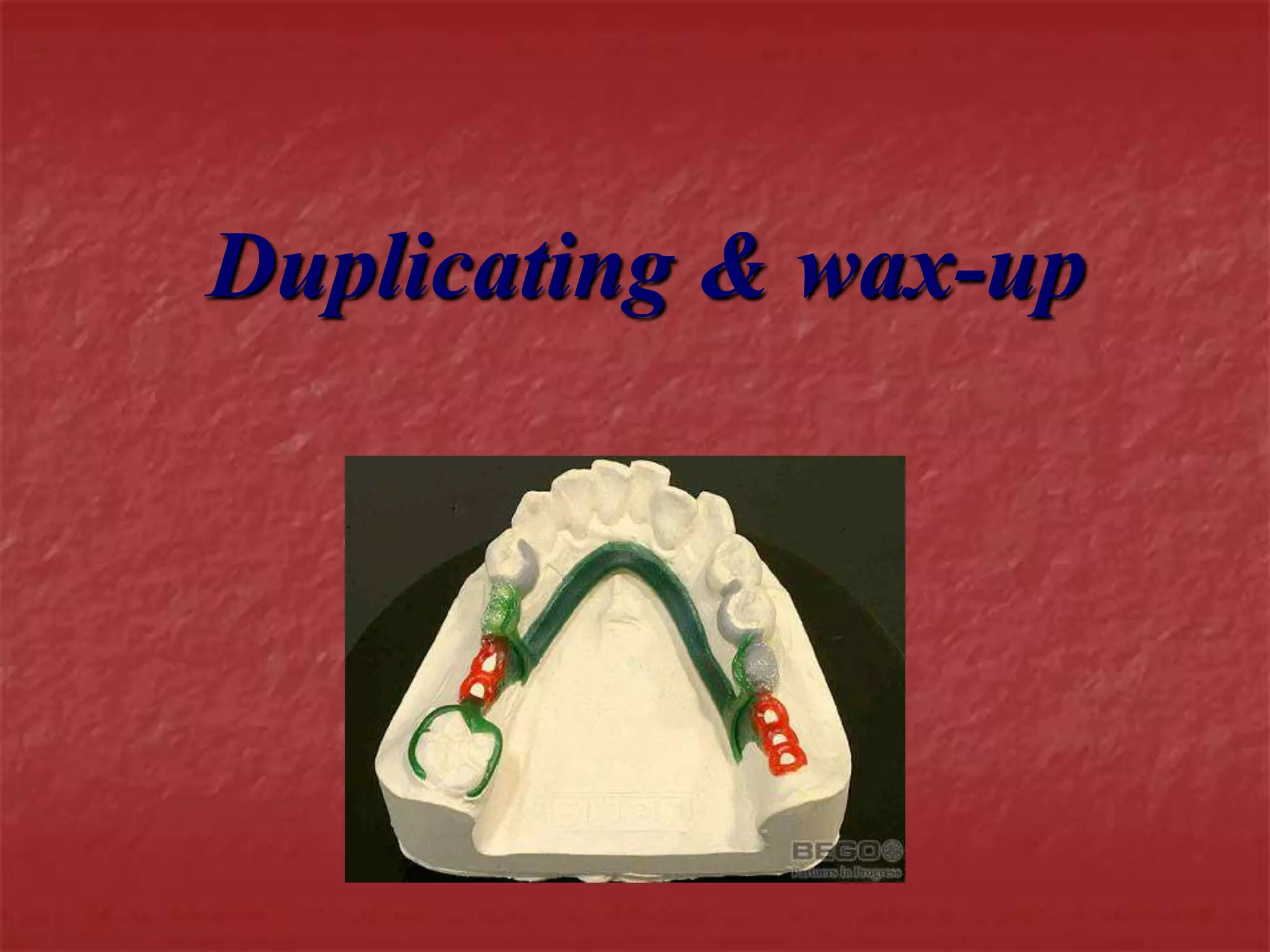
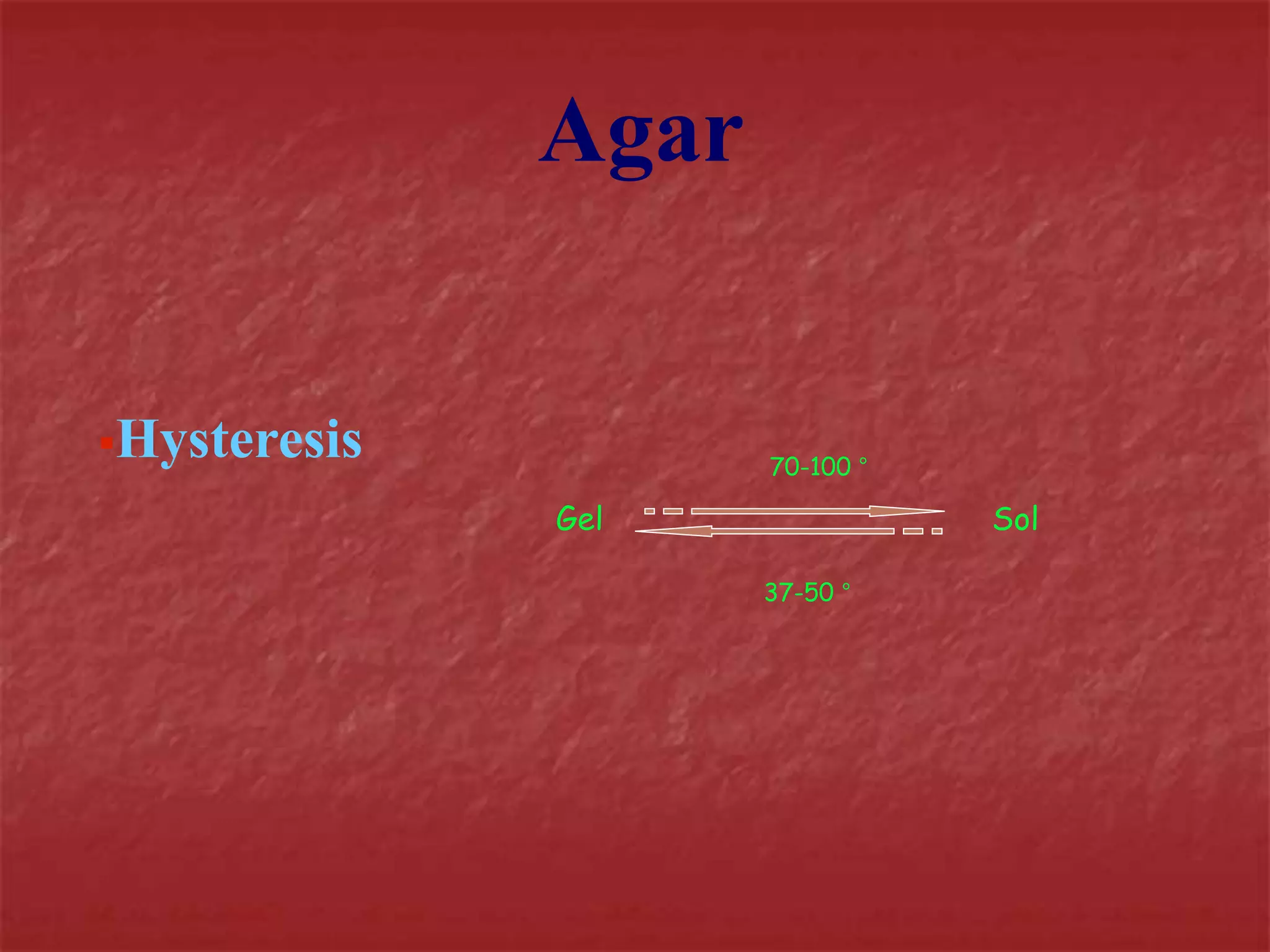
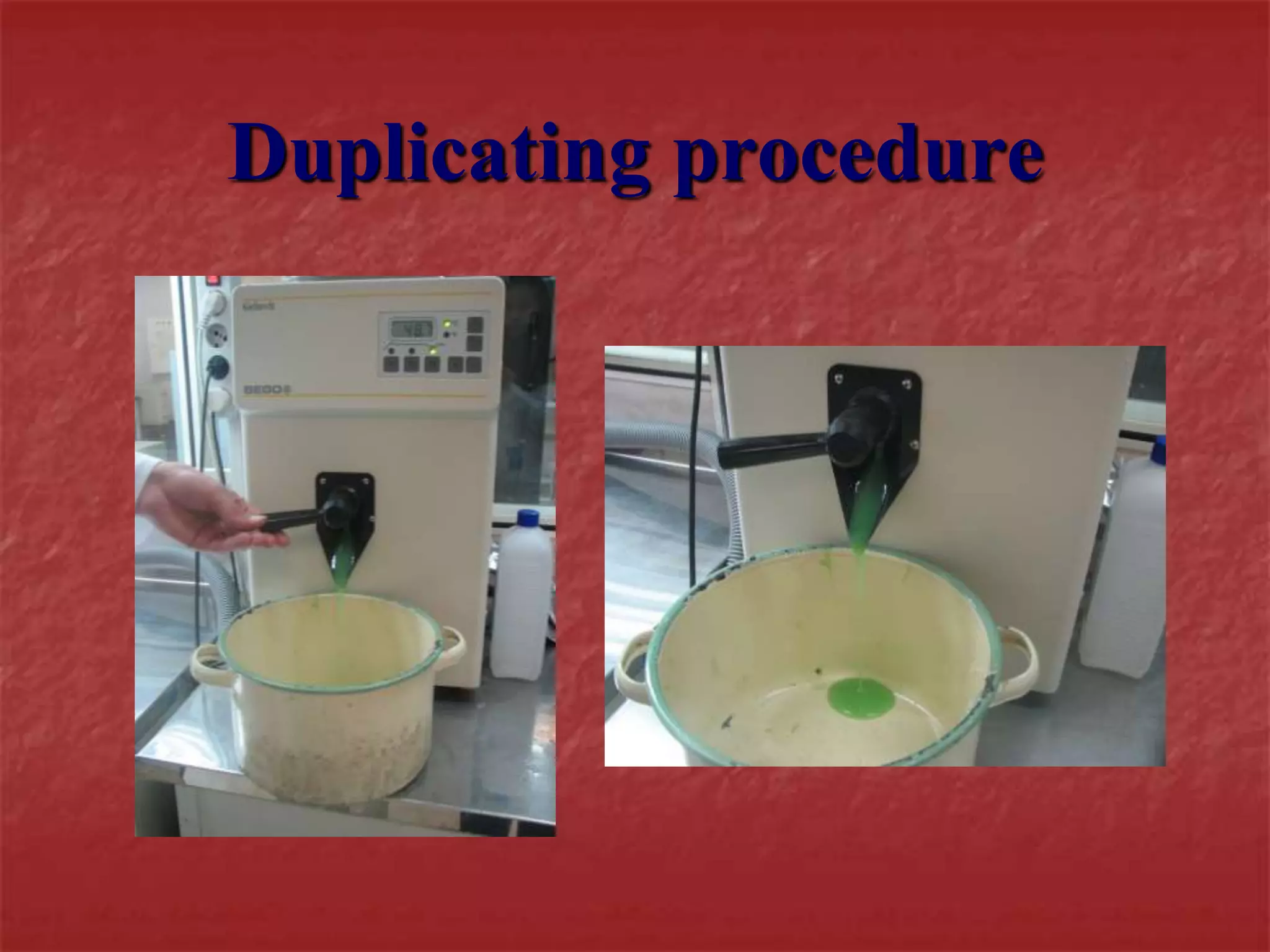
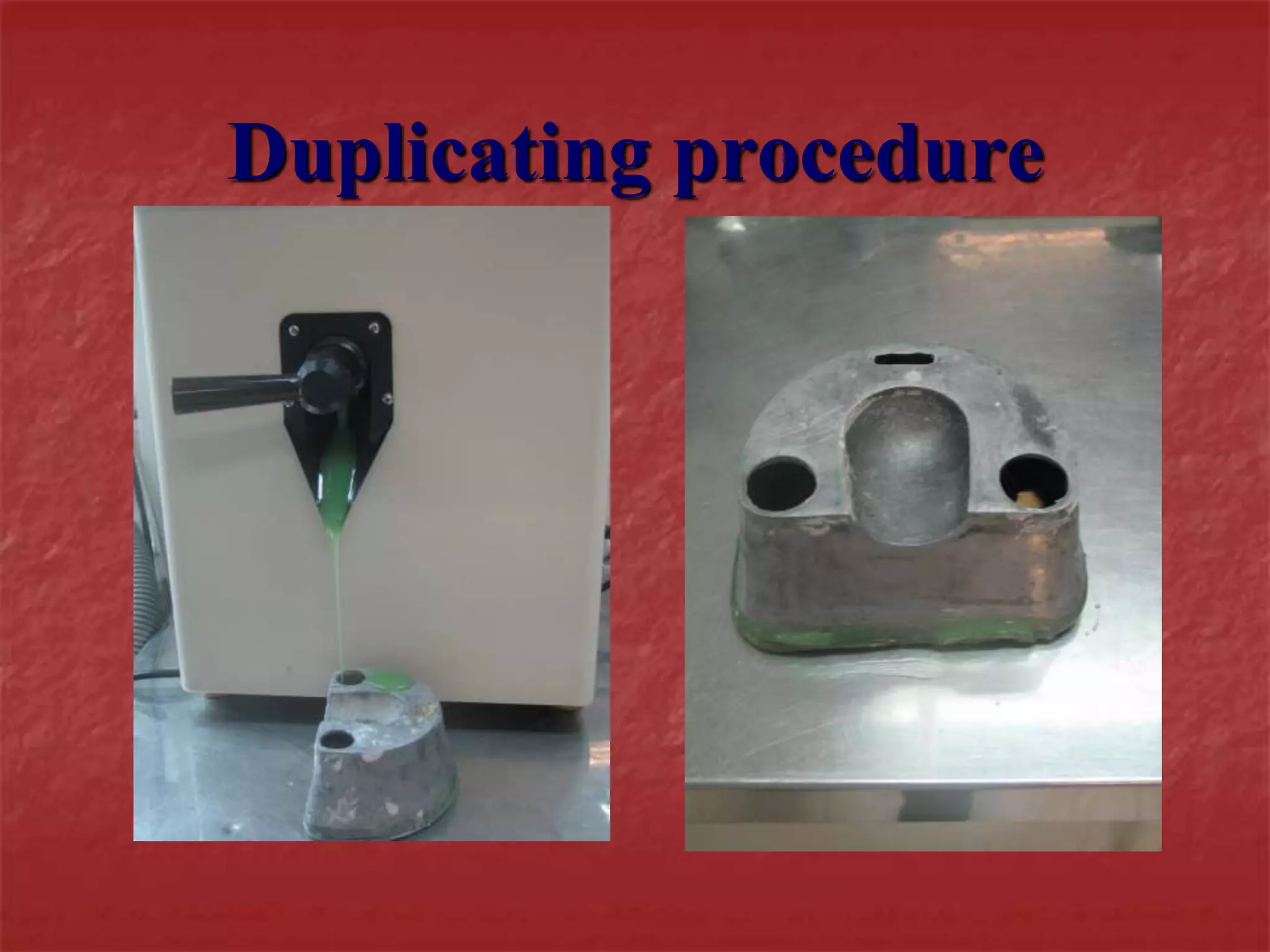
