This document provides an overview of different types of microeconomics analysis:
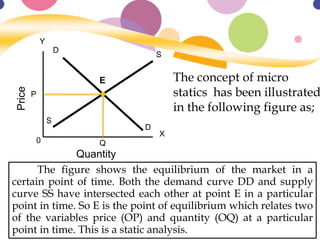
1) Micro statics refers to the equilibrium between economic variables at a single point in time. It shows the relationship between price and quantity at a moment when supply and demand curves intersect.
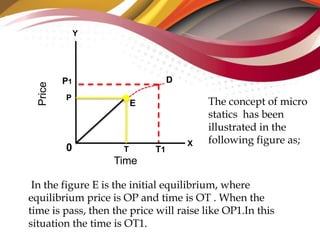
2) Micro dynamics analyzes how an initial equilibrium breaks down and a new equilibrium is established over time as prices and quantities change. It shows the disequilibrium process.
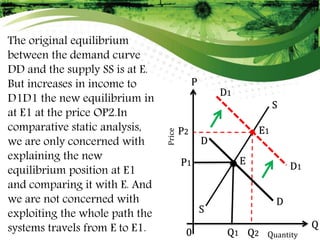
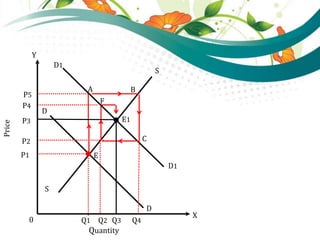
3) Comparative micro statics compares different equilibriums at different points in time as conditions change, but does not analyze the process of moving between equilibriums. It is concerned with explaining different equilibrium states rather than the transition between them.