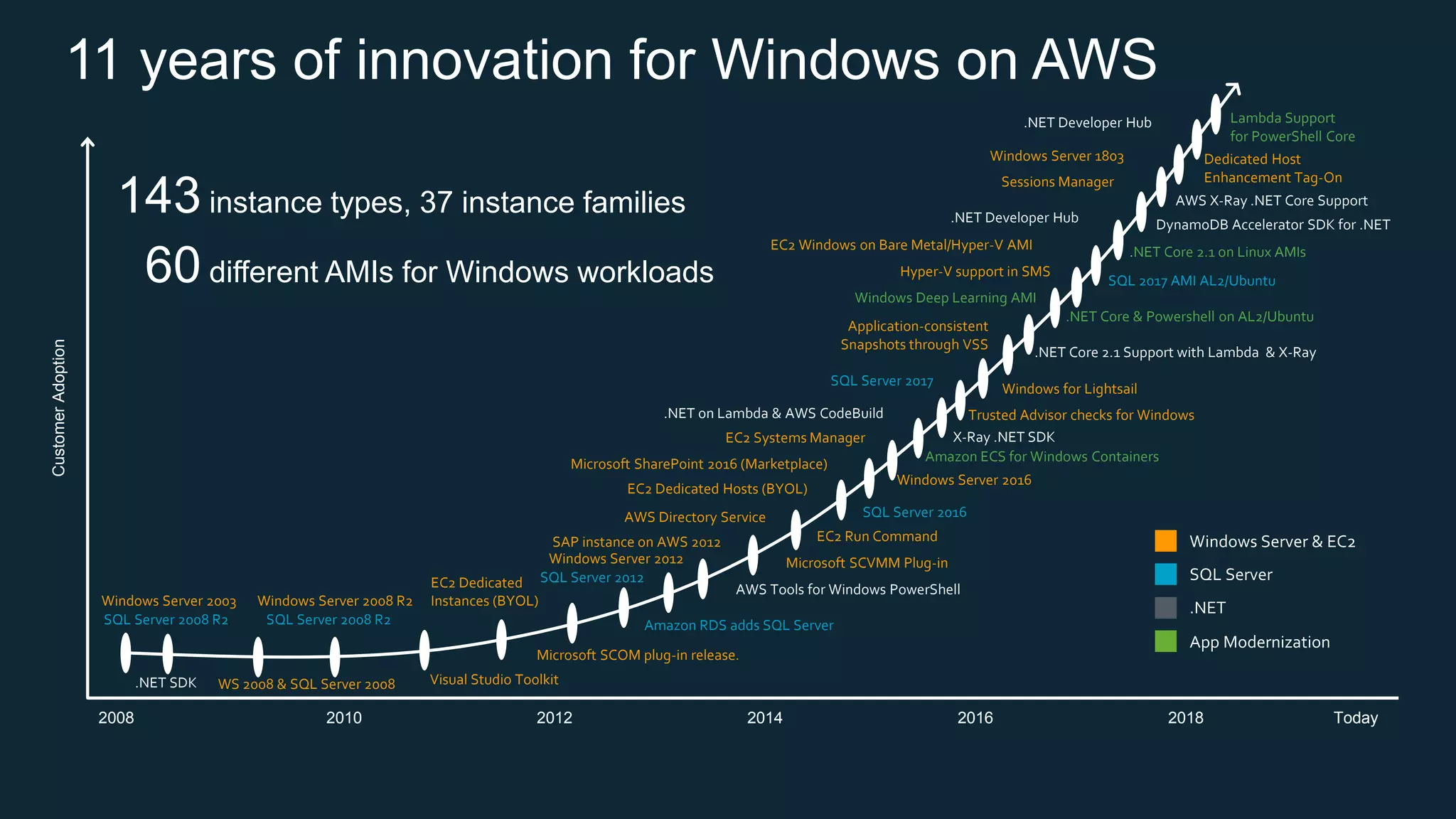
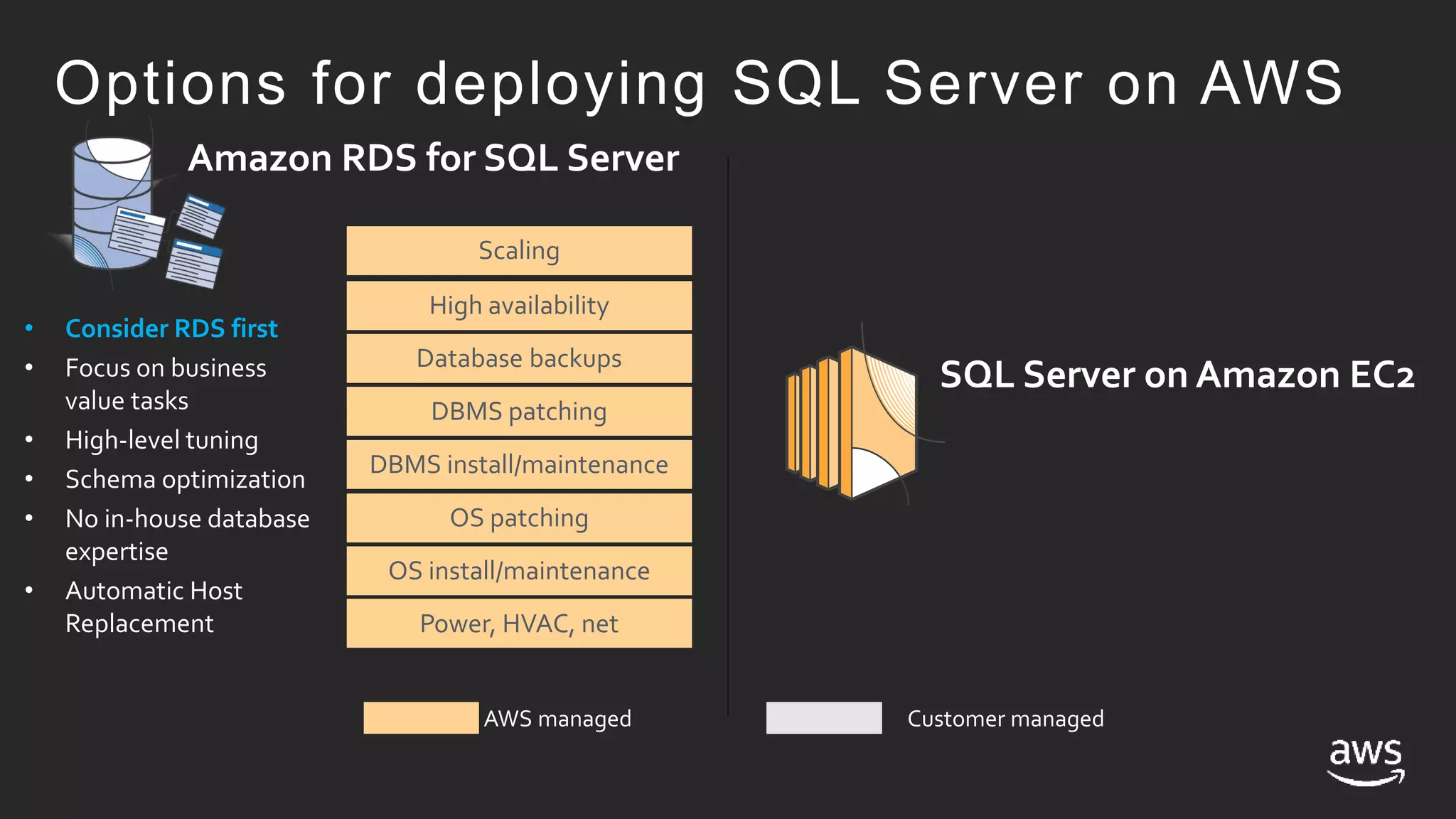
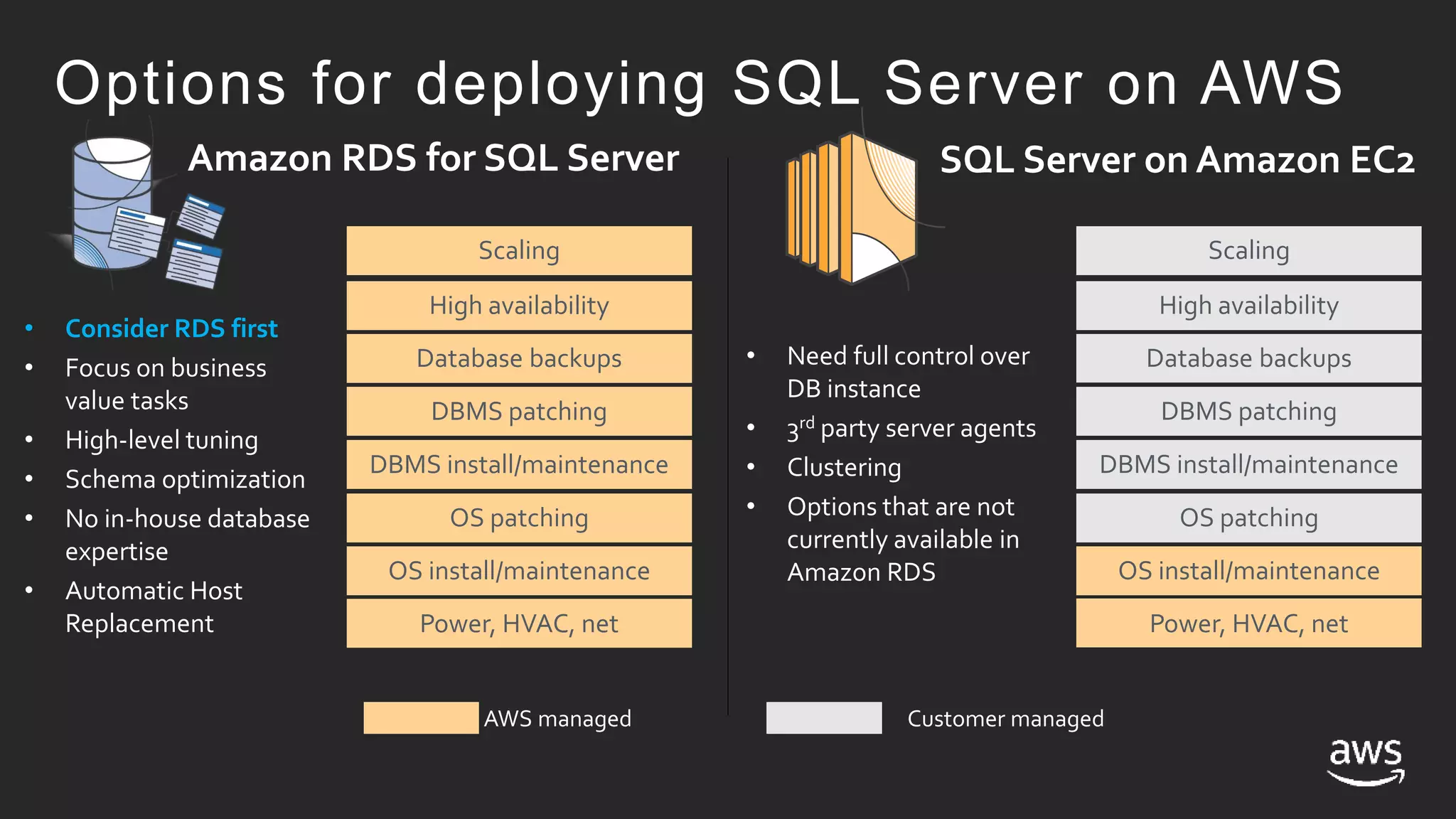
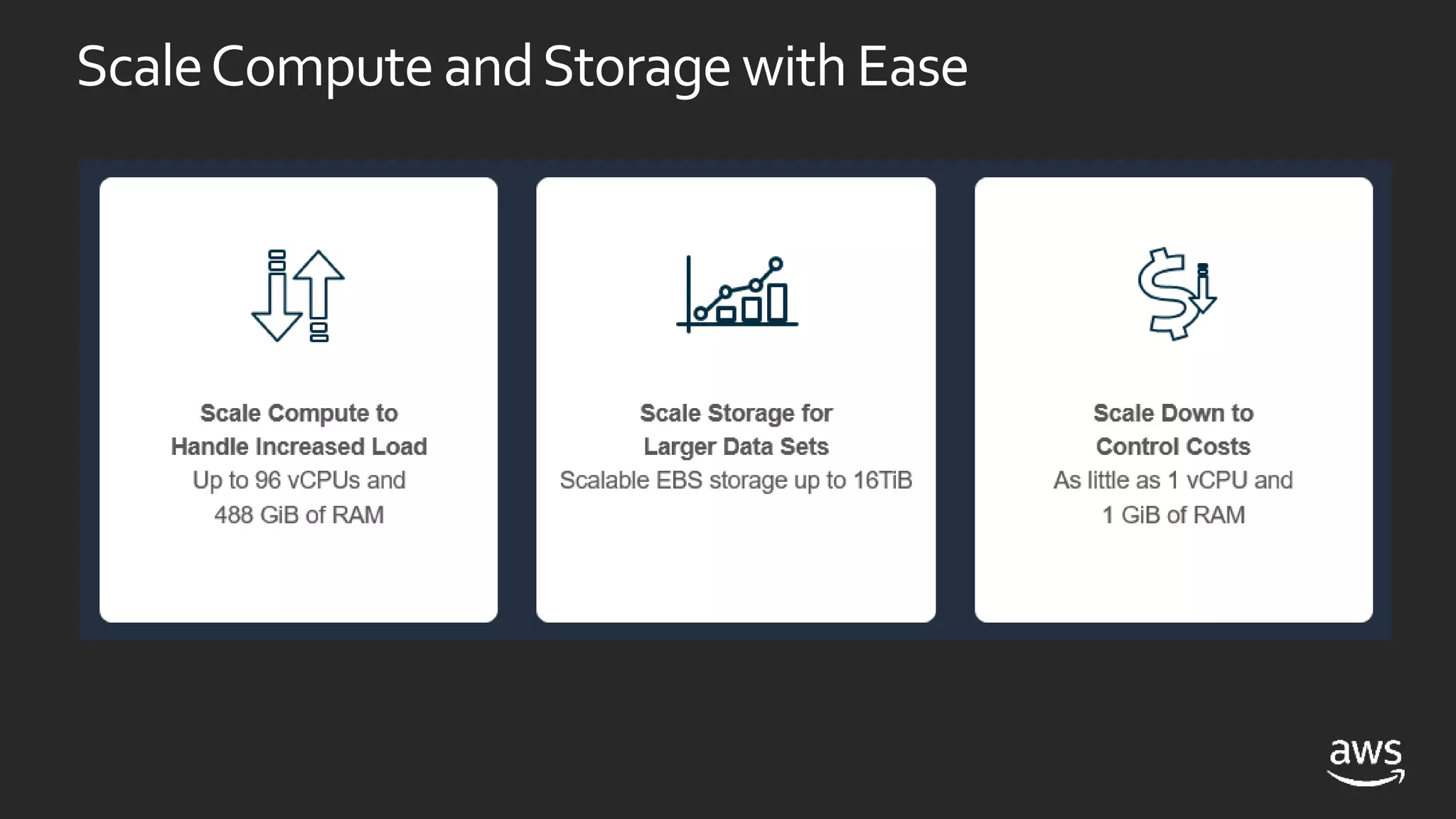
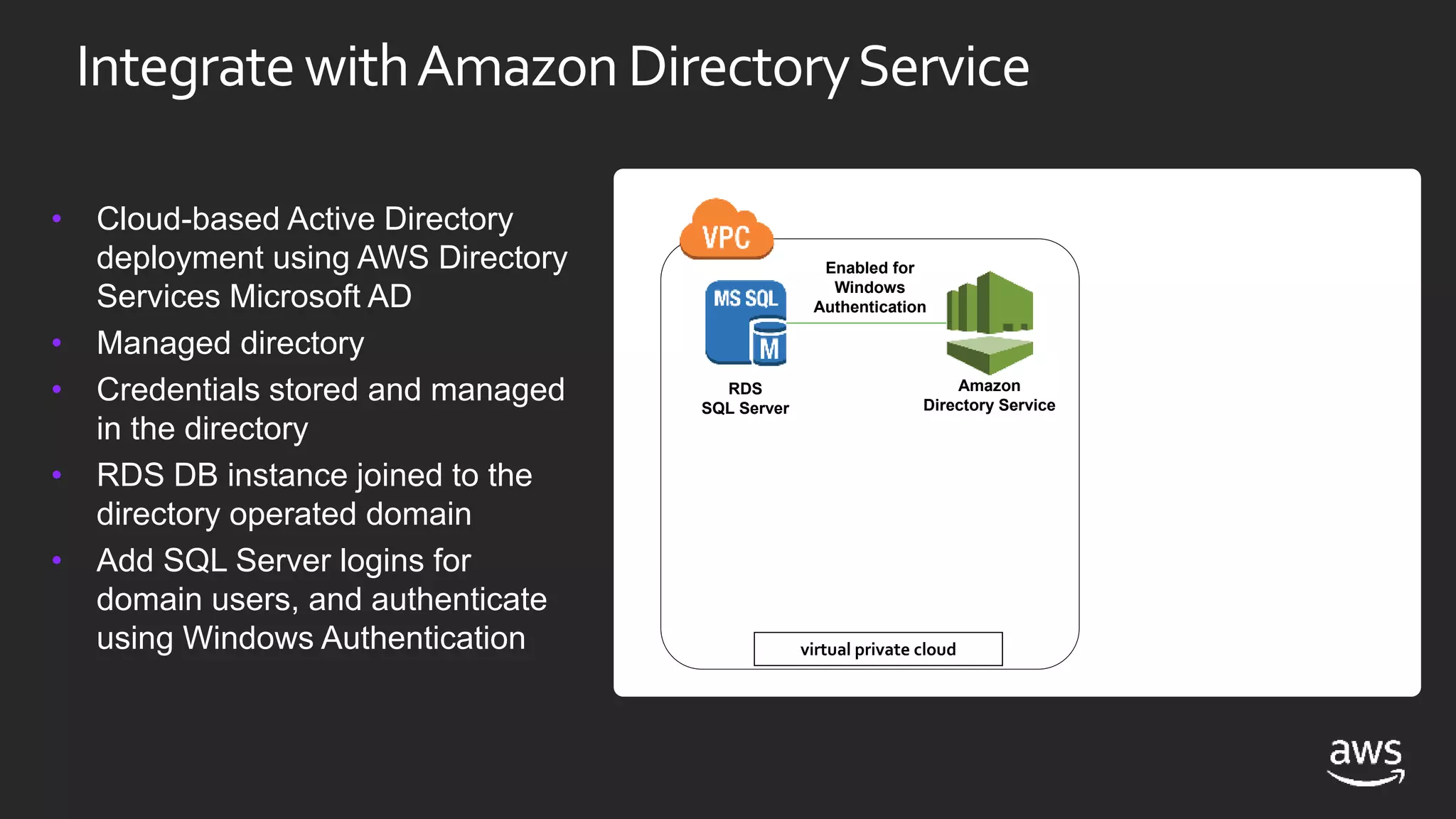
