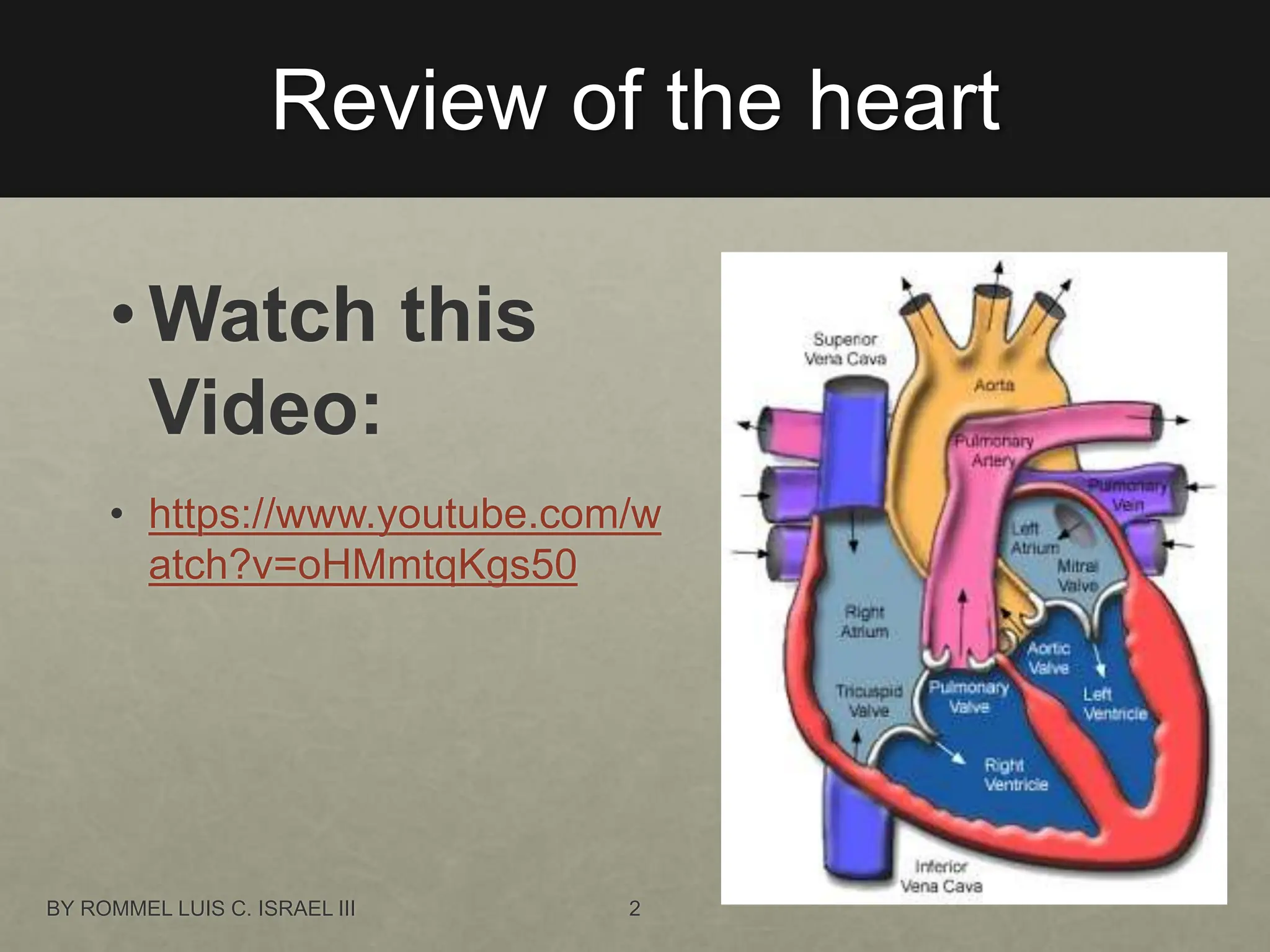
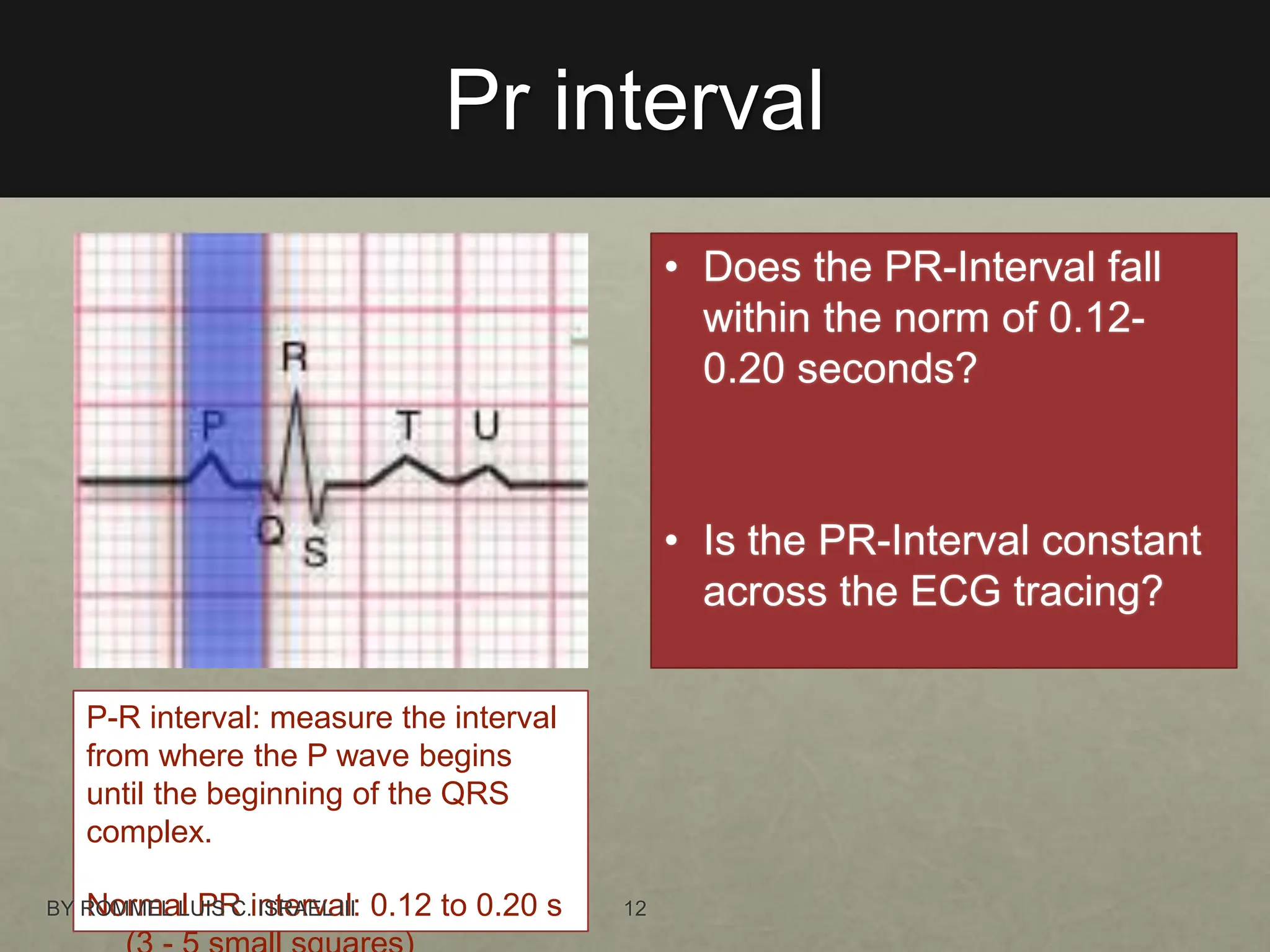
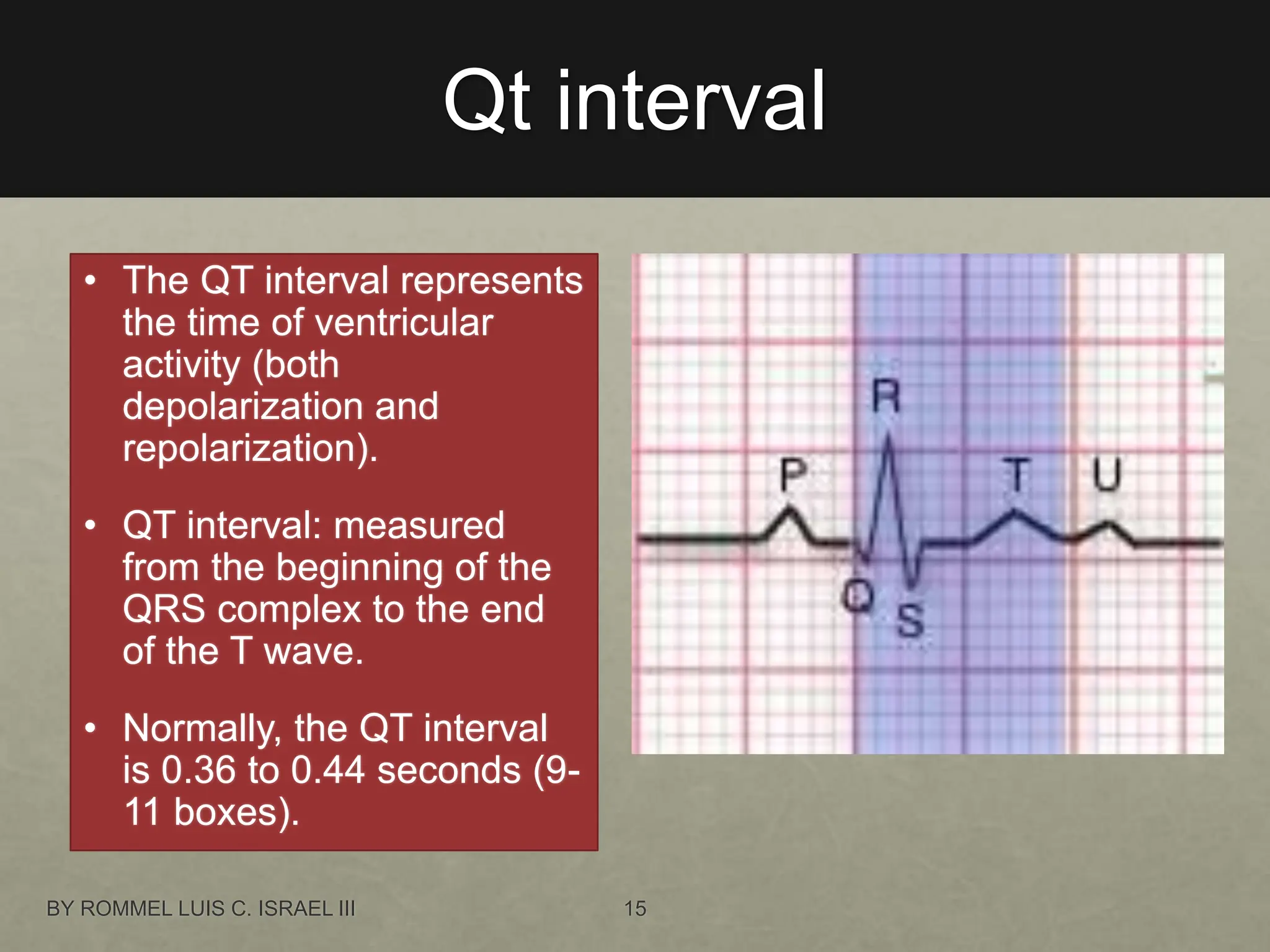
