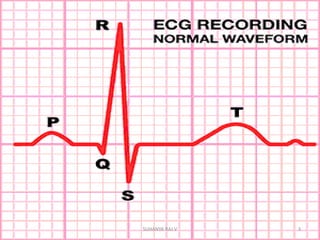
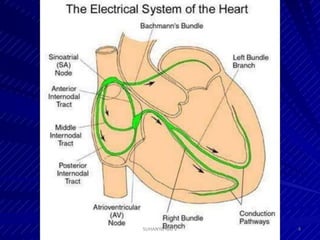
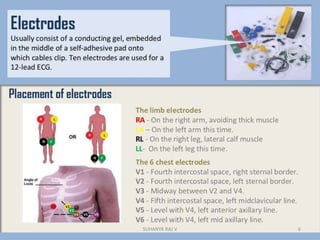
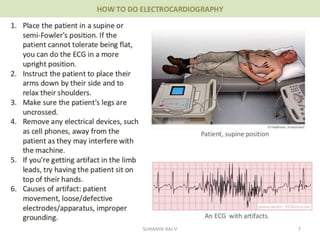
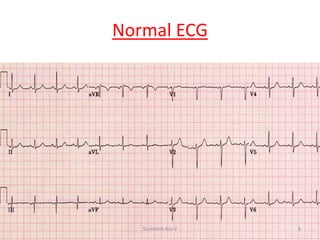
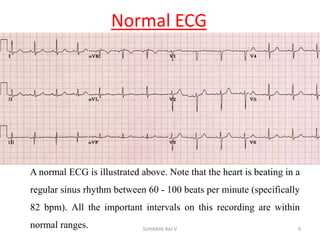
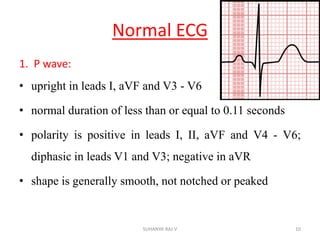
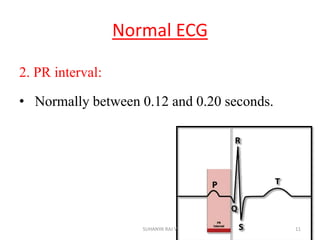
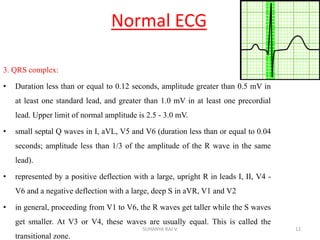
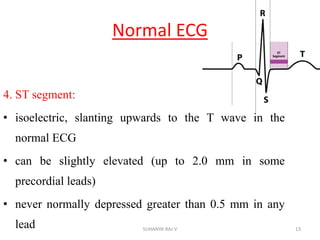
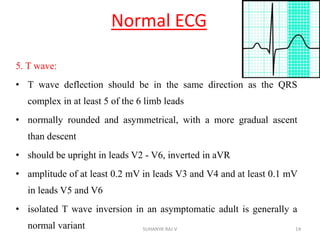
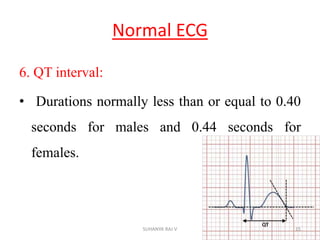
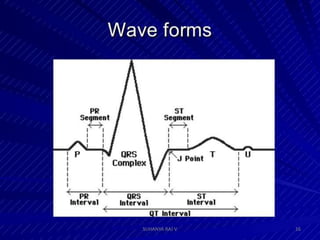
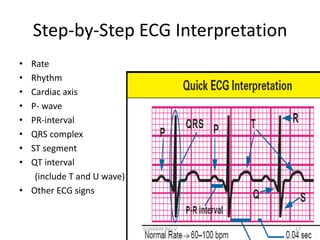
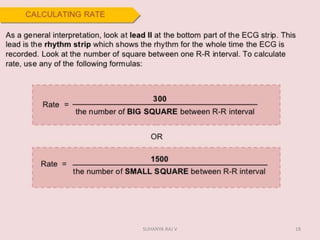
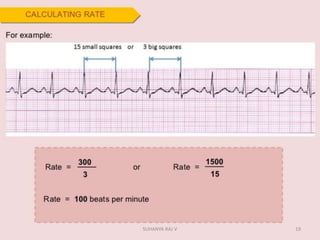
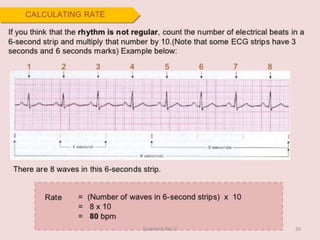
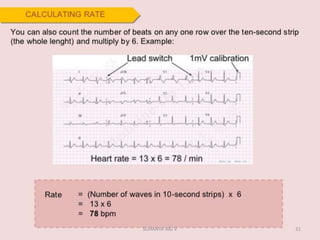