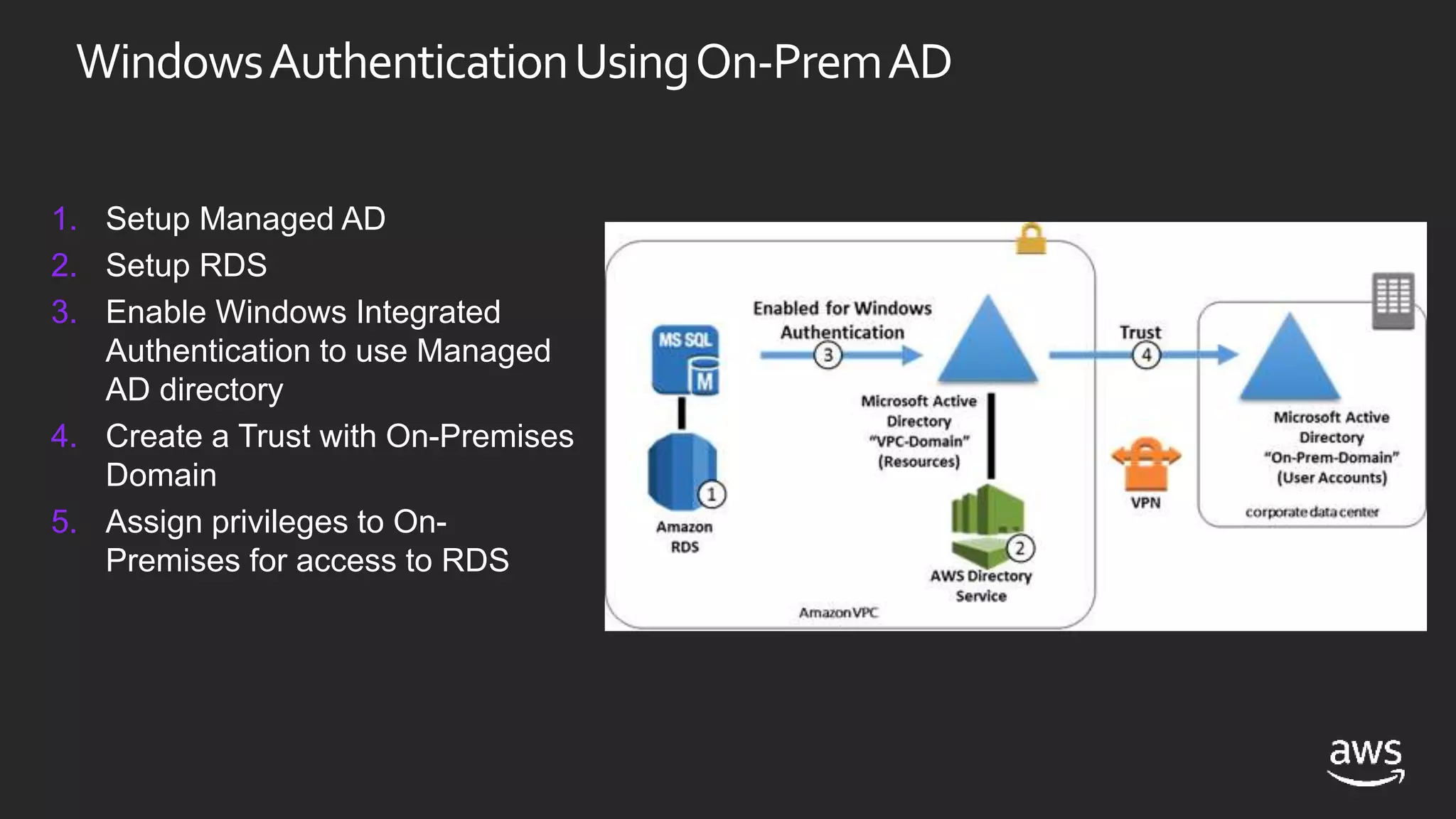
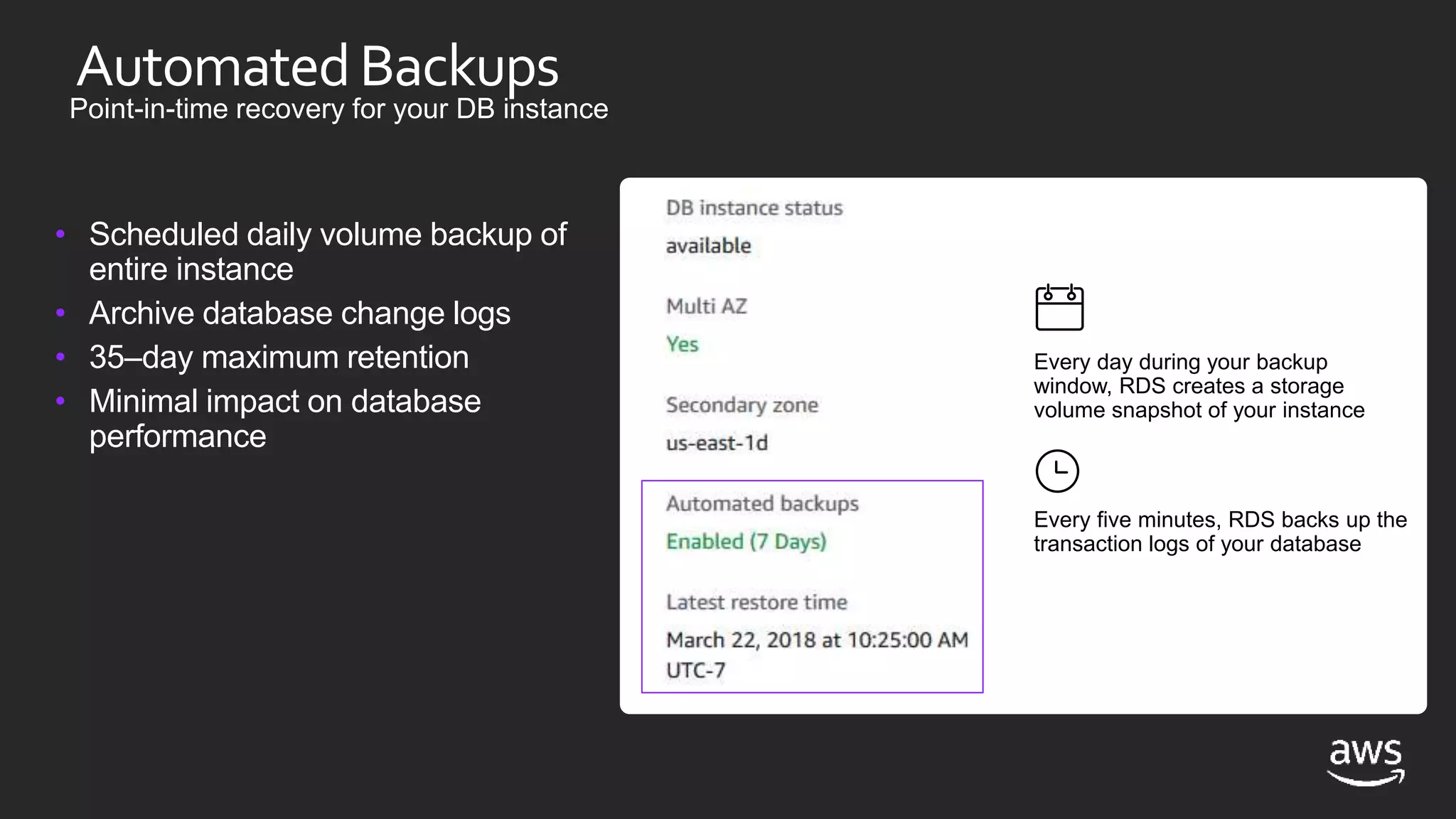
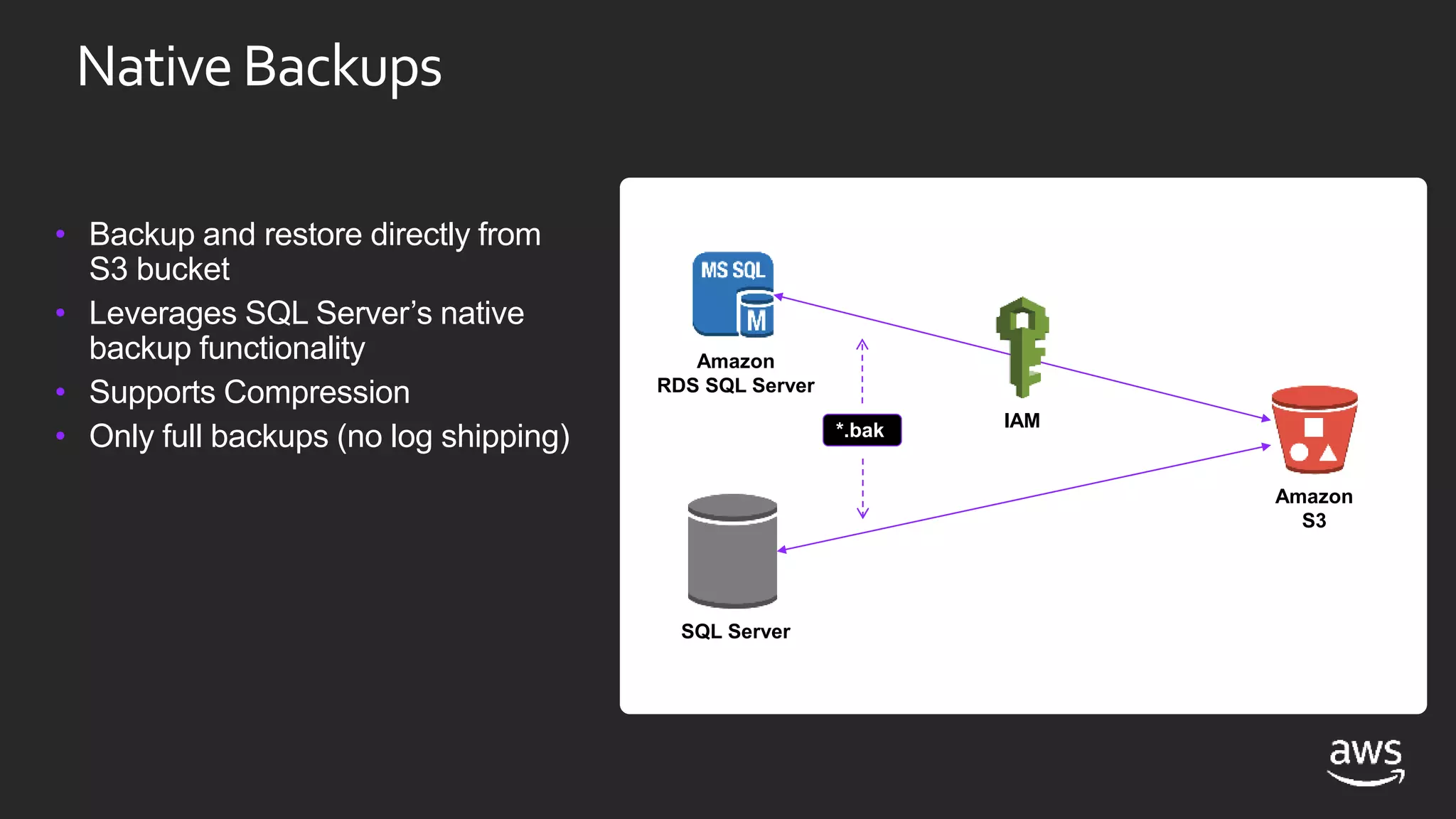
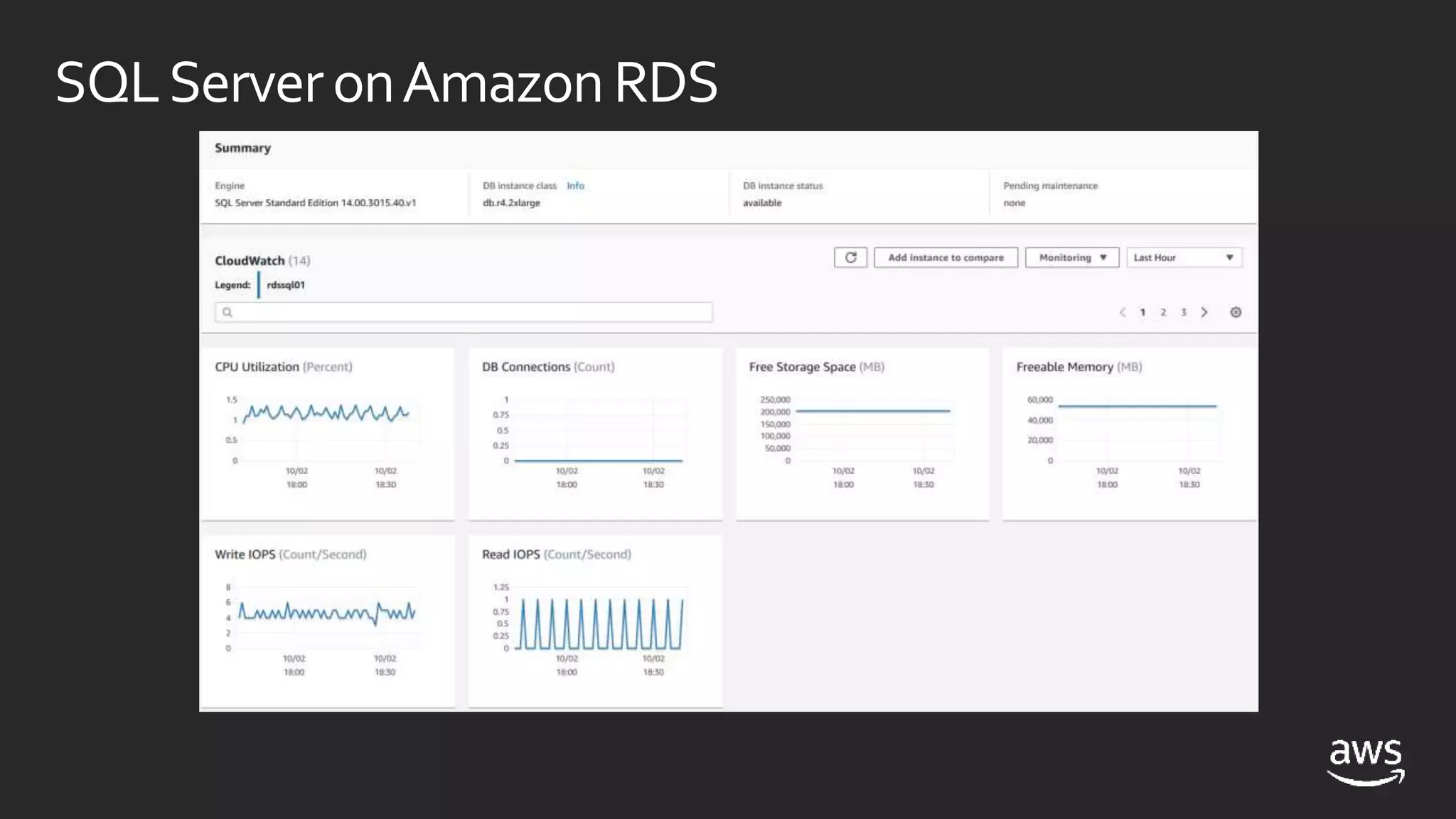
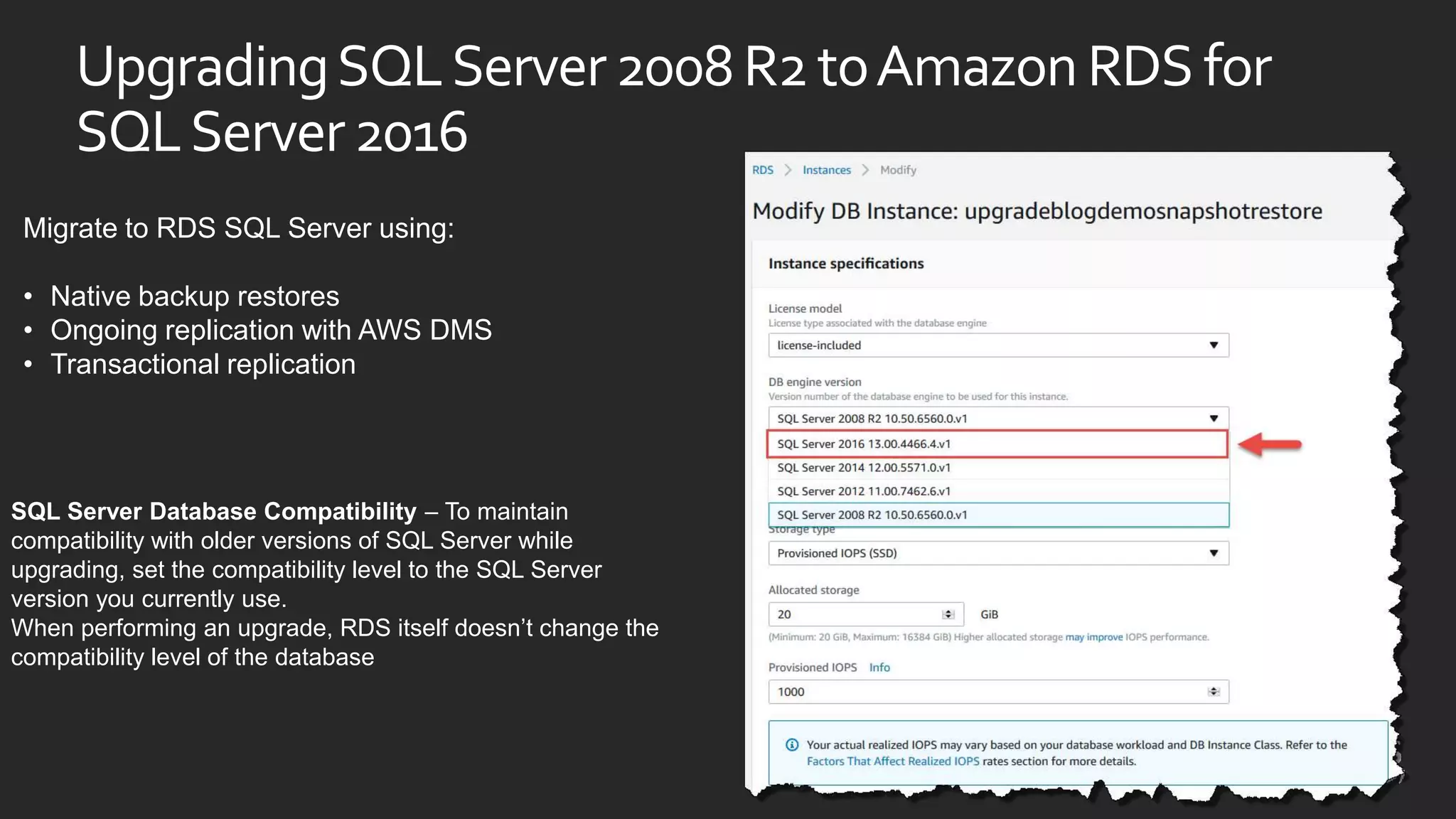
