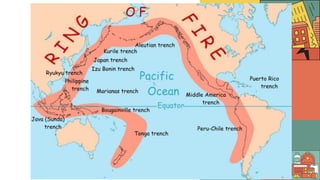
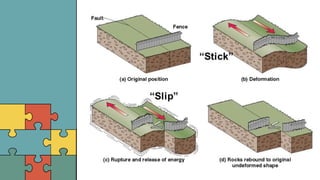
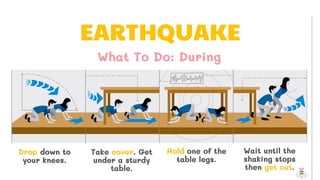
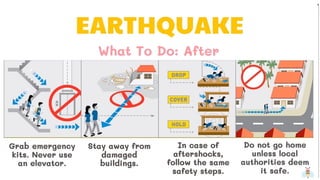
1. Earthquakes are caused by the sudden movement of rock materials below the earth's surface along faults or by volcanic activity. This movement releases stress that has accumulated along geological faults or within active volcanoes.
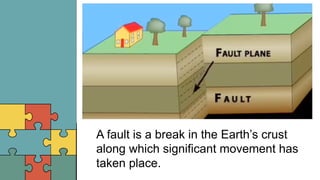
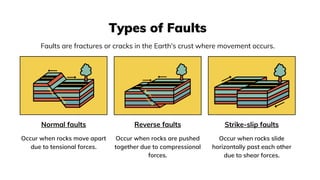
2. A fault is a break in the Earth's crust where significant movement has occurred. Common types of faults include normal faults, reverse faults, and strike-slip faults, which form due to different types of forces.
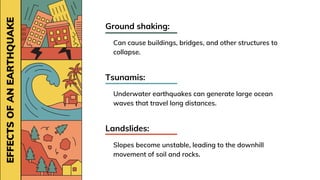
3. Effects of earthquakes include ground shaking that can damage structures, tsunamis generated by underwater quakes, and landslides caused by destabilized slopes.