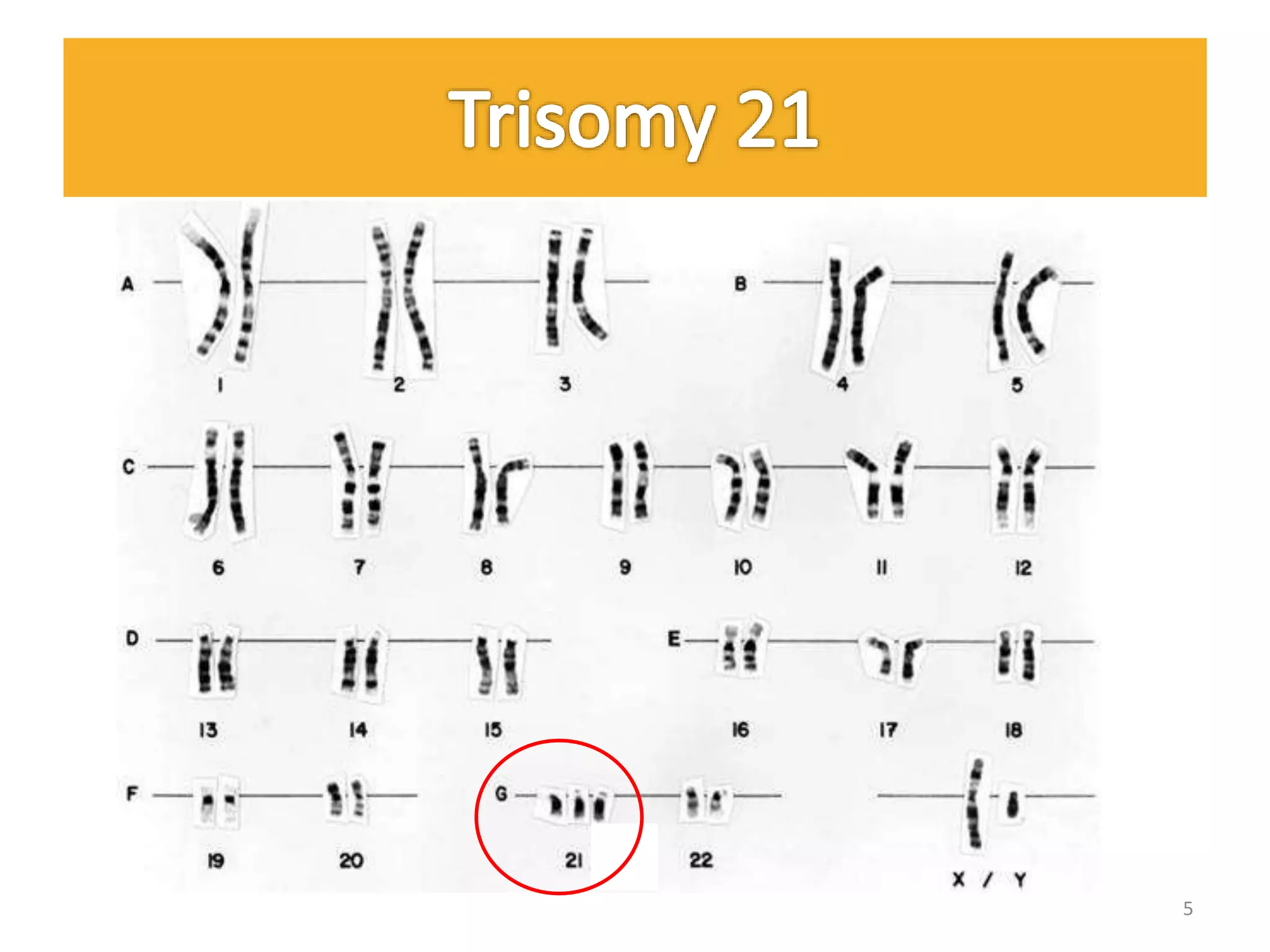
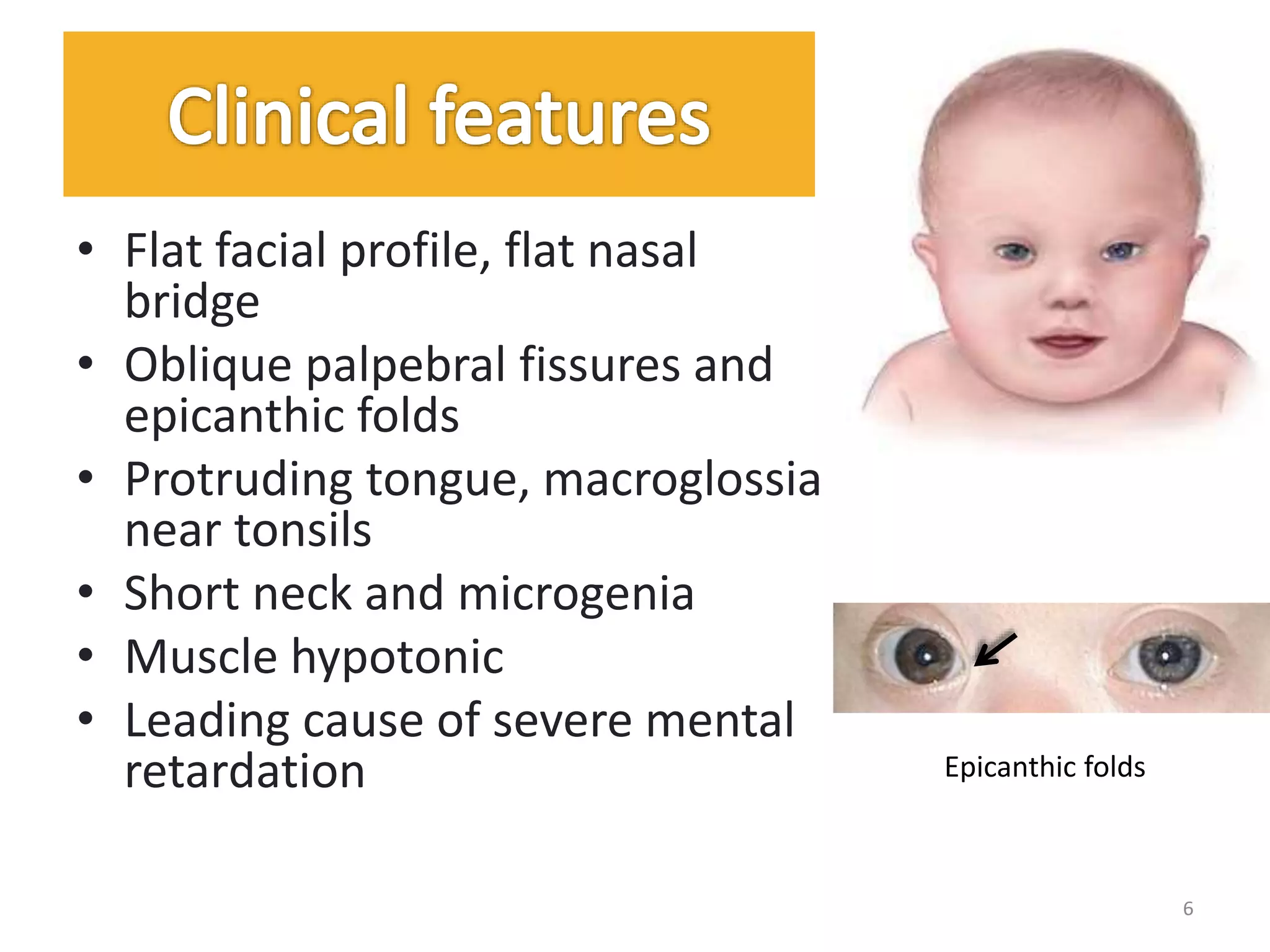
Down Syndrome and Klinefelter's syndrome are chromosomal disorders. Down Syndrome is caused by trisomy of chromosome 21 and is characterized by distinctive facial features and cognitive impairment. Klinefelter's syndrome affects males and is caused by one or more extra X chromosomes, leading to hypogonadism and reduced masculine features. Both conditions can be detected prenatally by techniques like amniocentesis.