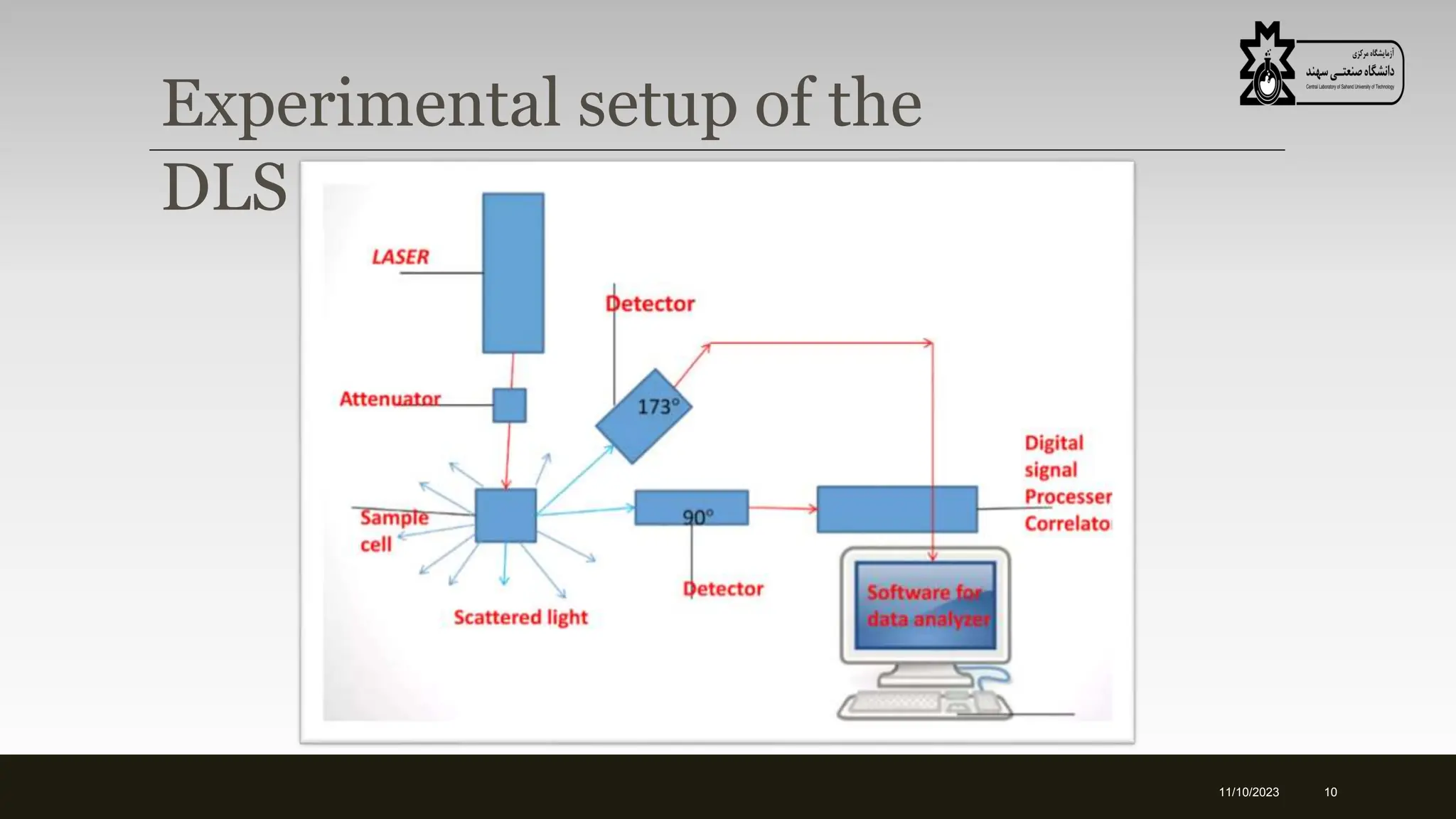
Dynamic light scattering (DLS) measures the hydrodynamic size of nanoparticles and proteins in solution by analyzing the scattering of laser light off particles undergoing Brownian motion. DLS works by measuring the rate of intensity fluctuations in scattered light using an optical technique called photon correlation spectroscopy and the Stokes-Einstein equation to relate particle diffusion to size. The measurement yields the particle size distribution and average hydrodynamic radius of the sample without requiring sample preparation.