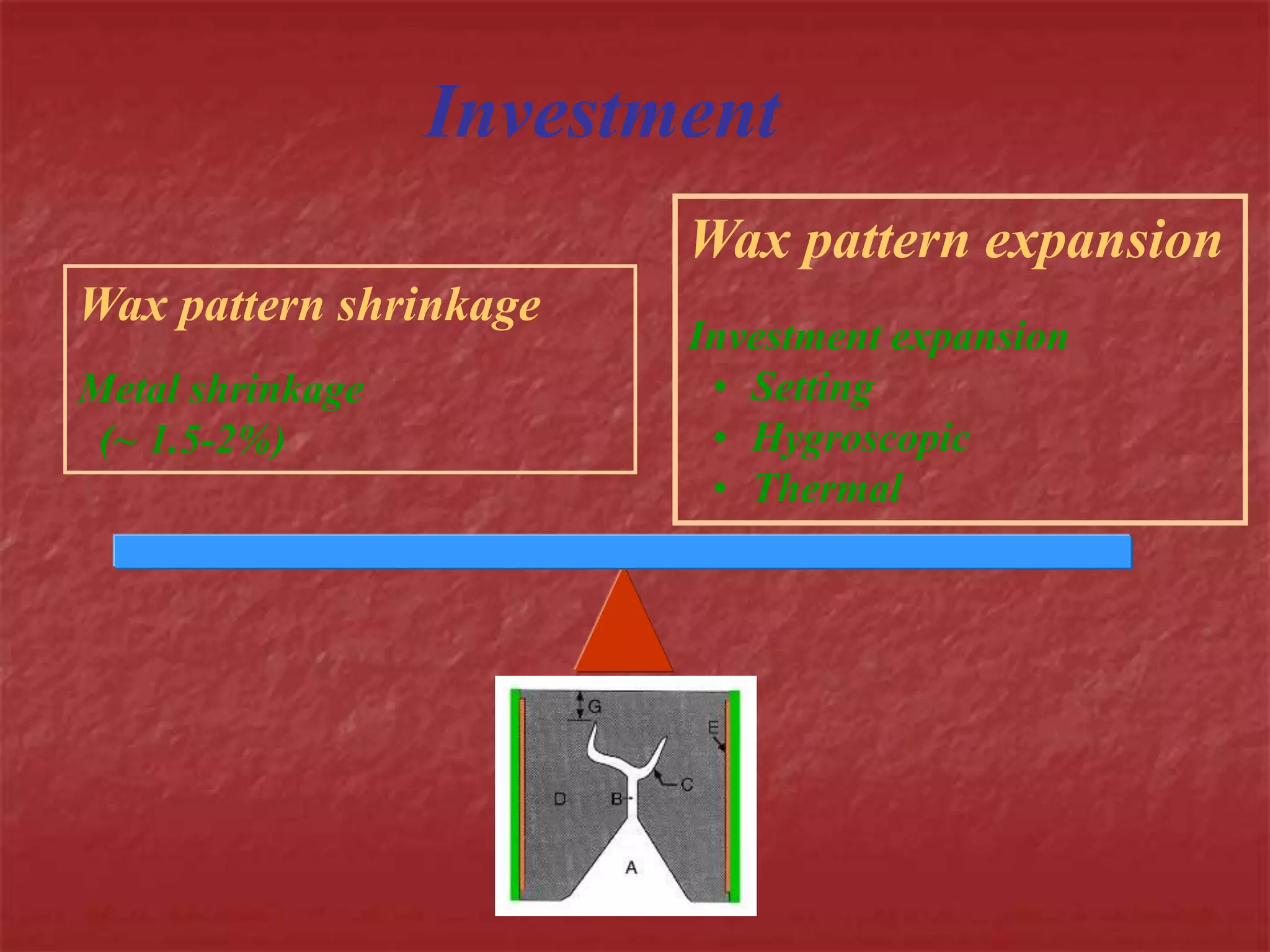
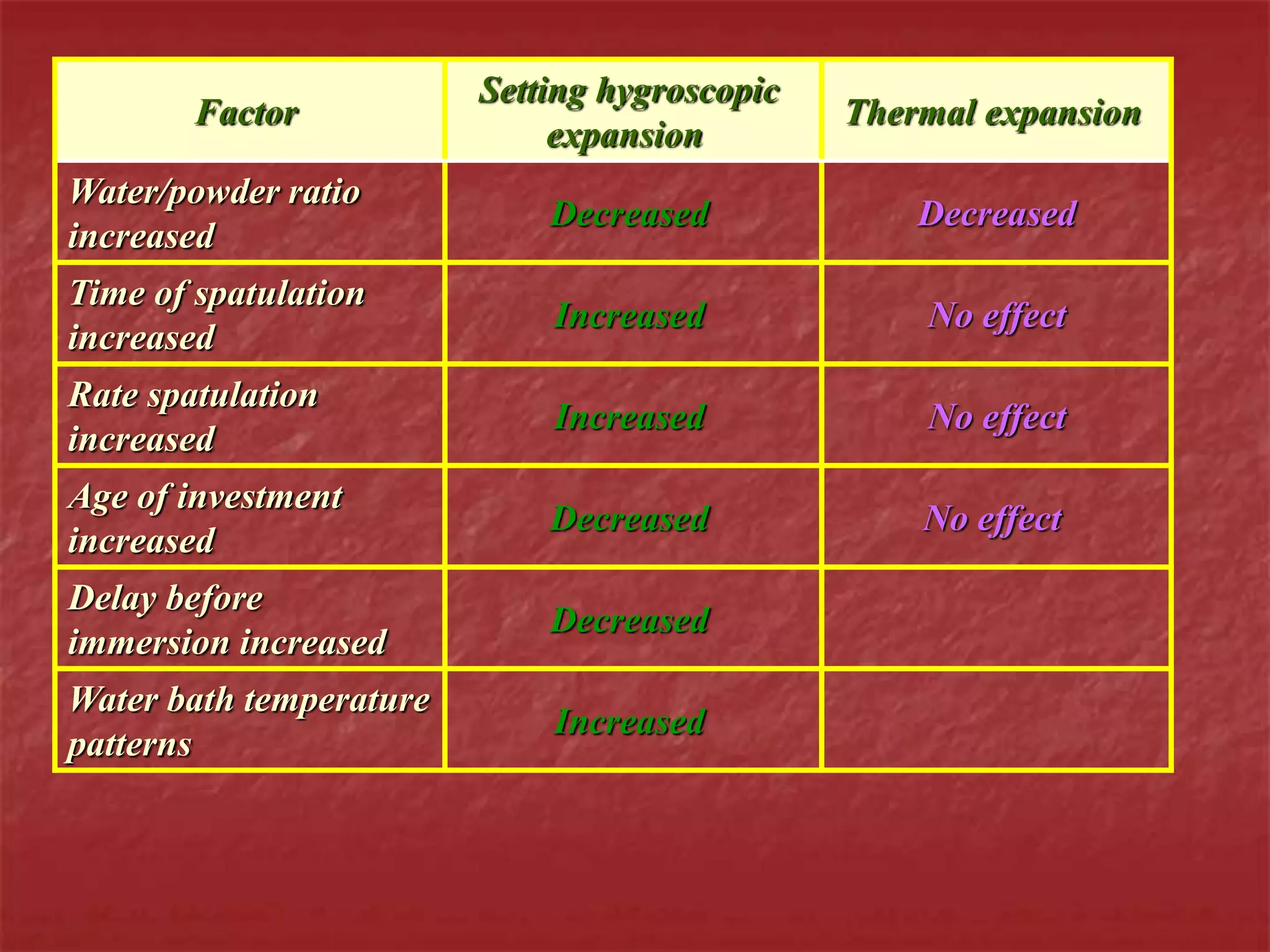
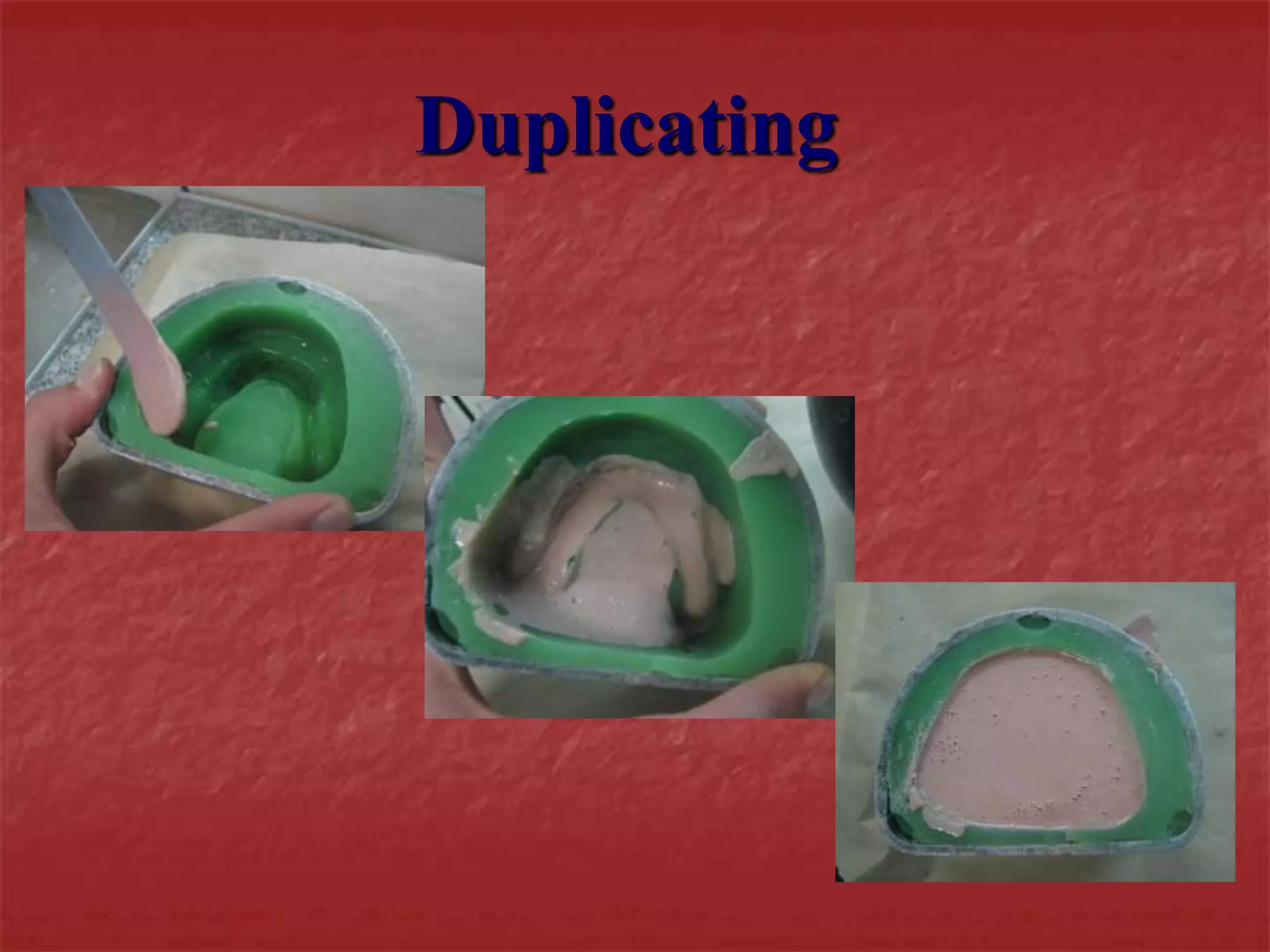
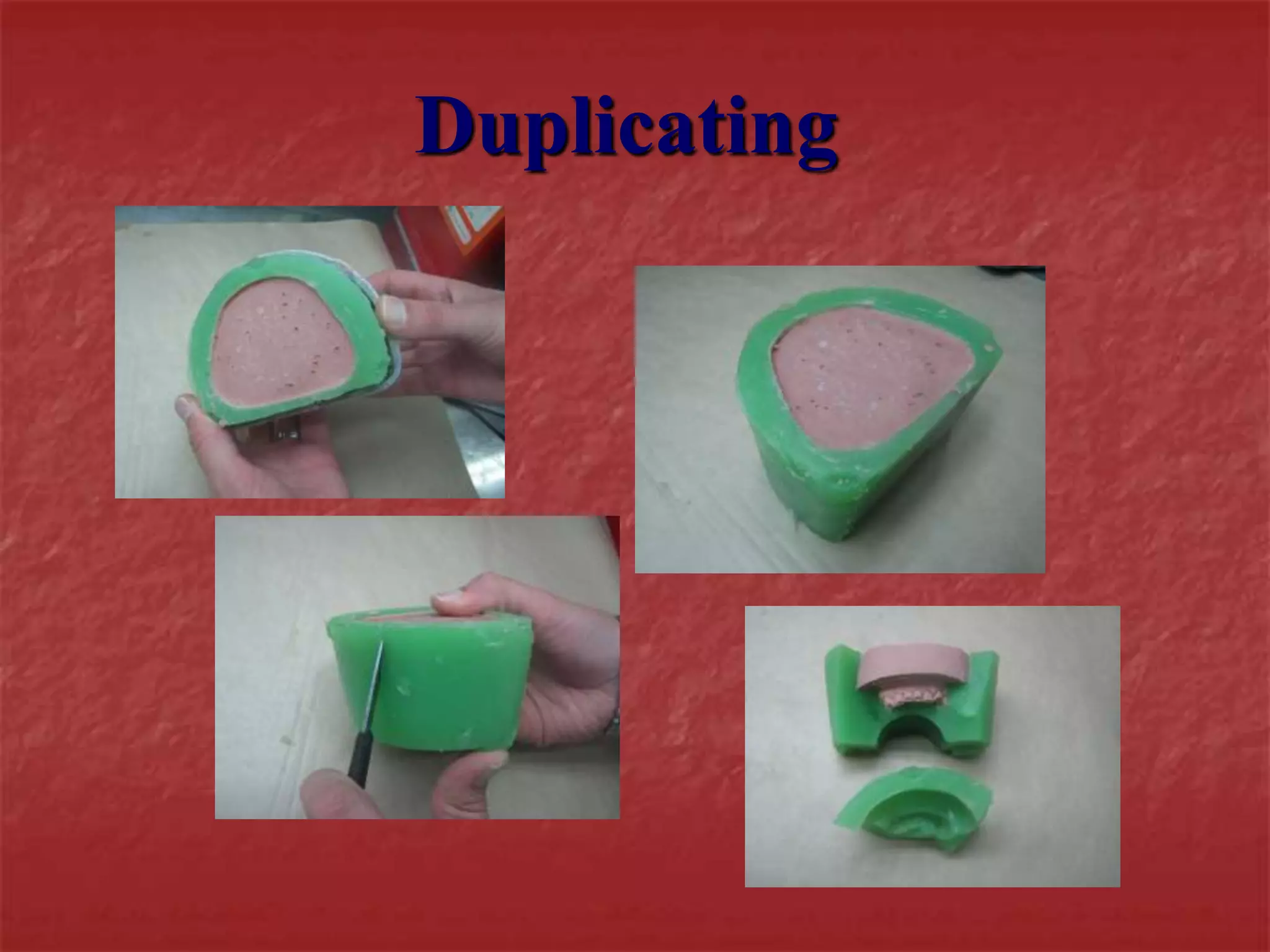