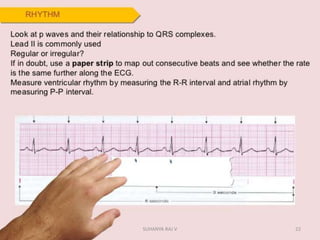
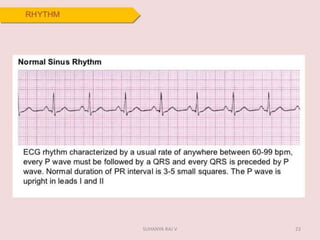
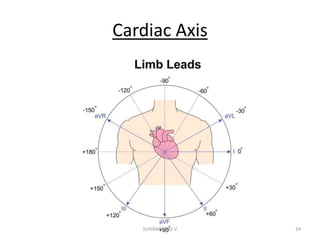
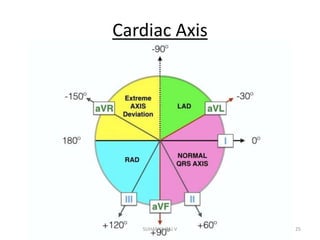
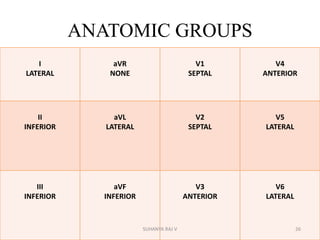
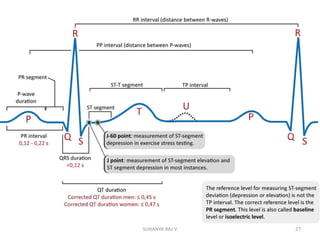
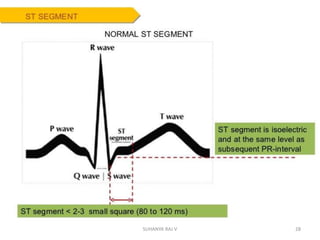
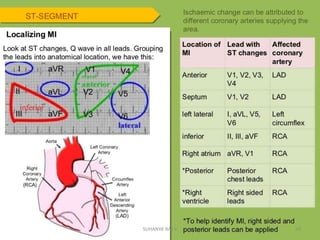
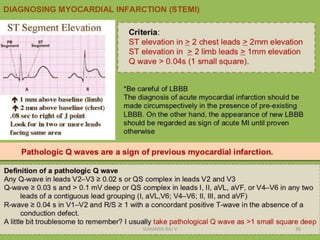
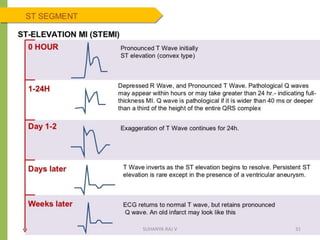
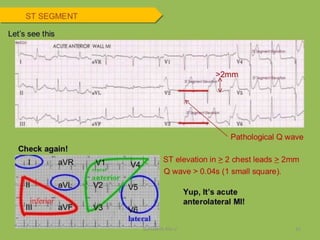
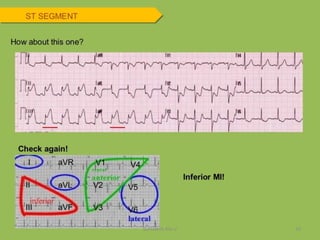
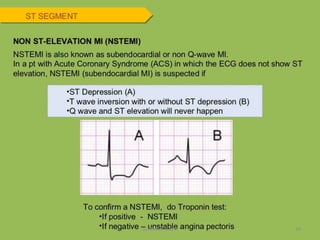
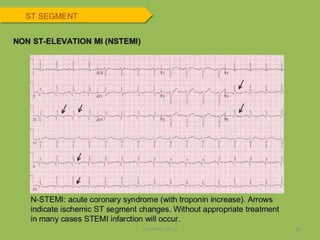
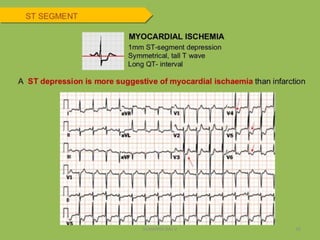
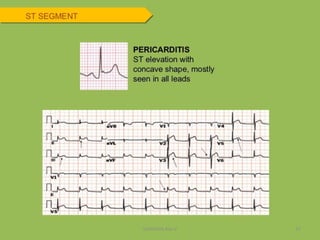
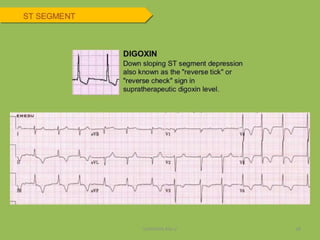
