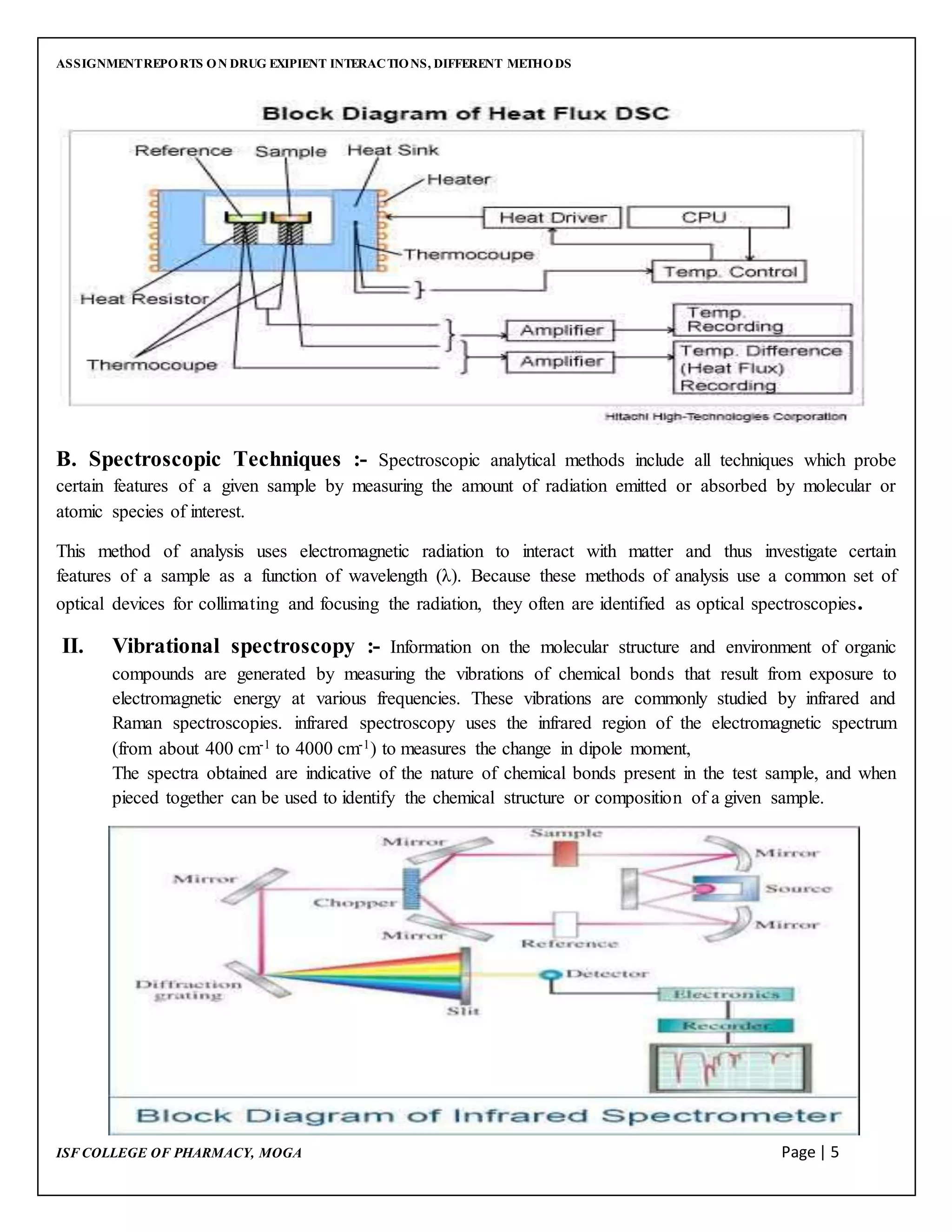
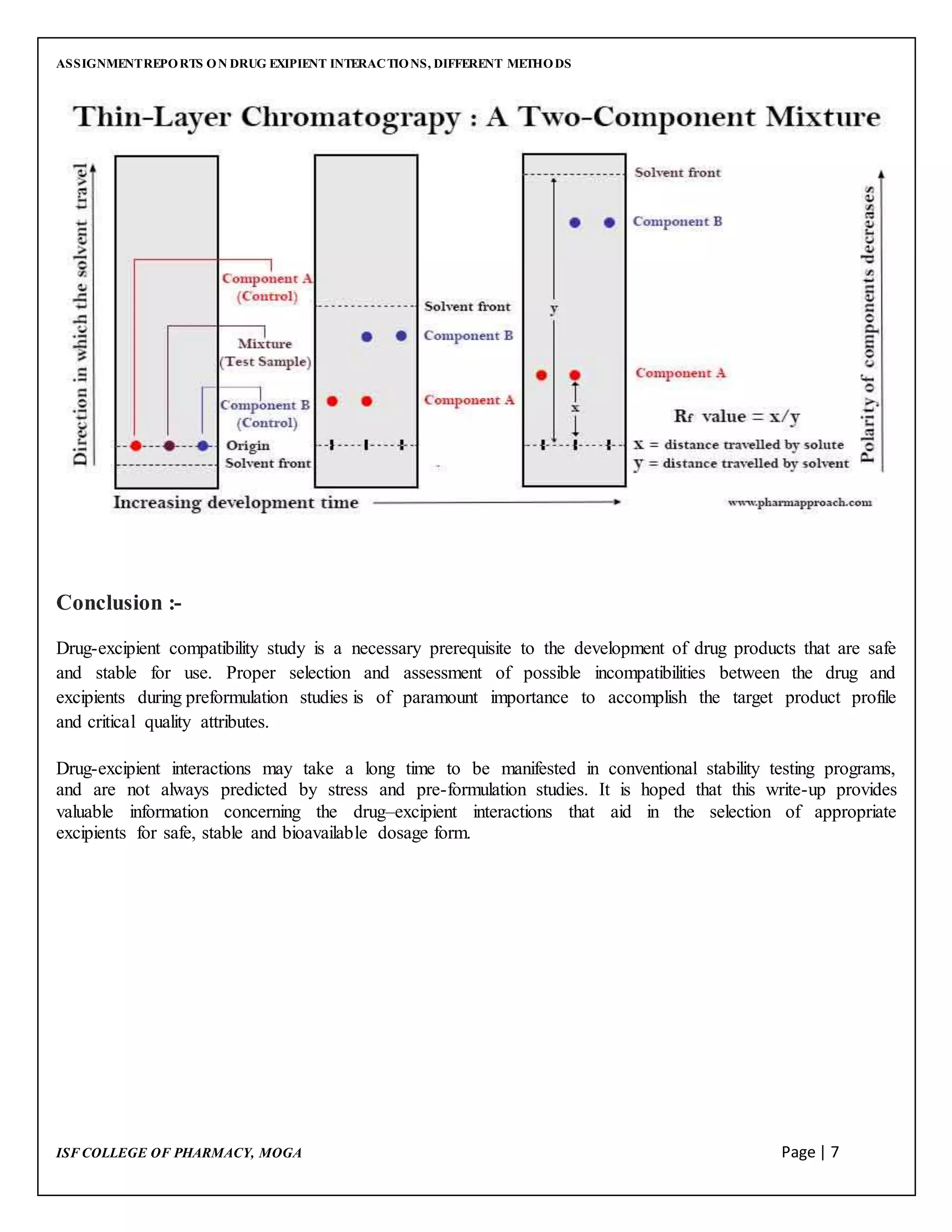
This document discusses drug-excipient interactions and methods used to detect compatibility between drugs and excipients. It defines excipients as inactive ingredients used to deliver active pharmaceutical ingredients. There are four main types of drug-excipient interactions: physical, chemical, biopharmaceutical, and excipient-excipient. Analytical techniques like differential scanning calorimetry, vibrational spectroscopy, thin layer chromatography, and high performance liquid chromatography are used to detect interactions. Detecting interactions is important to ensure stability of drug formulations and avoid problems during development and production.