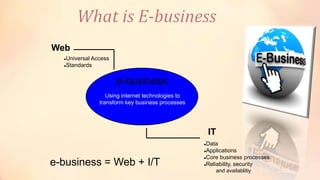
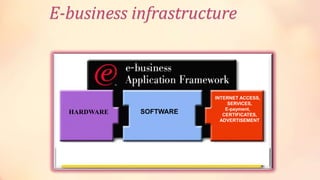
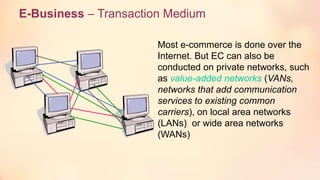
IBM began marketing the term "e-business" in 1997 to describe using internet technologies to transform key business processes. IBM invested $1 billion to promote its expertise in e-business. While IBM did not trademark the term, "e-business" became widely used to describe electronically mediated business exchanges within and between organizations using technologies like intranets, extranets, and the internet. E-business involves using web technologies and IT systems together to connect consumers, businesses, and other stakeholders globally 24/7.