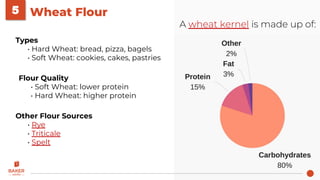
The document is a comprehensive guide on baking ingredients, covering essential elements like baker’s percent, flour types, leavening systems, and the roles of various ingredients such as water, eggs, and fats in baking. It explains the functions and characteristics of different components and their impact on baking outcomes, as well as guidelines for achieving consistency and quality in baked products. The resource aims to provide foundational knowledge for aspiring bakers to master baking techniques.