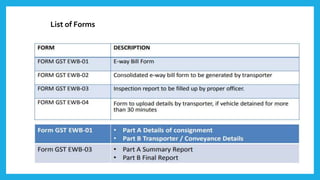
The document discusses e-way bills under the GST system. It provides that e-way bills must be generated for the transportation of goods over Rs. 50,000 in value, and outlines who must generate them. It discusses when e-way bills are required or not required, their validity periods, required documents and details, their purpose for ensuring tax compliance, enforcement methods, and related forms.