This document discusses options for running SQL Server workloads on AWS, including using Amazon RDS and Amazon EC2. It provides a high-level overview of the features and capabilities of SQL Server when used with each AWS service. Key points include:
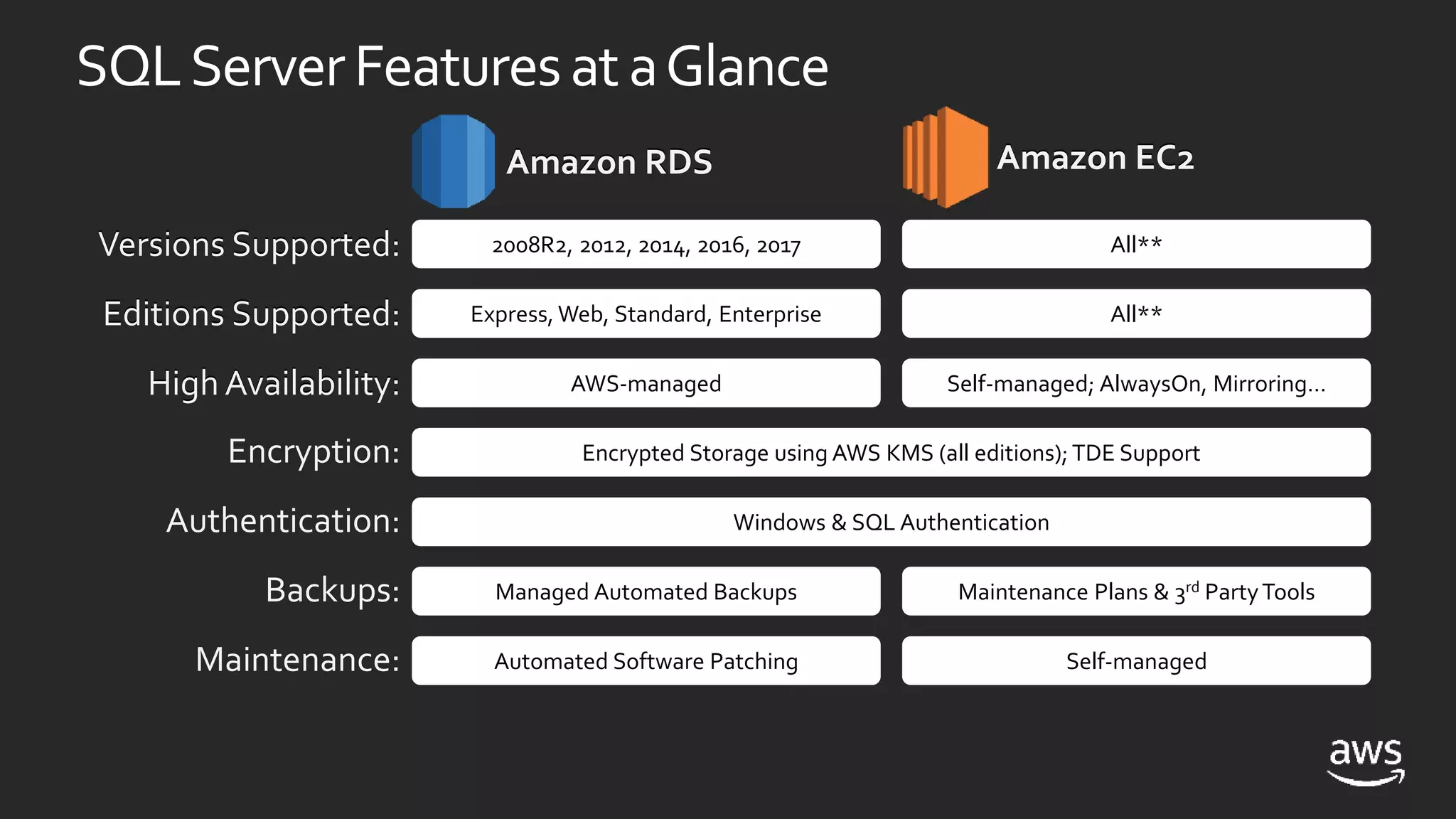
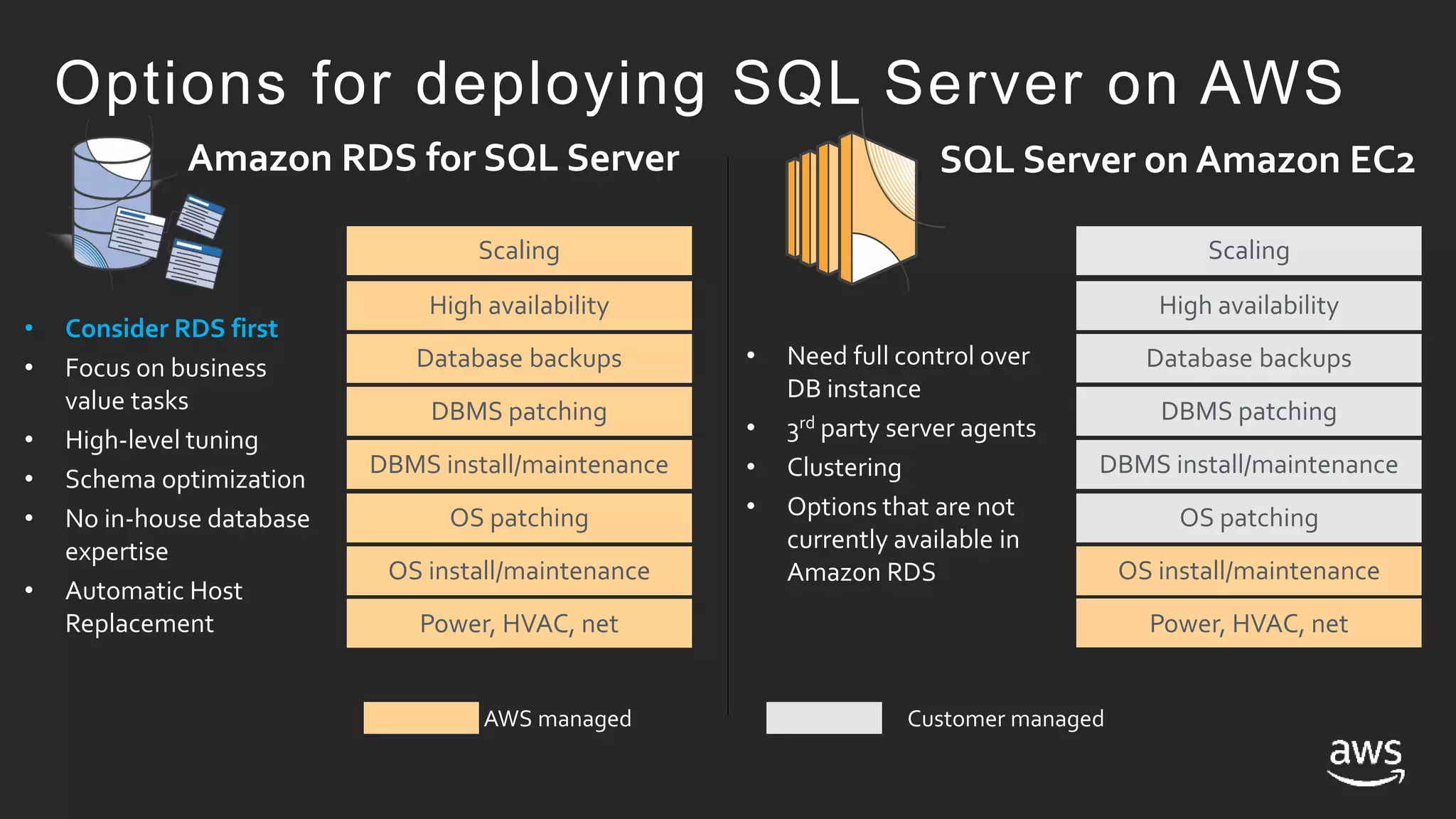
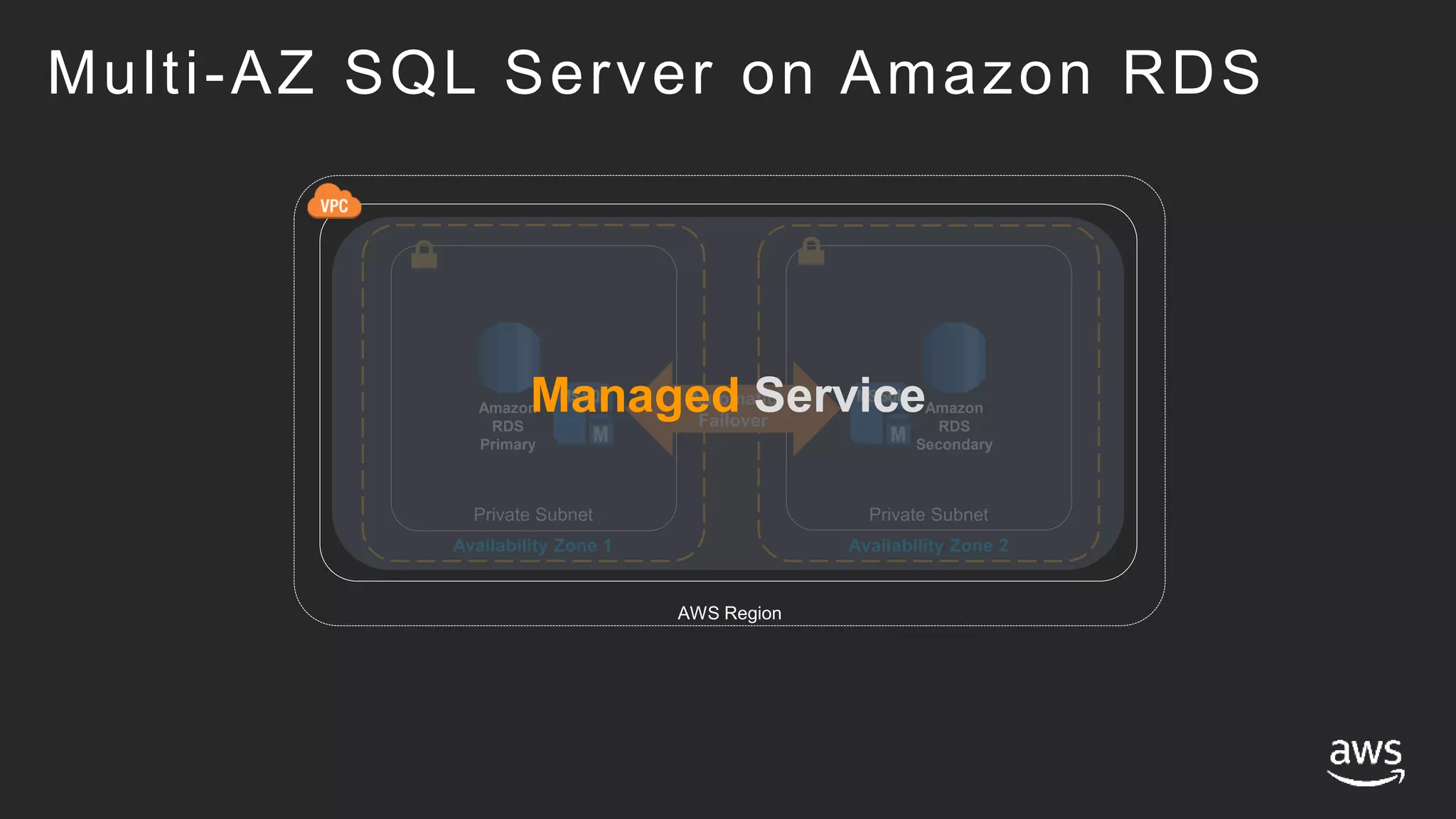
- Amazon RDS provides a managed service for deploying SQL Server, handling tasks like maintenance, patching, backups and high availability. EC2 provides an unmanaged option where the customer handles these tasks.
