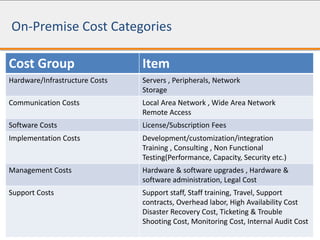
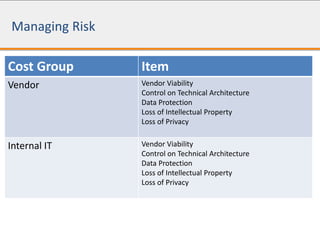
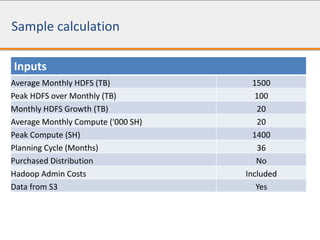
The document discusses the total cost of ownership (TCO) for Hadoop implementation, highlighting the challenges of estimating costs due to hidden expenses such as integration and management. It outlines different deployment methods including on-premise and Hadoop as a service, and details various cost categories related to hardware, software, and management. It also addresses risk management regarding vendor viability and technical architecture, providing considerations for on-premise implementation versus Hadoop as a service.