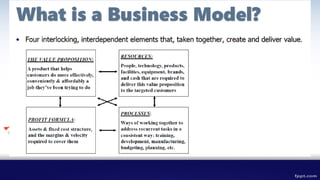
The document discusses e-commerce business models, including their definitions, value propositions, and revenue models such as advertising, subscription, transaction fee, sales, and affiliate models. It highlights the importance of market opportunity, strategy, and organizational development in successful e-commerce operations. Additionally, it outlines individual tasks focused on analyzing e-commerce platforms and their failures for assessment purposes.