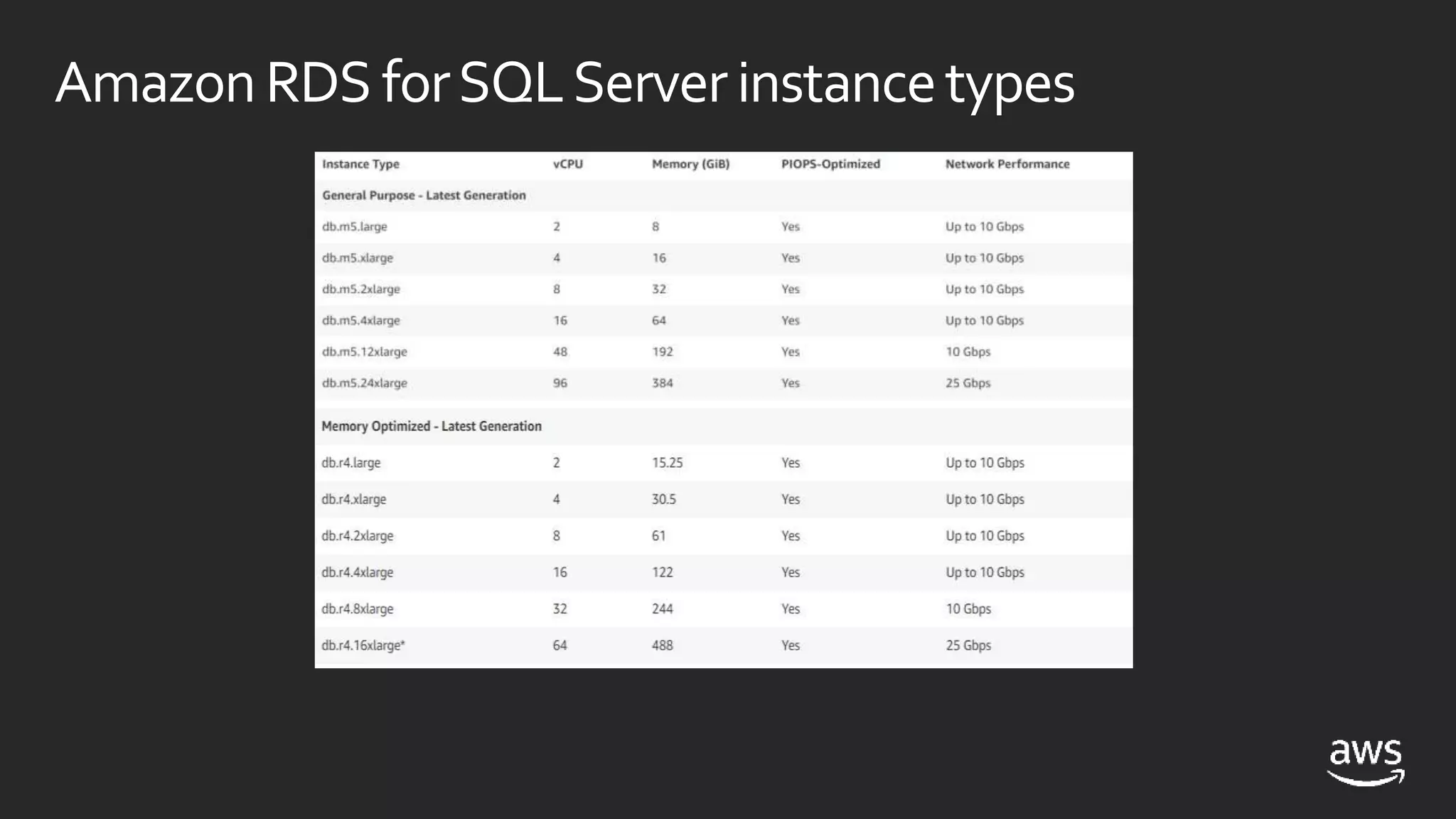
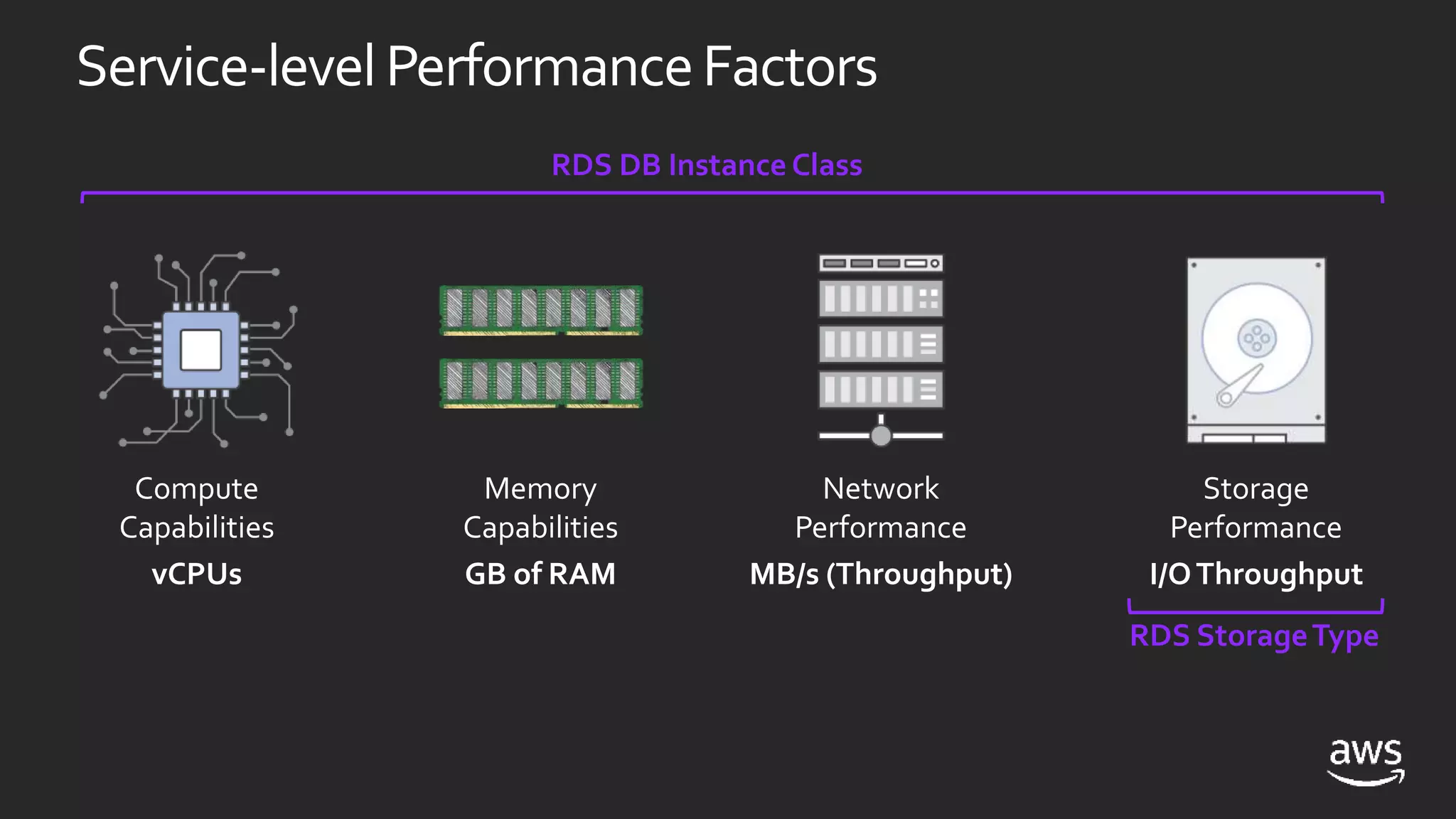
- Both RDS and EC2 support multiple versions of SQL Server. RDS automates tasks while EC2 gives more control over the SQL instance.