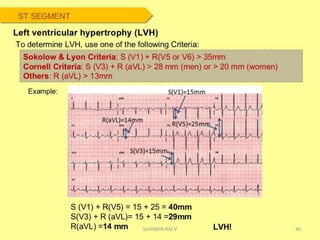
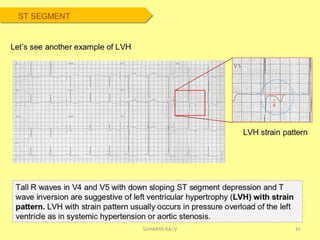
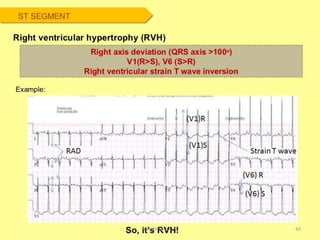
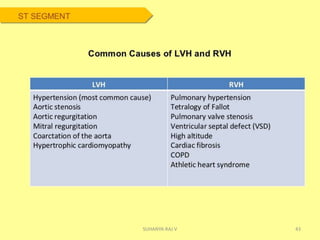
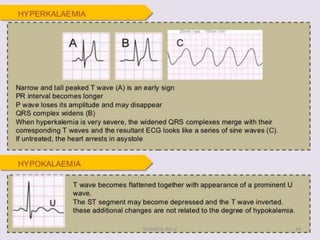
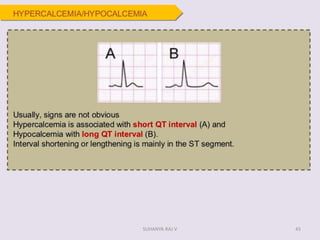
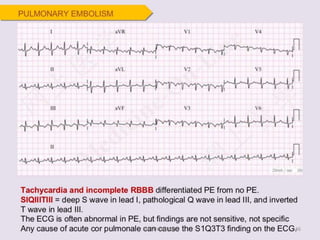
Electrocardiography is the process of recording the heart's electrical activity through an electrocardiogram (ECG) via electrodes on the skin. A normal ECG shows a regular sinus rhythm with specific characteristics in wave patterns, intervals, and segments, all falling within defined normal ranges. Key components of interpretation include the rate, rhythm, cardiac axis, and the shapes and measurements of the P wave, QRS complex, ST segment, and T wave.