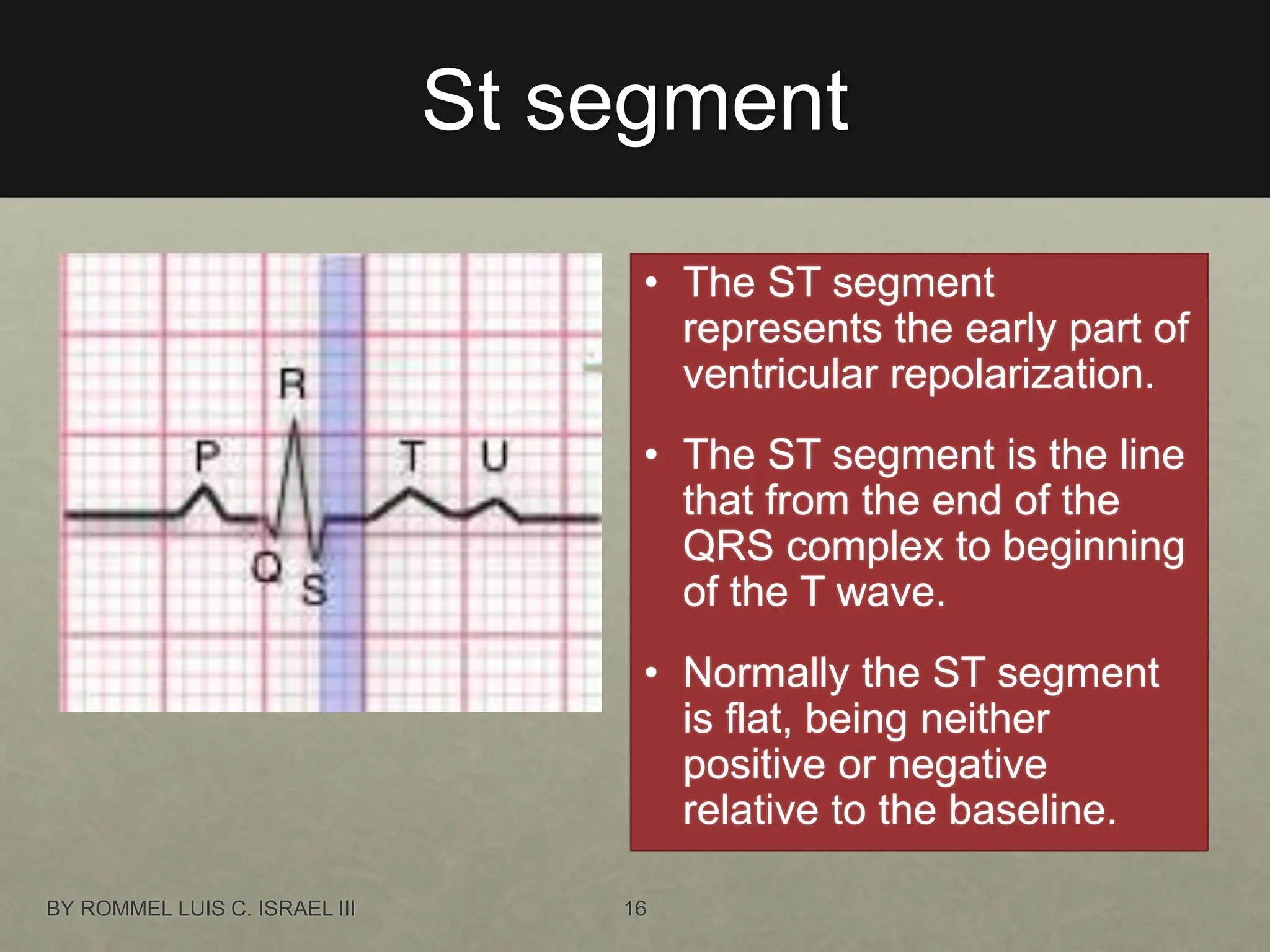
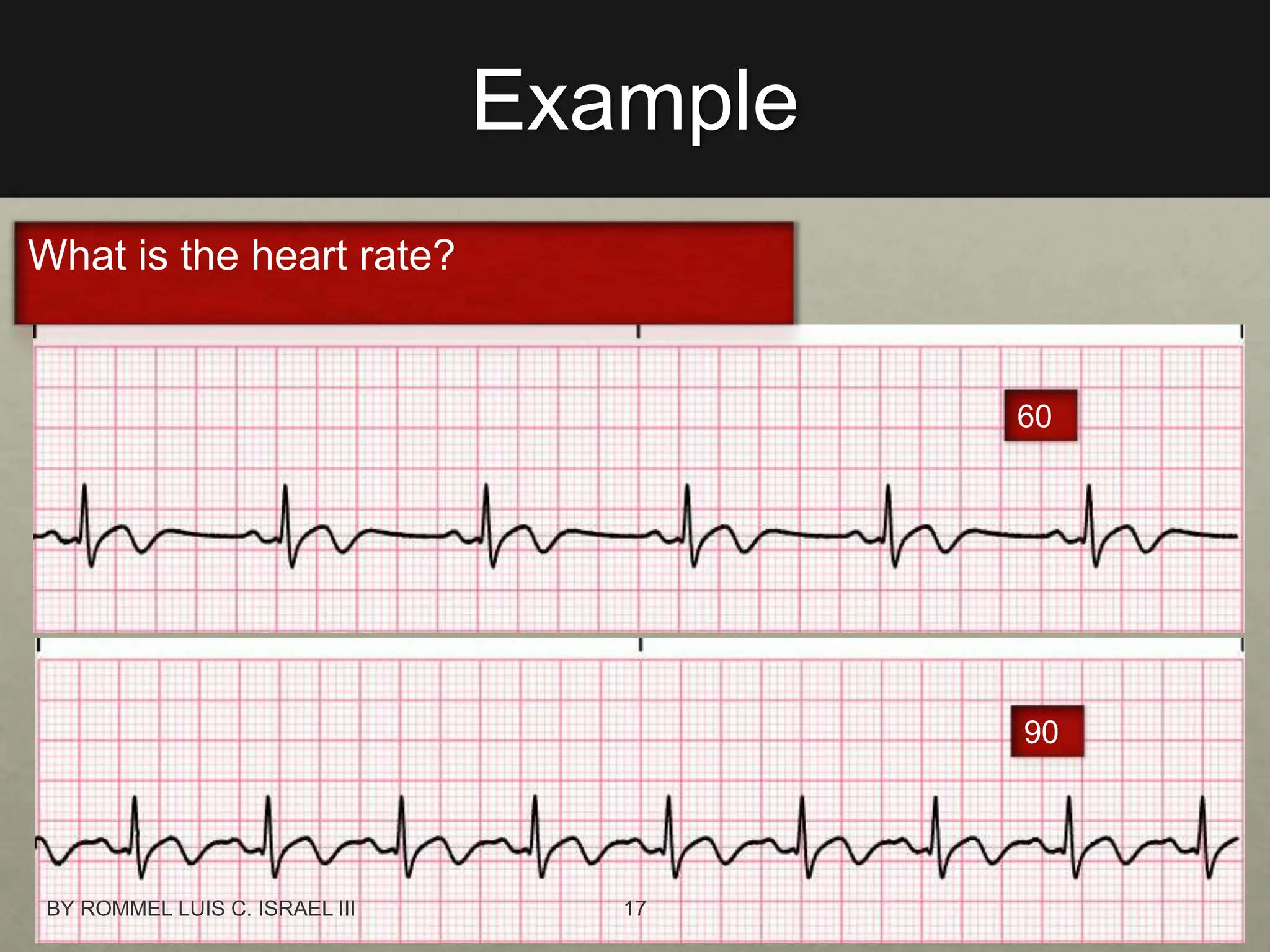
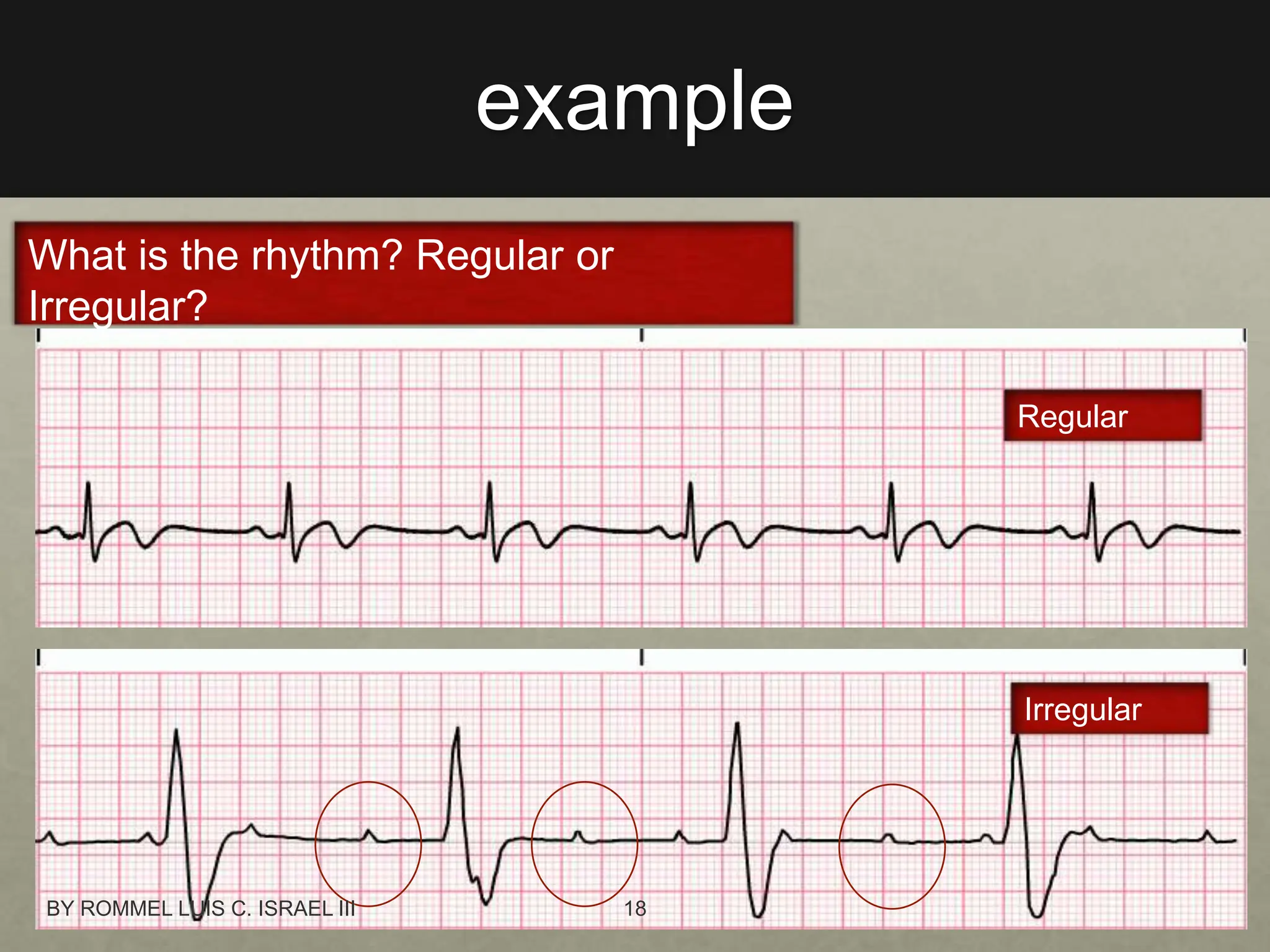
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the electrical conduction system of the heart and how to interpret ECG strips. It outlines the components of a normal ECG, including the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave, and details an 8-step procedure for ECG reading. Key metrics like heart rate, rhythm, PR interval, QRS interval, T wave, QT interval, and ST segment are described with normal ranges and interpretation tips.