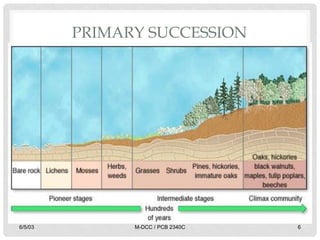
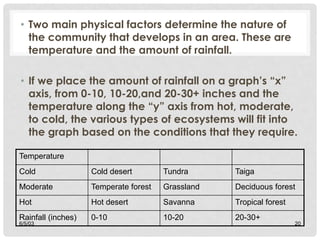
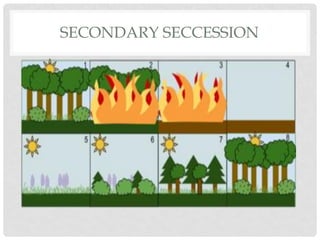
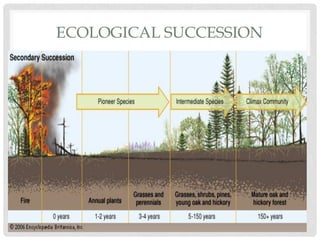
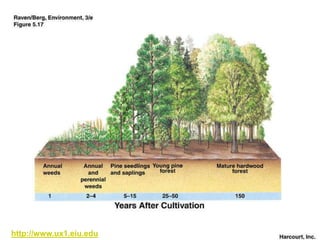
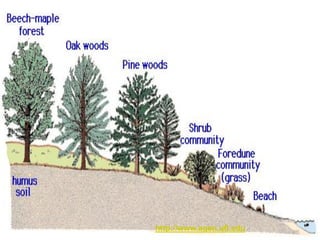
Ecological succession describes the natural process of environmental change through which biological communities develop over time. Primary succession occurs in areas without previous life, like new lava flows, while secondary succession follows a disturbance in an existing ecosystem. Succession proceeds through a series of changes as pioneer species like lichens establish and modify the environment, allowing other species to colonize until a climax community develops.