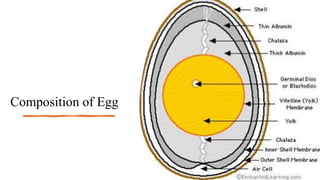
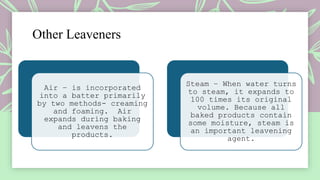
This document provides information about preparing and producing bakery products. It begins with definitions of various baking terms like acid, bake, batter, blend etc. It then discusses major ingredients used in baking like flour, sugar, eggs, shortening, leavening agents and liquid ingredients. Flour is made from wheat and other grains and comes in varieties like bread flour, all-purpose flour, cake flour depending on gluten content. Sugar comes in types like granulated, confectioner's and brown. Eggs provide structure, leavening and binding in baked goods. Shortening like butter, oil and margarine tenderizes baked items. Leavening agents cause dough to rise through biological or chemical processes using yeast or baking powder