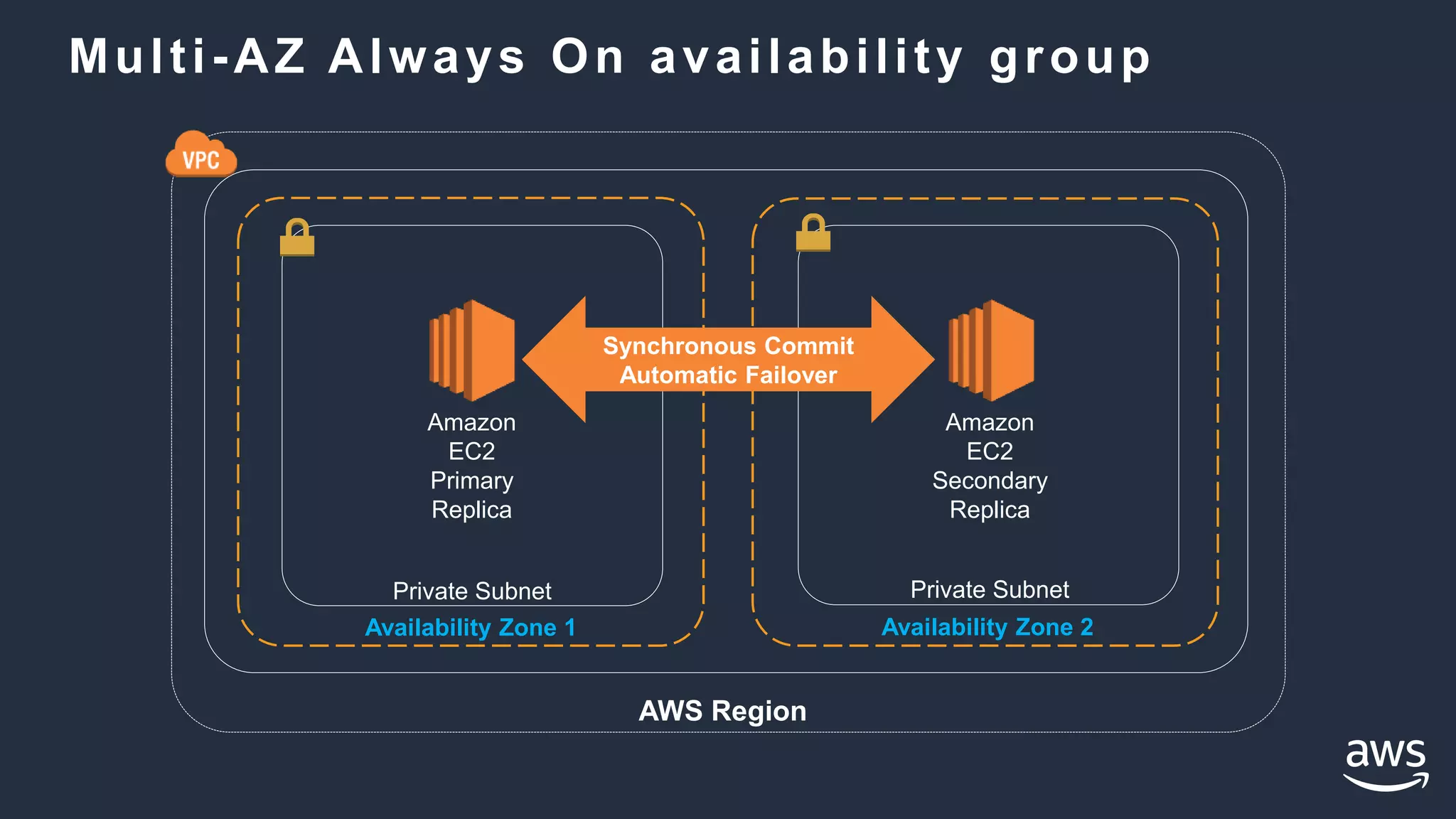
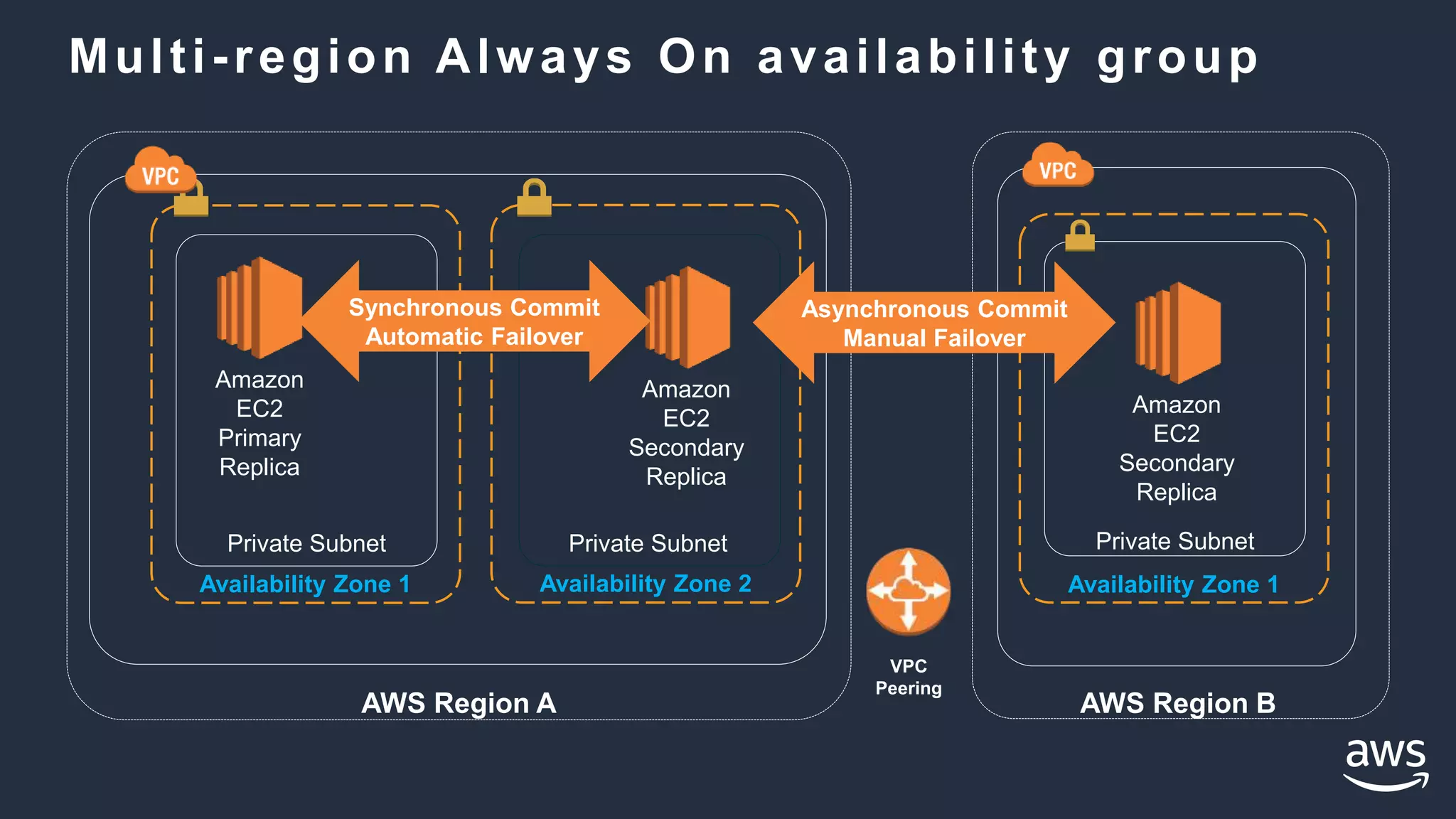
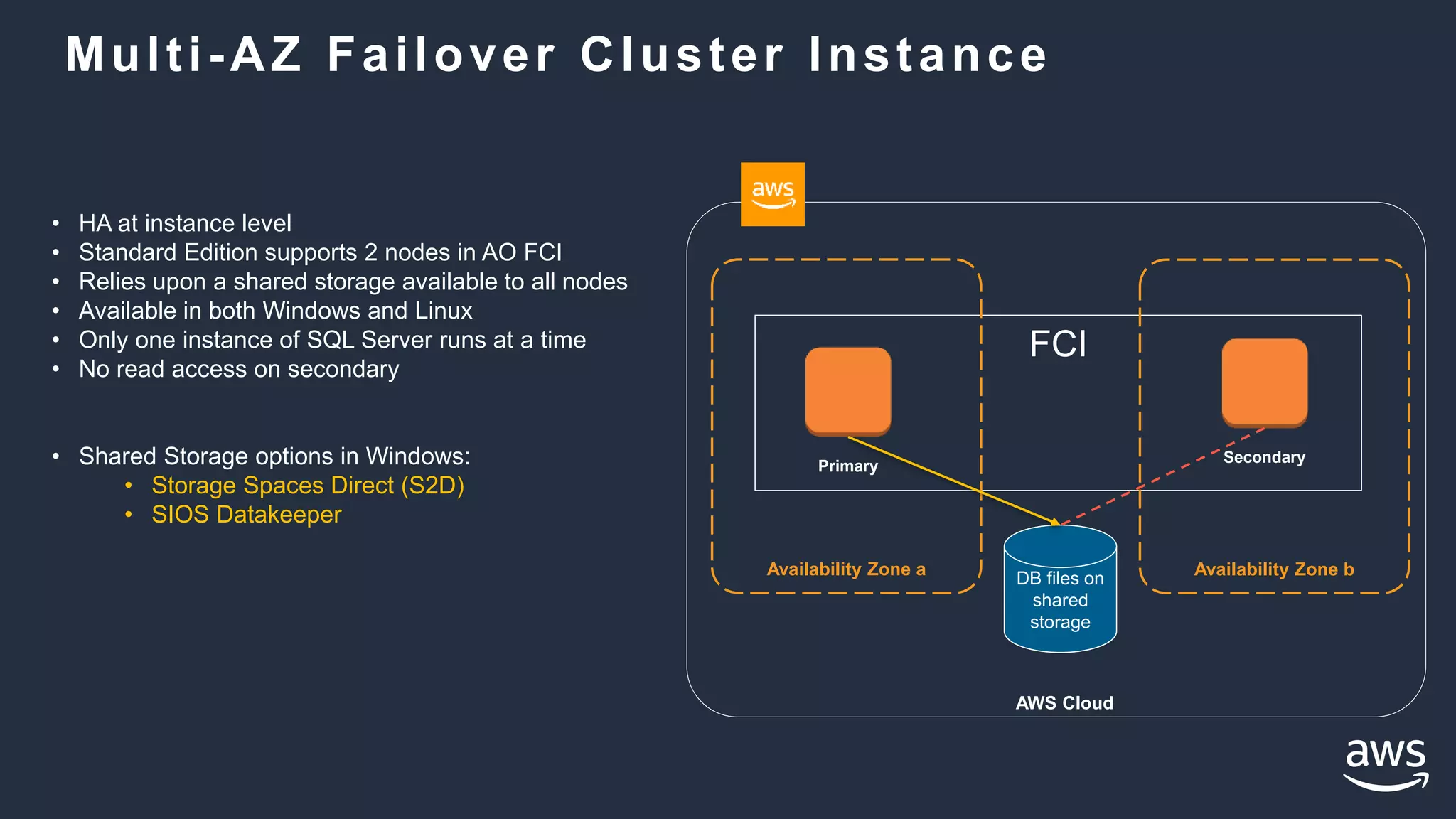
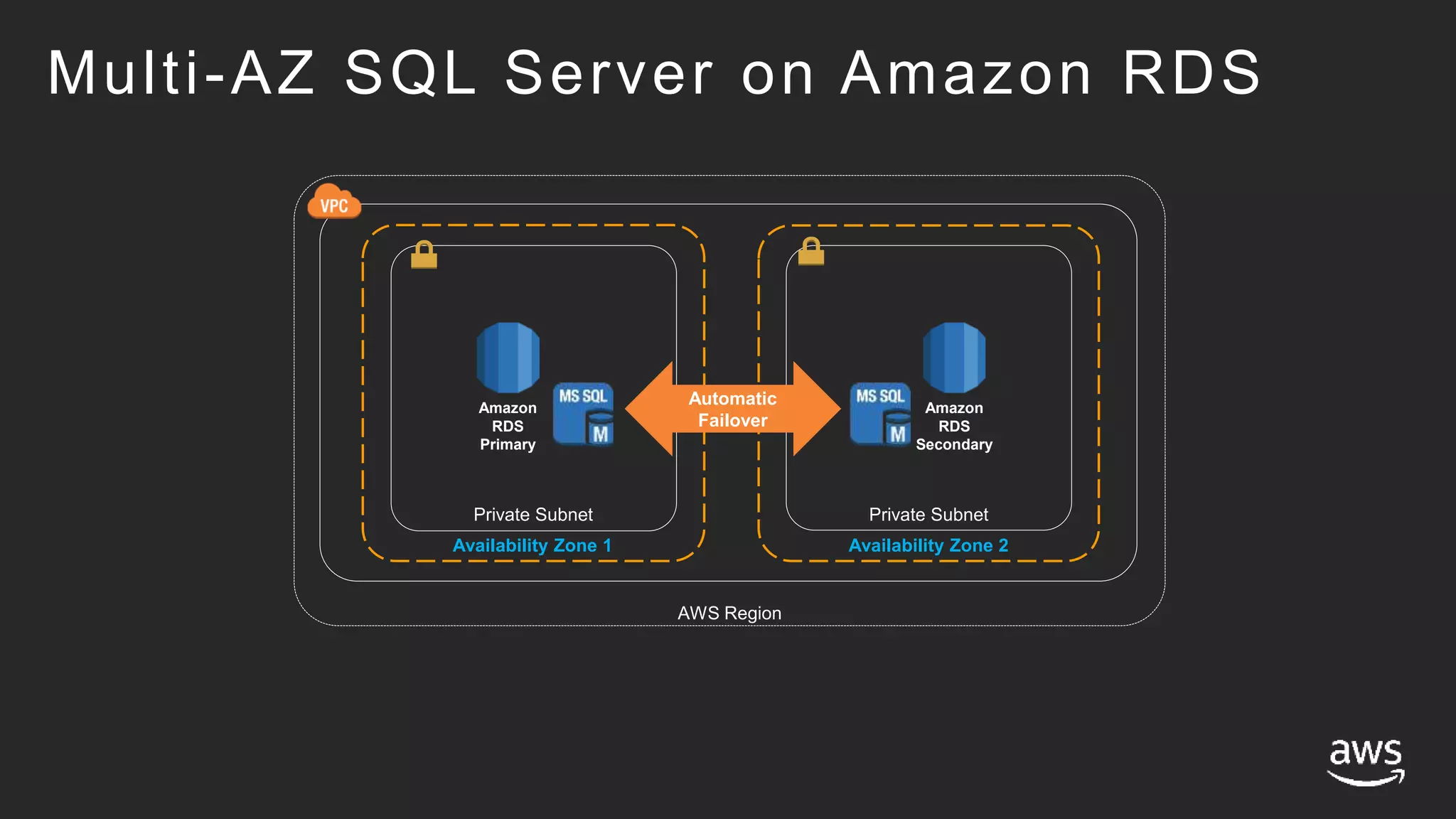
