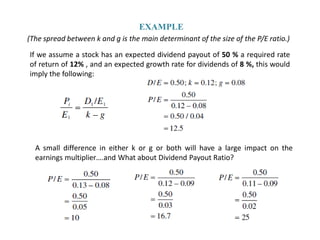
This document discusses the earnings multiplier model for estimating the value of common stocks. [1] It states that the value of any investment is the present value of future returns, and for stocks the returns are the firm's net earnings. [2] Investors estimate a stock's value by determining how many rupees they are willing to pay for each rupee of expected earnings. [3] Factors like the dividend payout ratio, required rate of return, and expected growth rate determine the prevailing price-to-earnings ratio, or earnings multiplier, in the market.