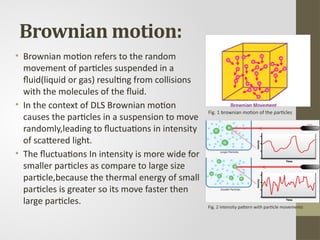
Dynamic light scattering (DLS) is a technique used to determine the size distribution of small particles in suspension or solutions, based on the analysis of scattered light fluctuations caused by Brownian motion. The method, developed in the 1960s and theoretically grounded by Berne and Pecora in the 1970s, utilizes a monochromatic laser to observe these fluctuations, providing valuable data on particle dynamics through the autocorrelation function. DLS offers insights into the motion and size of particles, where smaller particles exhibit greater intensity fluctuations due to their faster movement.