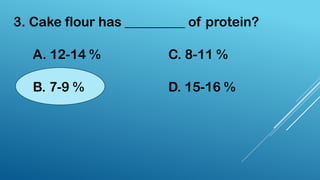
The document outlines the major baking ingredients, their functions, and uses, categorizing them into flour, liquids, shortening, sugar, leavening agents, eggs, and flavorings. It describes the different types of each ingredient, such as whole wheat flour for yeast breads, milk for moistness, and various sweeteners for flavor. Additionally, it explains the roles of leavening agents and flavorings in baking, highlighting how they contribute to texture, taste, and overall quality of baked products.