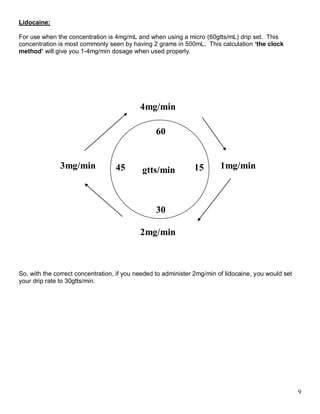
This document provides information and formulas for various medical calculations used in pre-hospital settings, including calculations for medication bolus doses, infusion rates, fluid flow rates, and weight-based infusions. It defines common medical abbreviations and covers metric conversions and basic arithmetic. Formulas are provided for intravenous bolus medications, intravenous infusions, weight-based infusions, and intravenous fluid flow rates. Additional "street rules" shortcuts are described for calculating dopamine and lidocaine infusion rates.