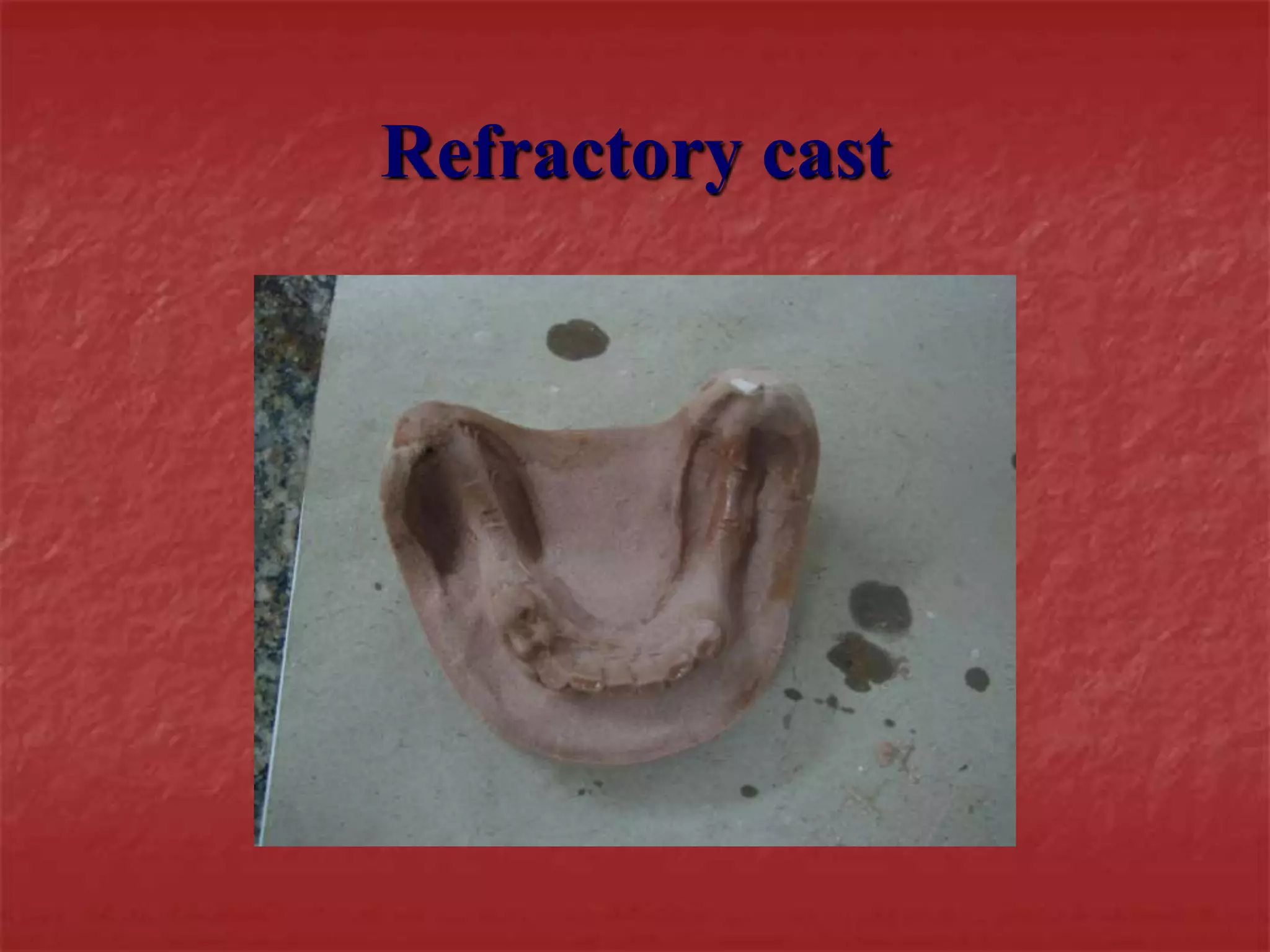
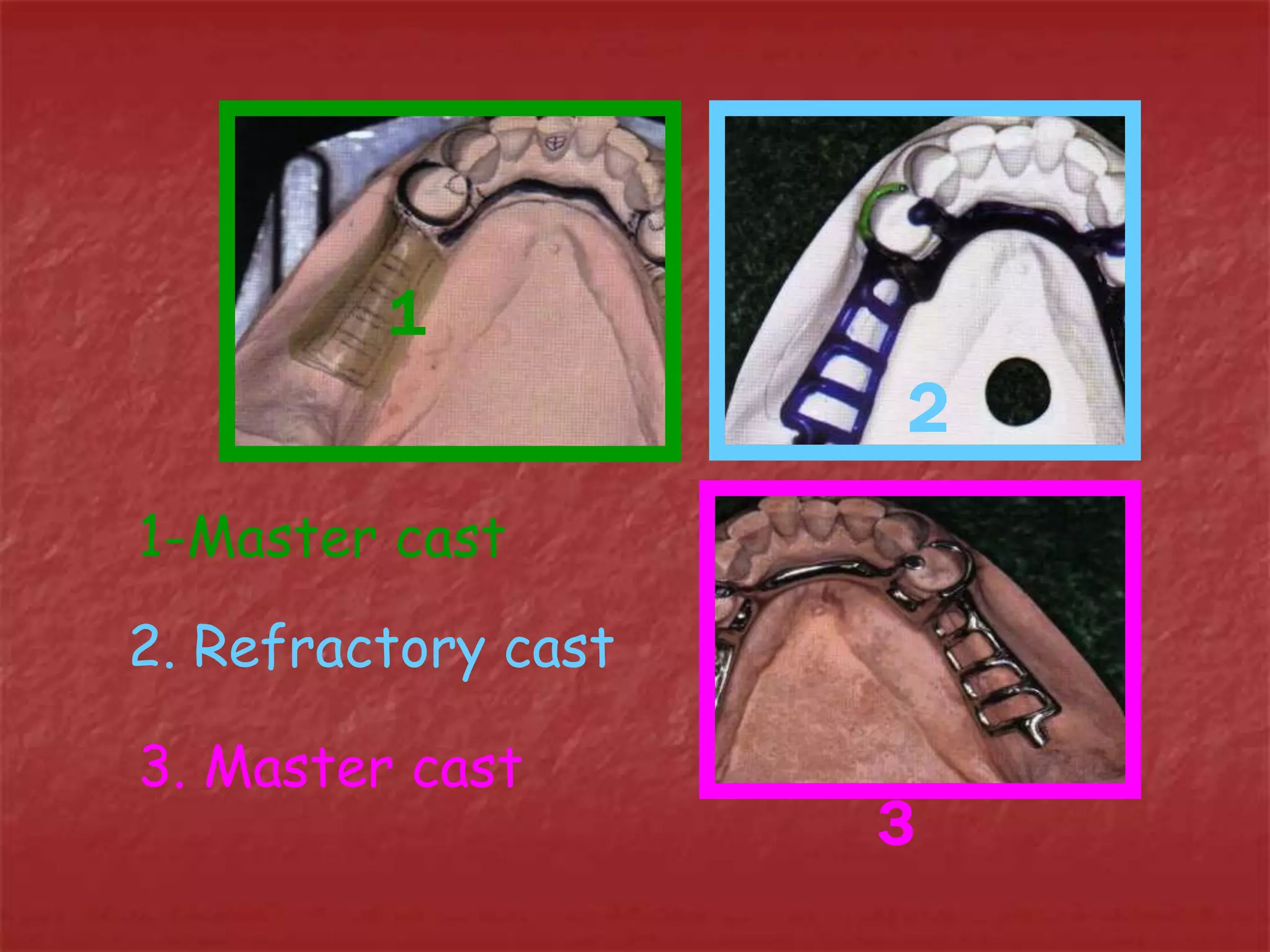
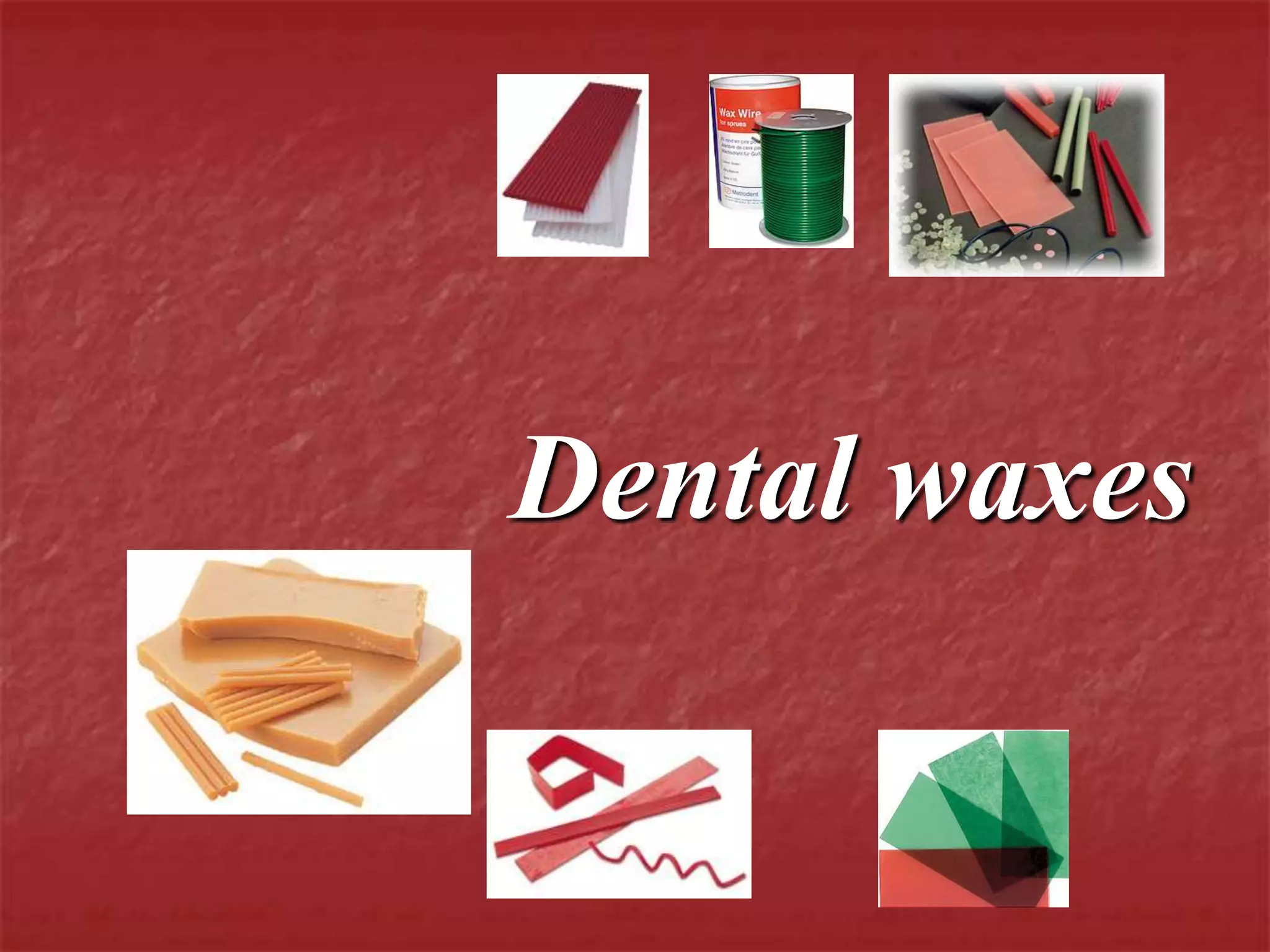
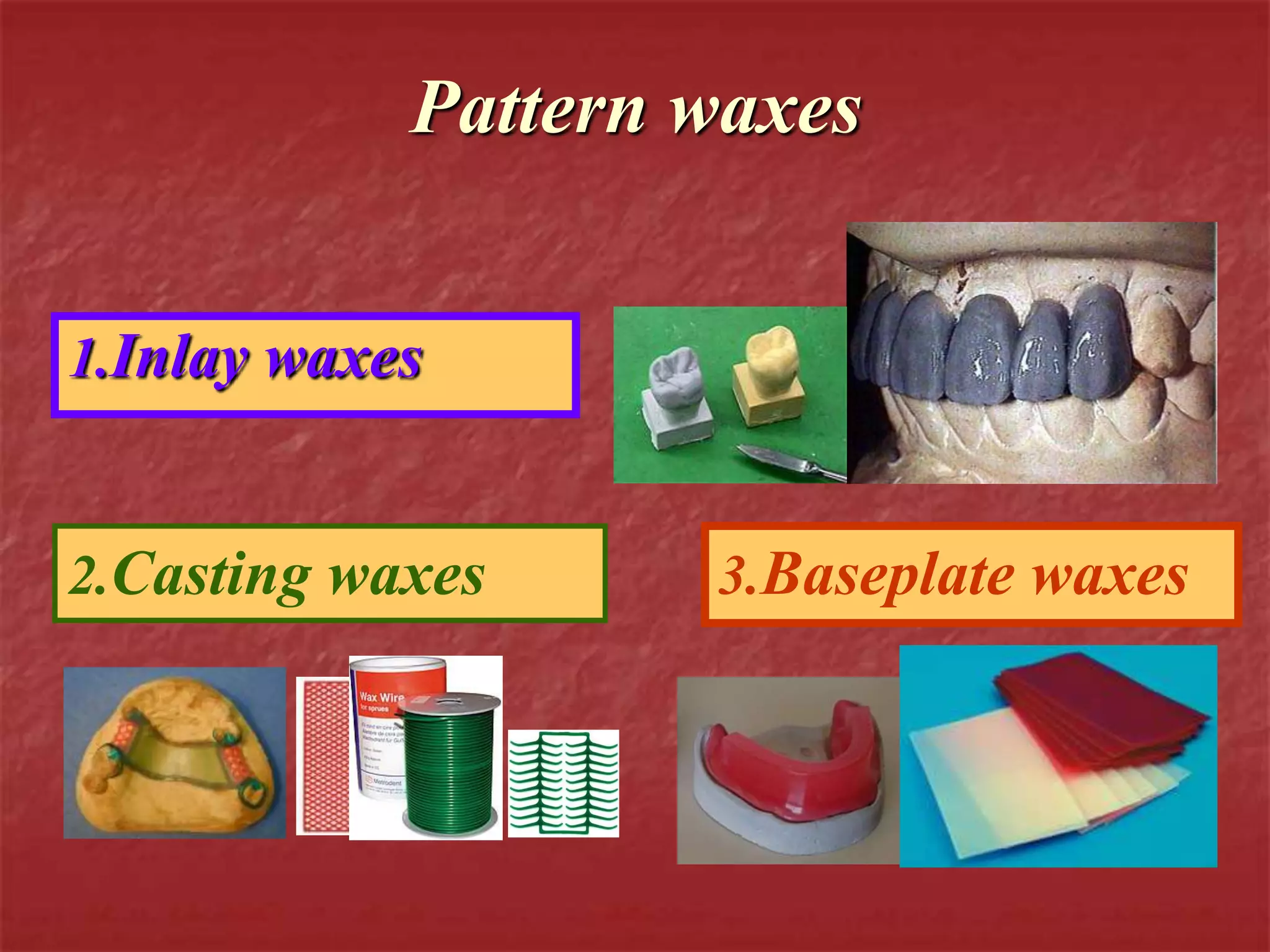