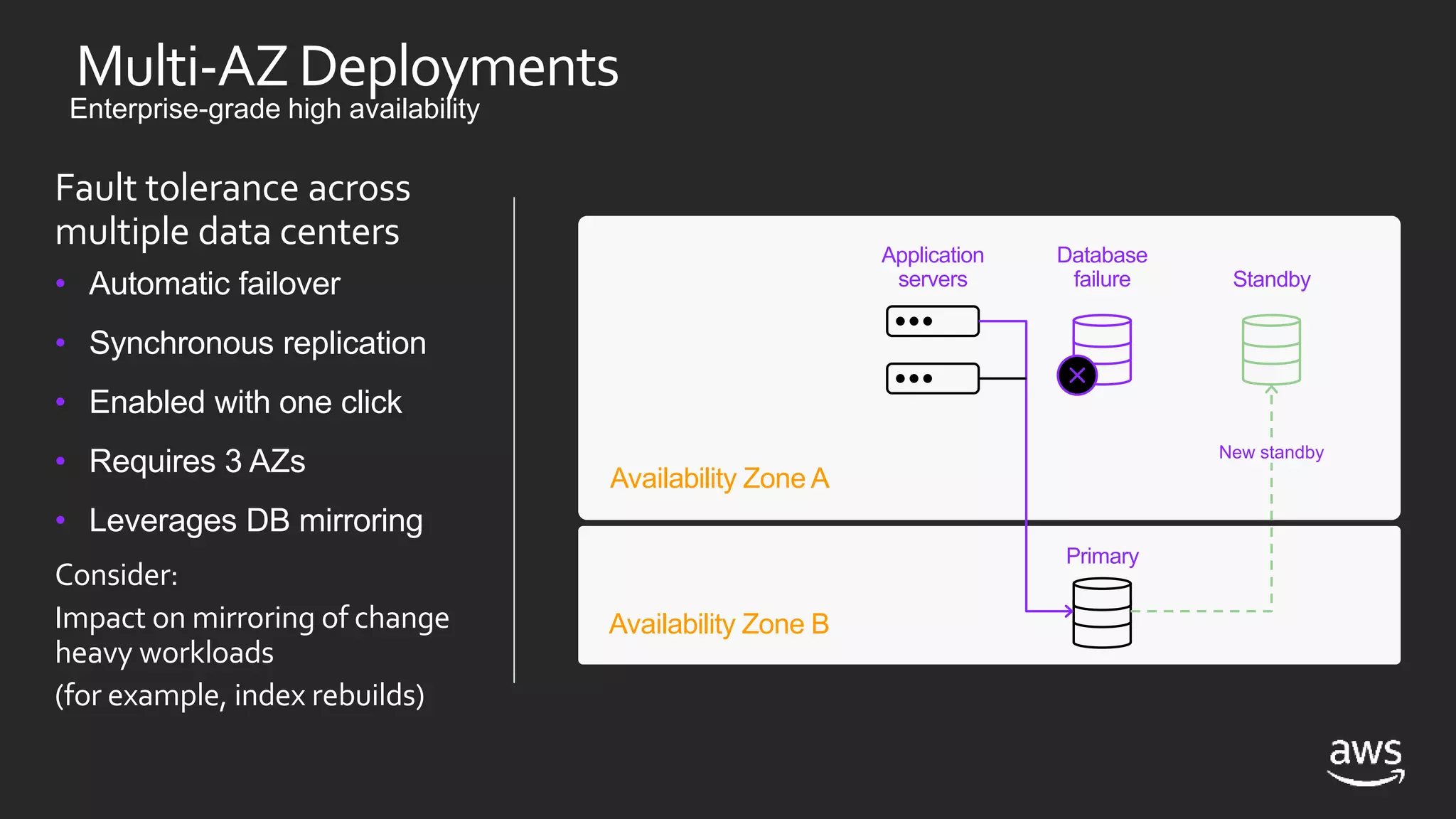
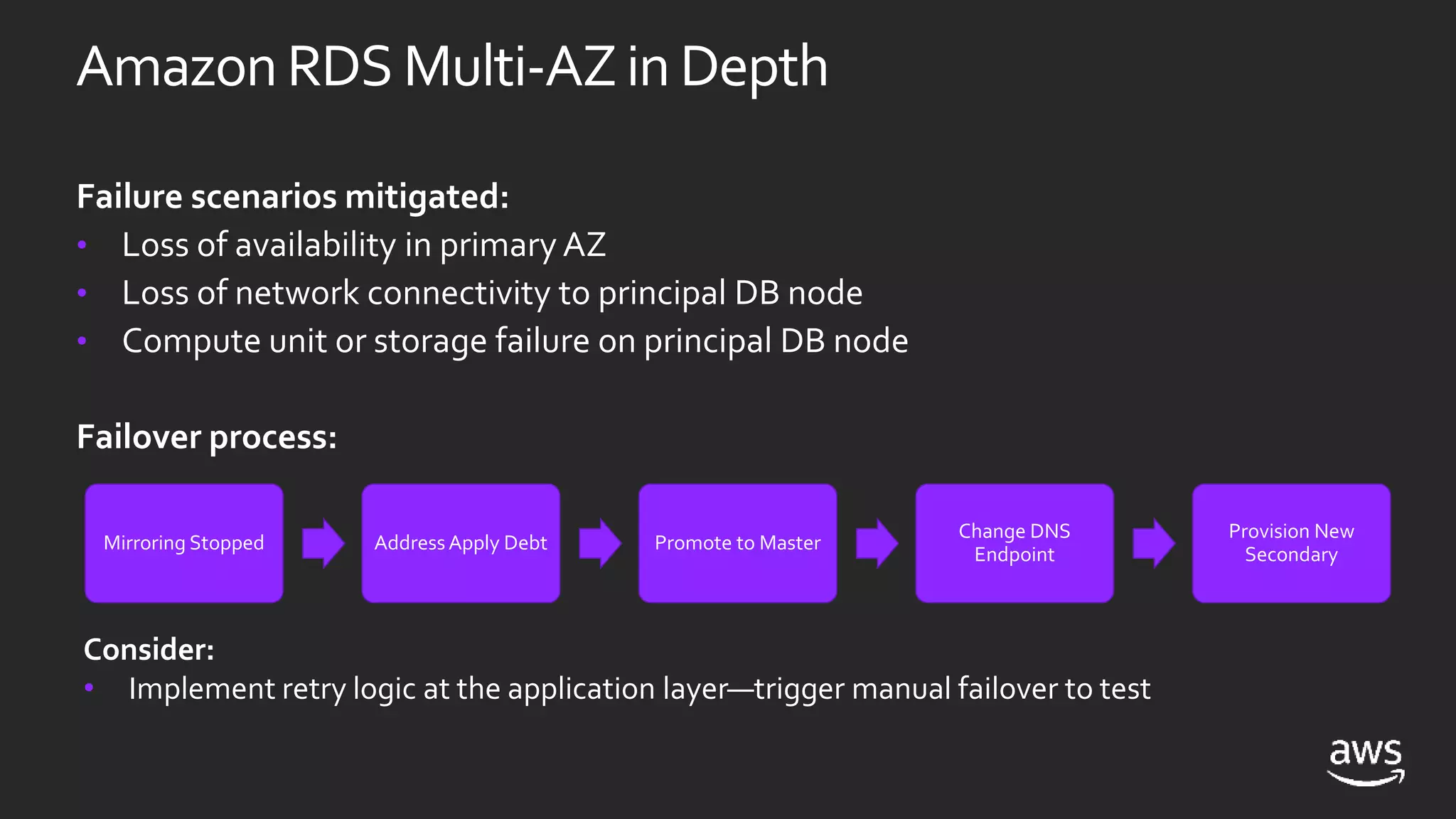
- High availability options with RDS include multi-AZ deployments for automatic failover. With EC2