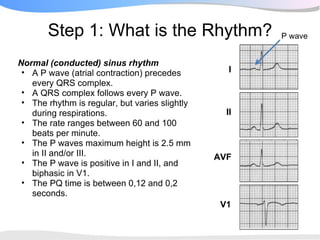
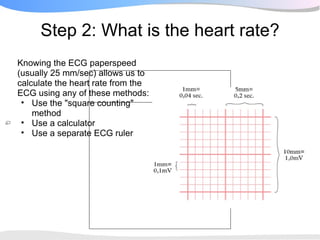
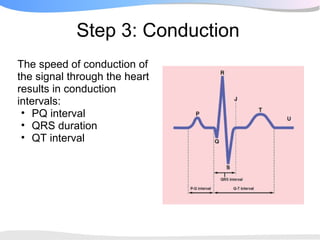
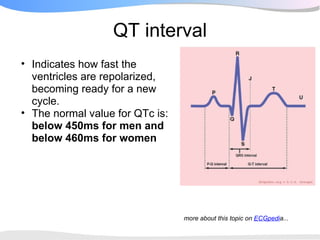
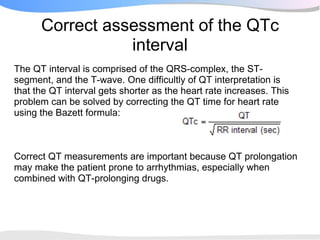
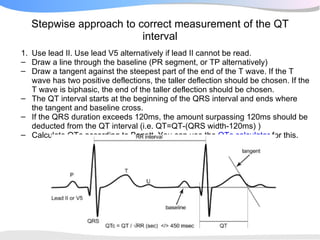
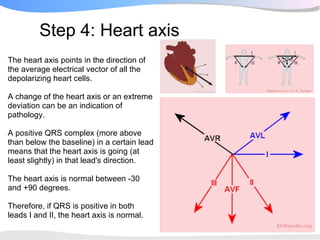
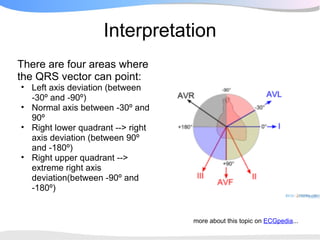
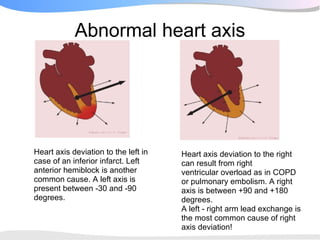
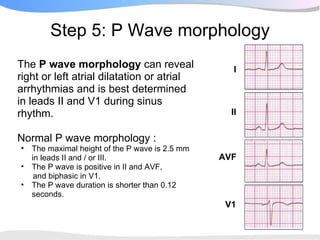
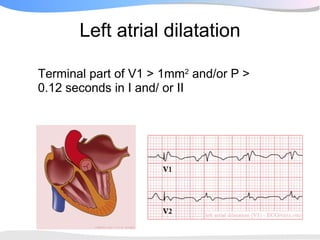
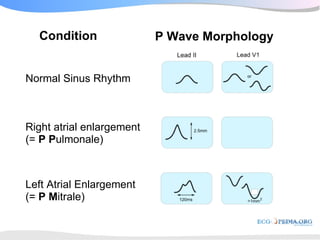
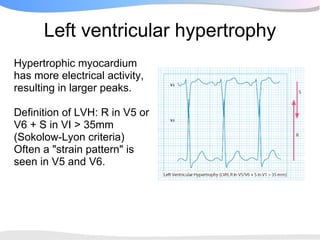
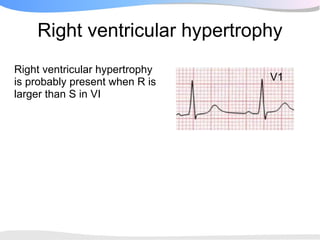
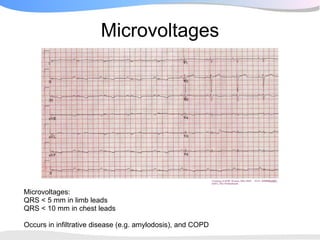
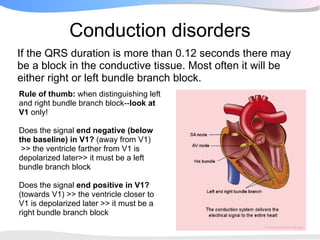
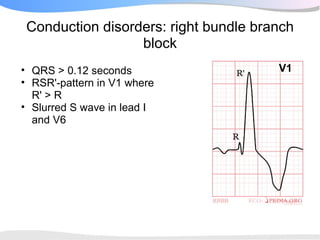
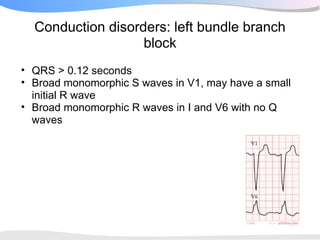
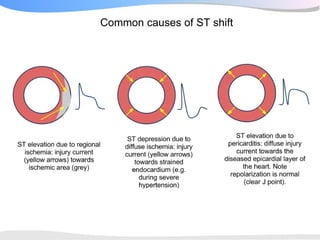
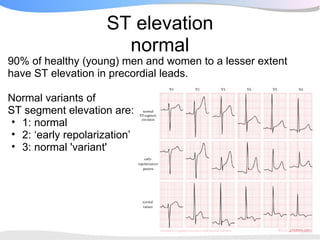
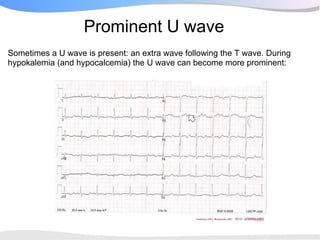
The document outlines a systematic 7+2 step approach for interpreting electrocardiograms (ECGs) that involves analyzing the rhythm, rate, conduction, axes, wave morphologies, segment changes, and comparing to previous ECGs to form a clinical conclusion. The 7 steps examine the rhythm, rate, conduction intervals, axes, P wave, QRS, and ST-T wave morphologies. The +2 steps involve comparing the ECG to previous tracings and formulating a concluding statement.