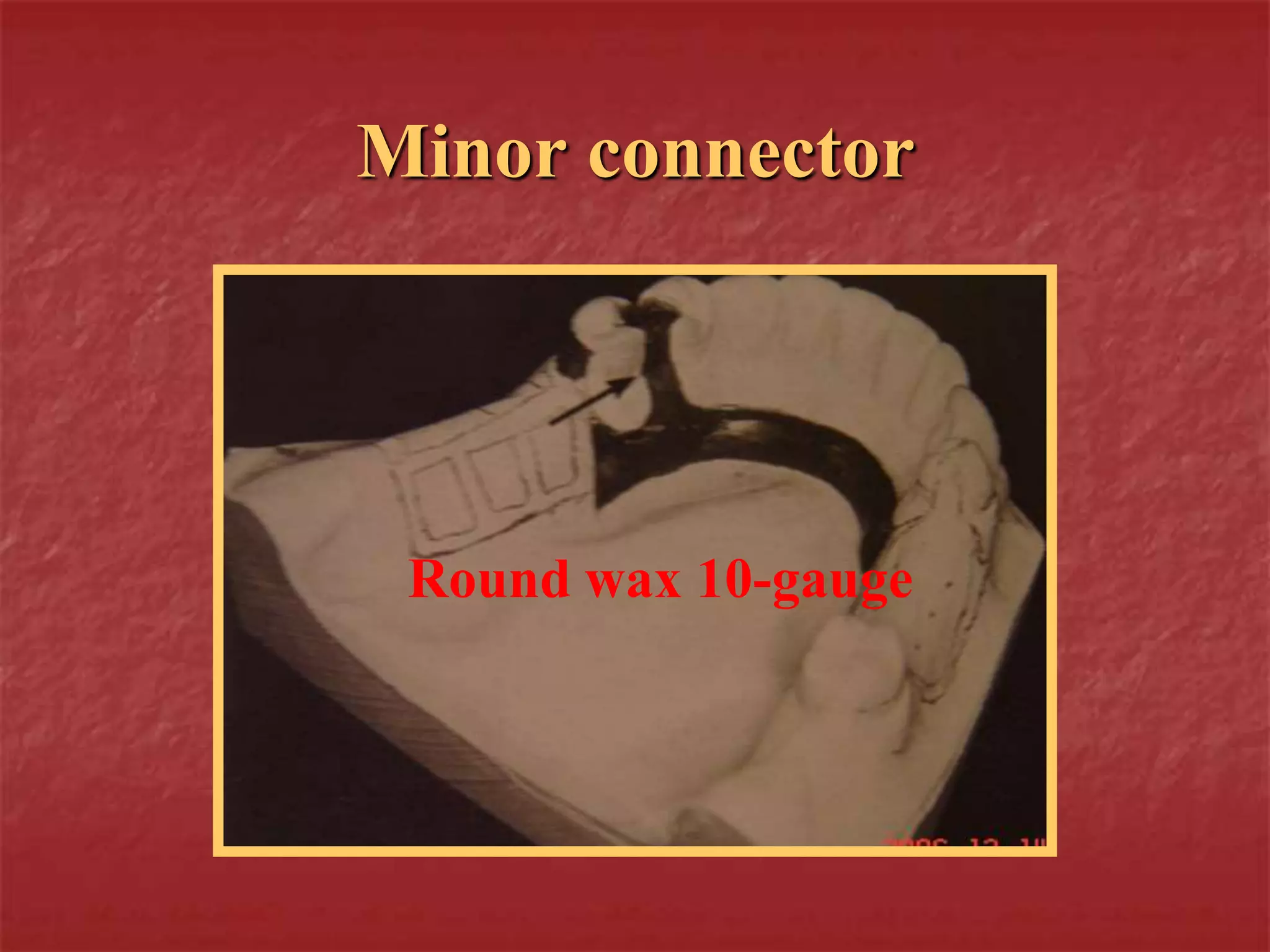
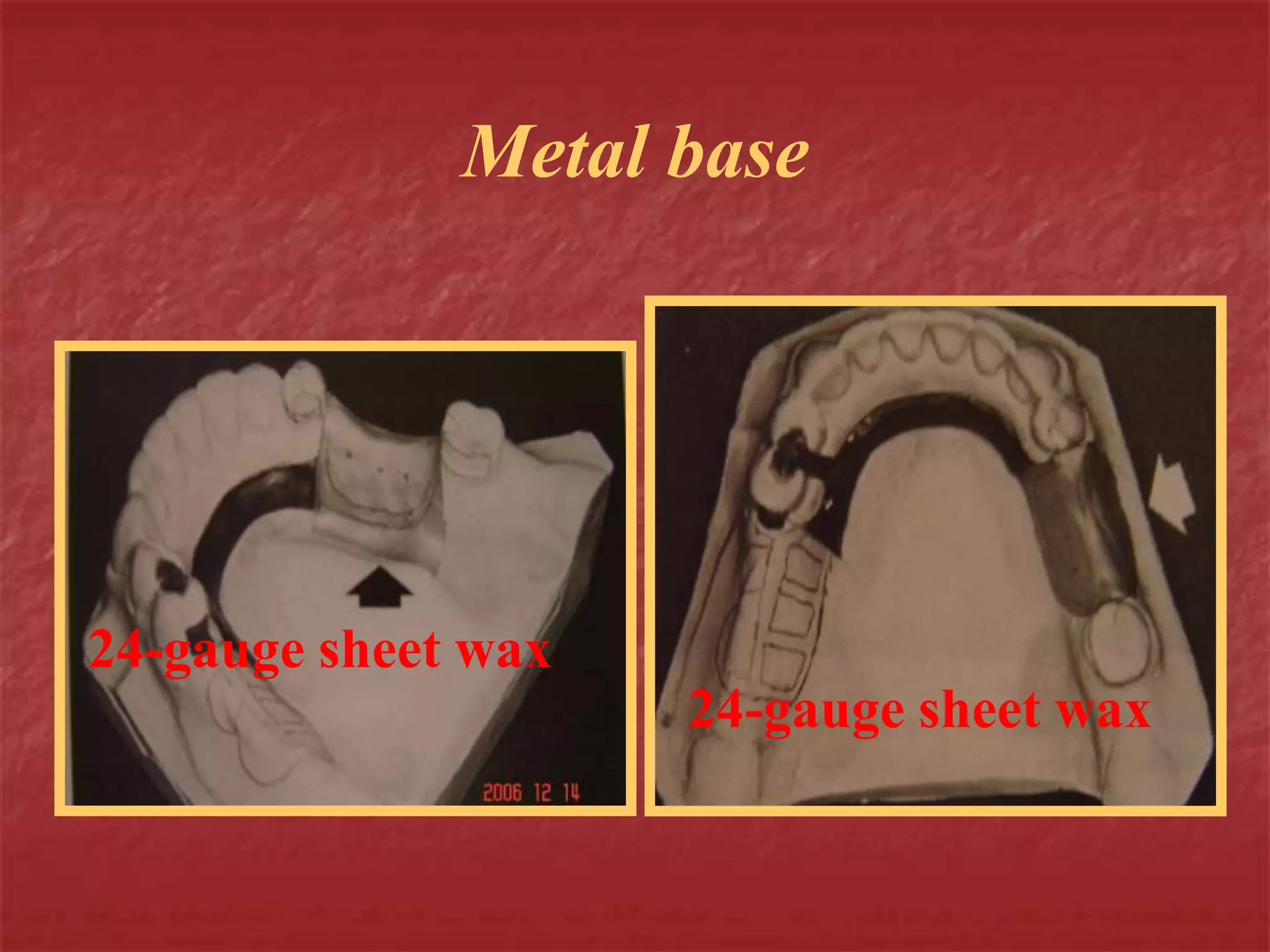
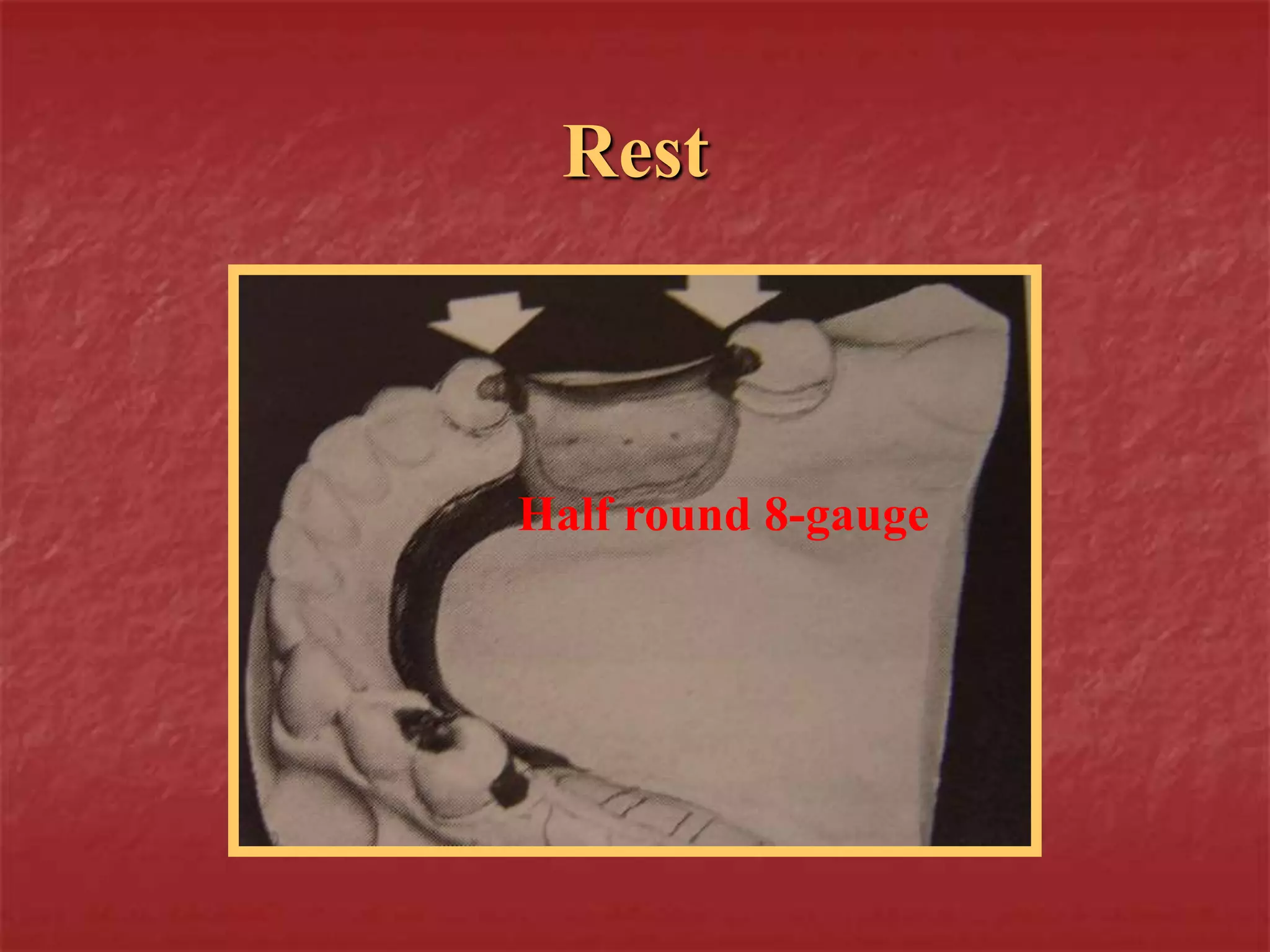
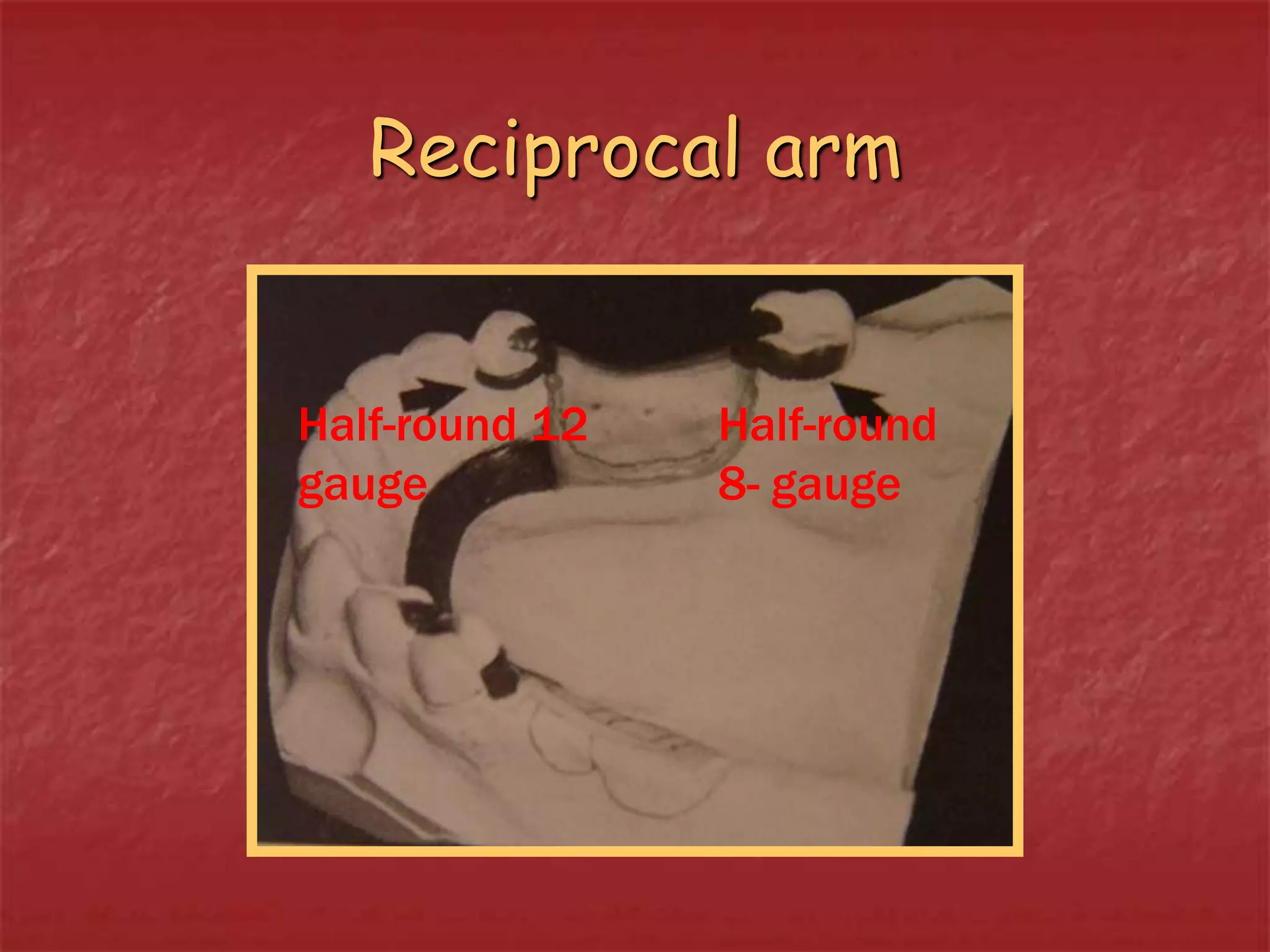
