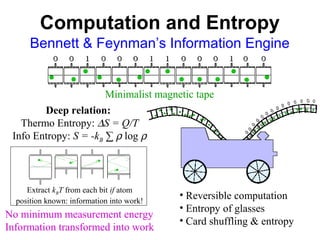
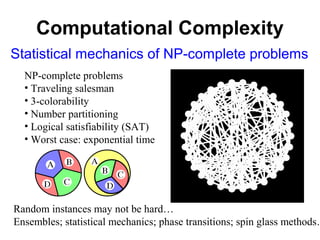
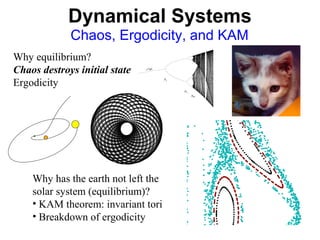
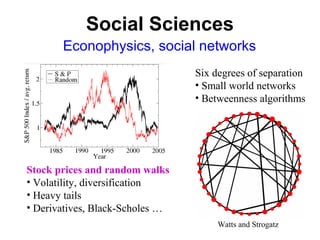
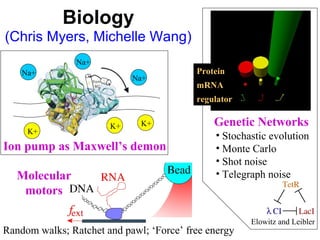
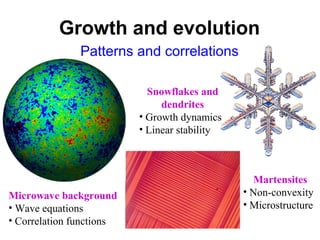
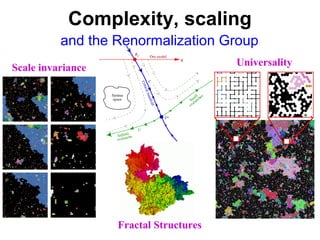
The document discusses updating the statistical mechanics curriculum to incorporate developments over the last 50 years. It notes how statistical mechanics is important to many fields beyond physics like biology, computer science, engineering, mathematics and social sciences. The document argues statistical mechanics will be taught across many fields in the next generation, and teaching it to a variety of fields enriches the subject for those with physics backgrounds.