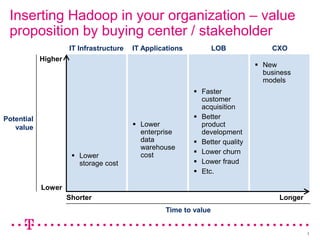
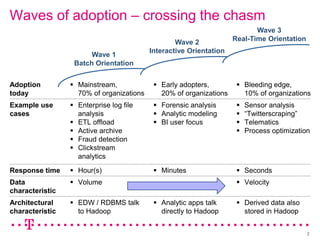
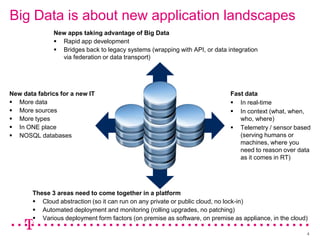
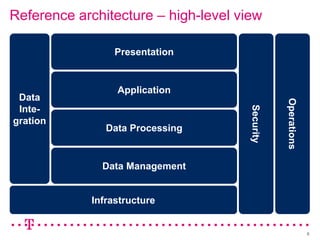
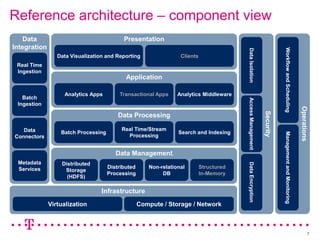
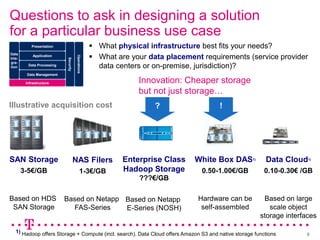
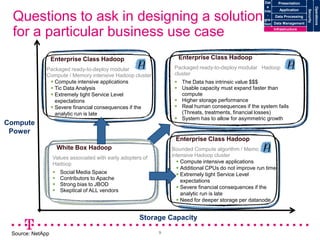
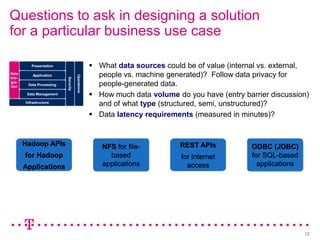
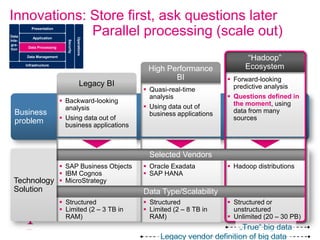
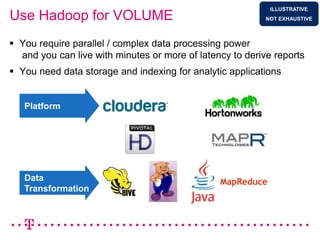
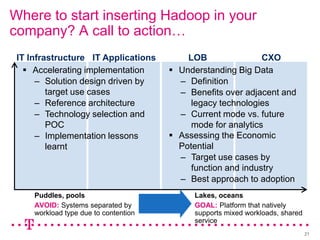
The document explores how Deutsche Telekom leverages big data through use case segmentation to inform solution design and technology selection, emphasizing the benefits of Hadoop for data storage and processing. It discusses various adoption waves and presents questions to guide the design of big data solutions, covering aspects like infrastructure, data sources, analytics types, and operational requirements. The emphasis is on integrating real-time processing capabilities and machine learning within a flexible architecture to harness the full potential of big data.