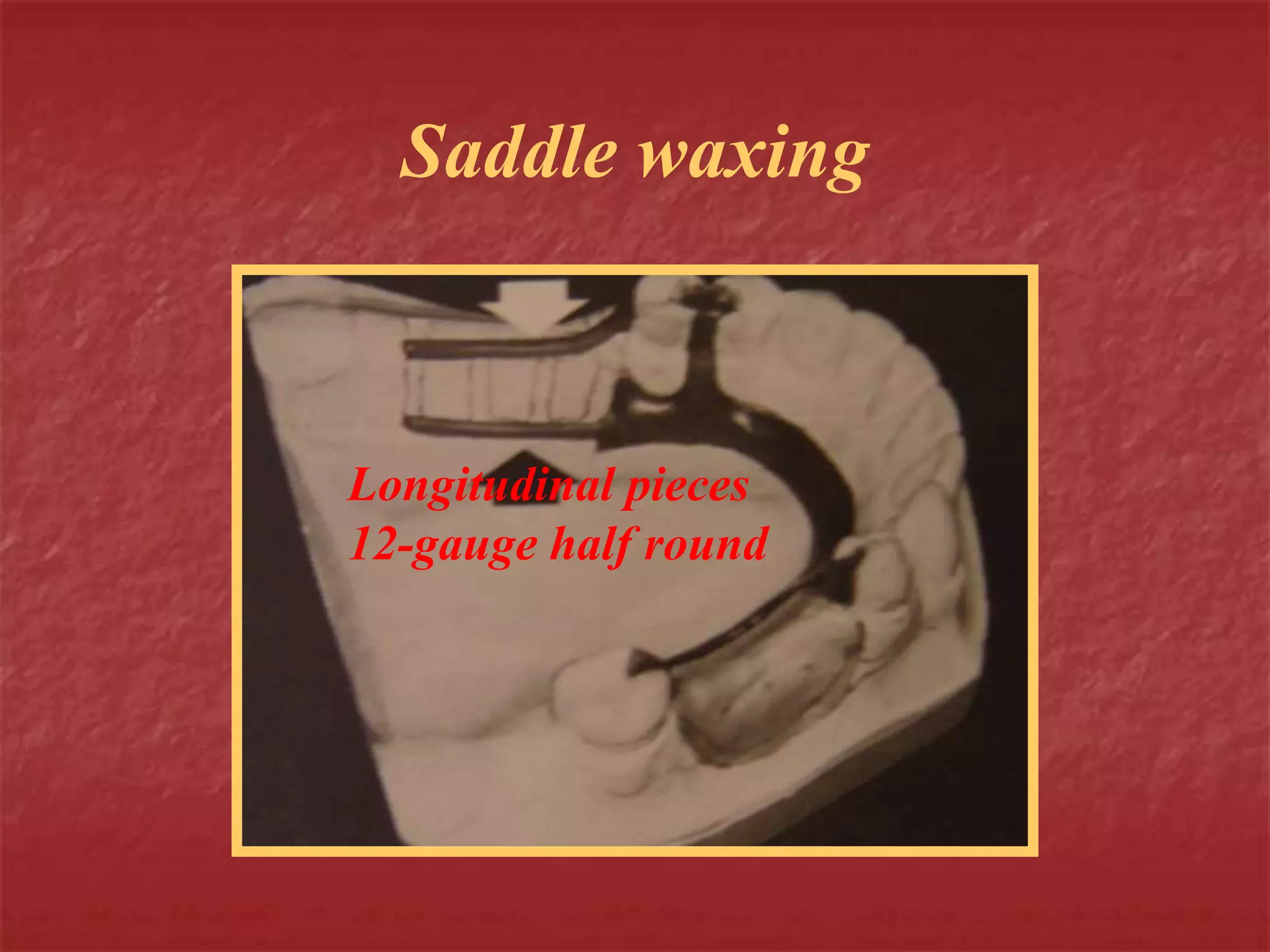
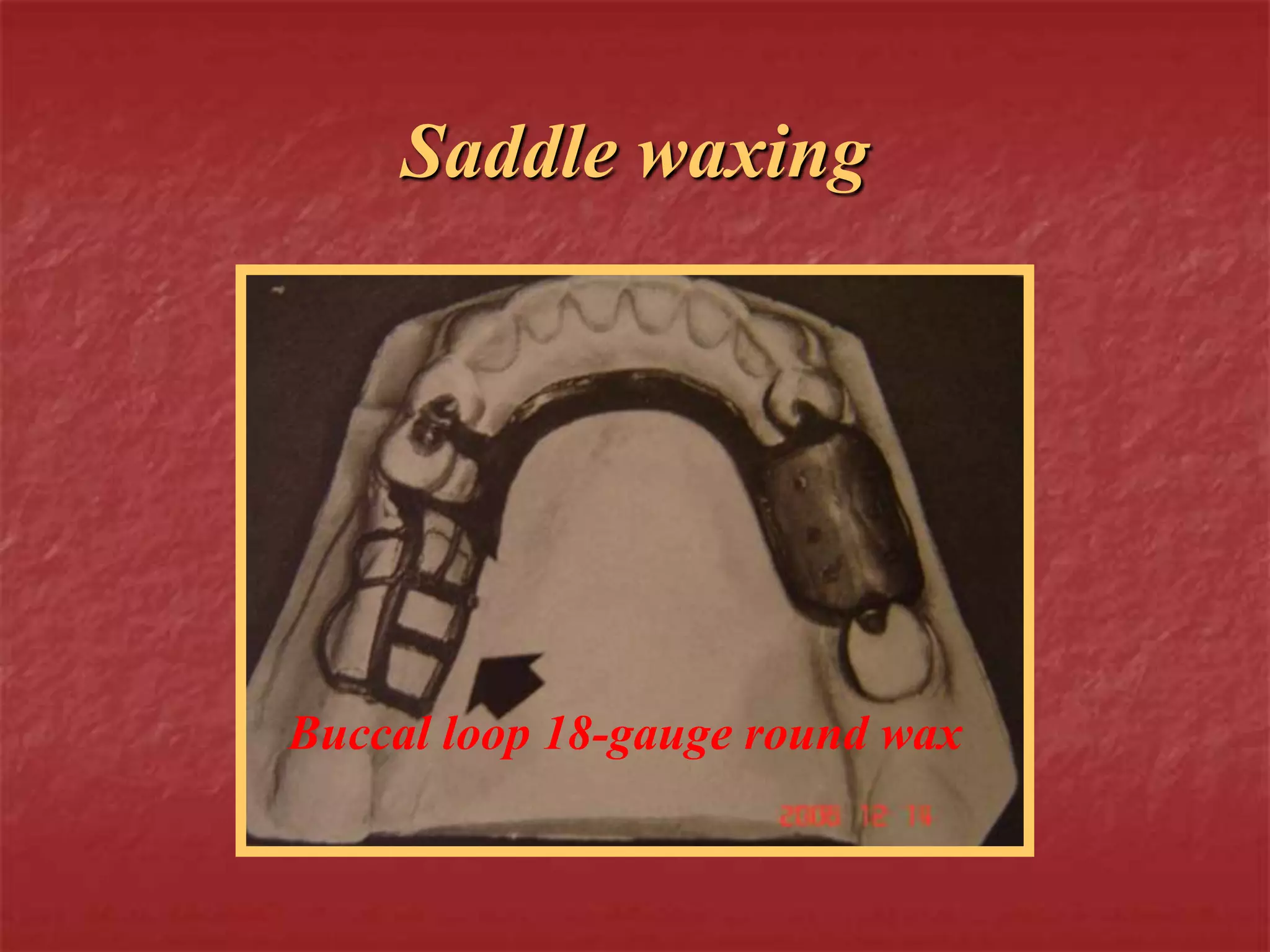
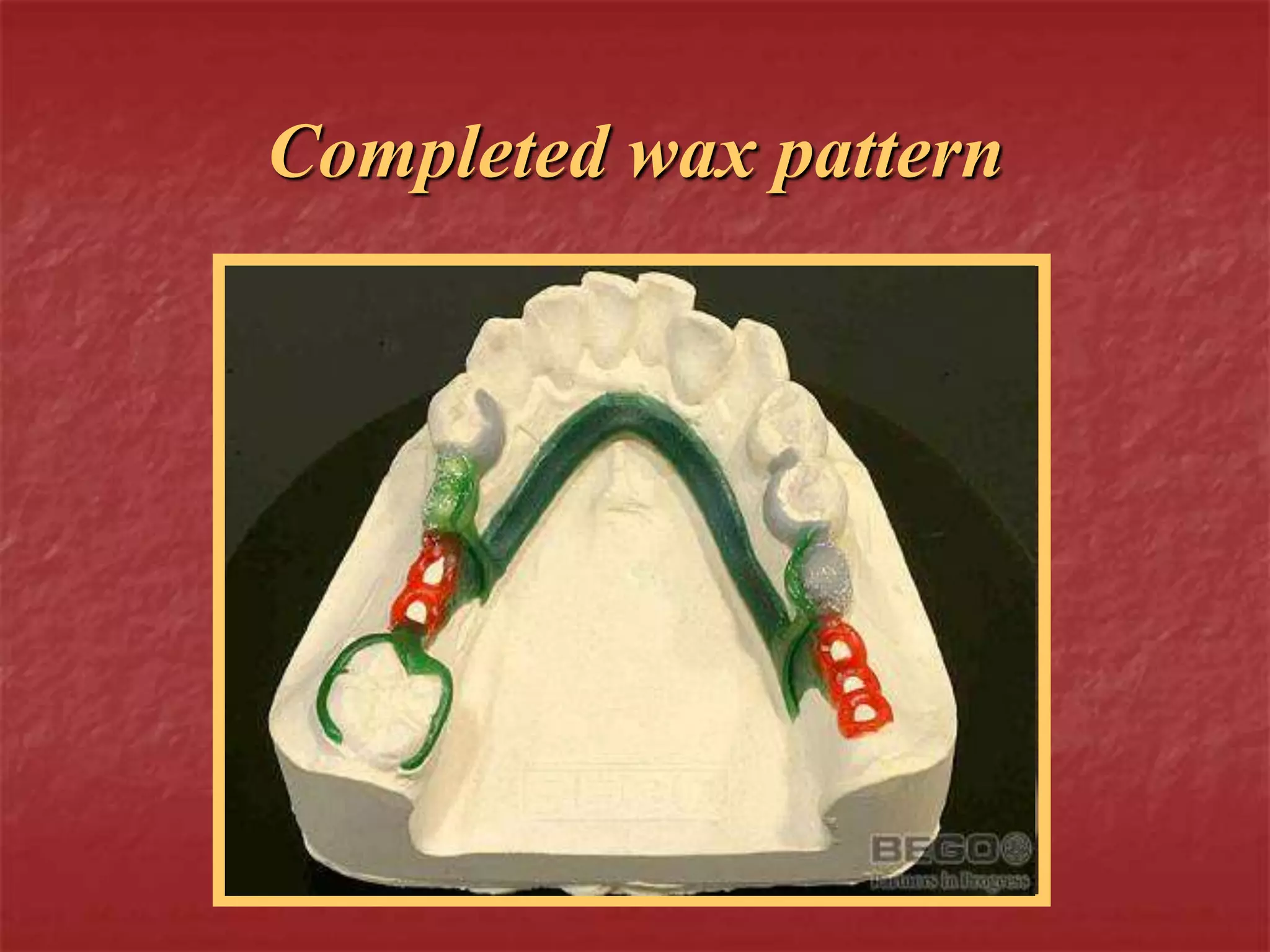
This document discusses the process of duplicating dental casts and wax patterns. It describes how duplicating materials like agar and silicones are used to make refractory casts from a master cast. Then, various dental waxes are used to form the pattern for a metallic dental framework on the refractory cast. Different gauges and shapes of wax are used for components like the lingual bar, connectors, saddles, and external finish lines. The completed wax pattern can then be invested and cast into metal.