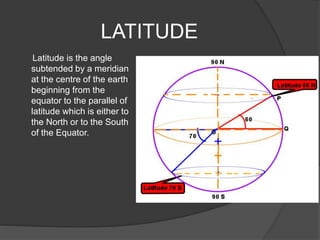
The document discusses latitude and longitude, which are used to locate places on Earth. Latitude is measured in degrees north and south of the equator, while longitude is measured in degrees east and west of the Prime Meridian in Greenwich, England. The document provides details on calculating distances between locations using their latitudes and longitudes, either along meridians of longitude or along the equator. It also discusses finding the shortest distance between two points, which follows a great circle route passing through the North and South Poles.