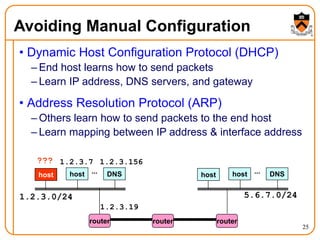
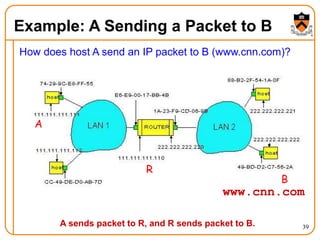
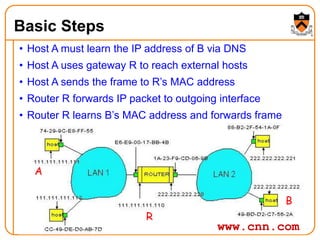
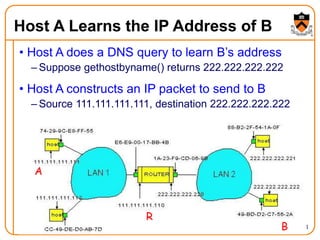
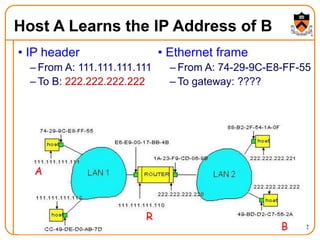
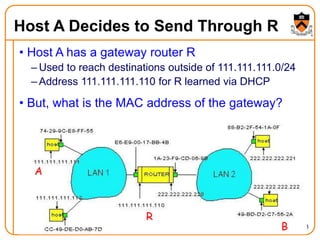
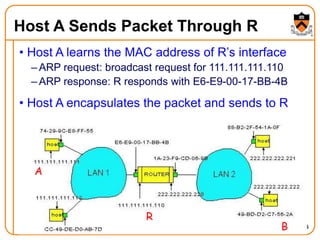
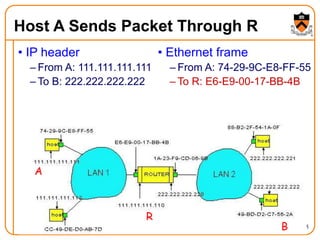
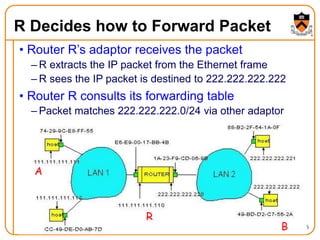
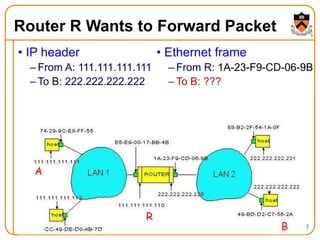
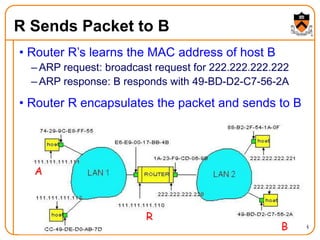
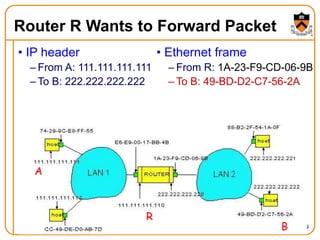
1. The document discusses several protocols used to translate between different address types on a network, including DNS, DHCP, and ARP. DNS is a hierarchical and distributed system that maps hostnames to IP addresses. DHCP dynamically assigns IP configuration to hosts, while ARP maps IP addresses to MAC addresses for sending packets on the local link.
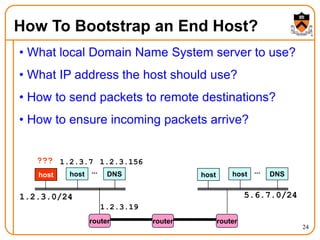
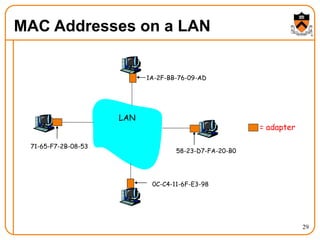
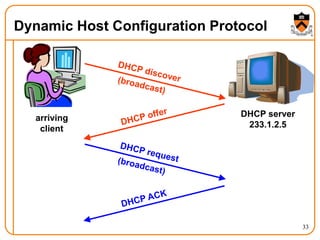
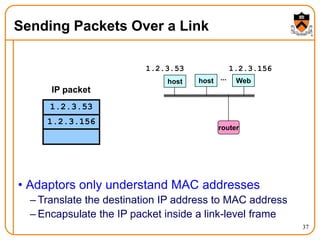
2. When a host first connects to the network, it uses DHCP to dynamically obtain its IP configuration including IP address, subnet mask, gateway, and DNS servers. It then uses ARP to discover the MAC address associated with destination IP addresses, allowing it to encapsulate IP packets for transmission on the link.
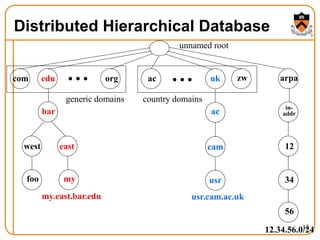
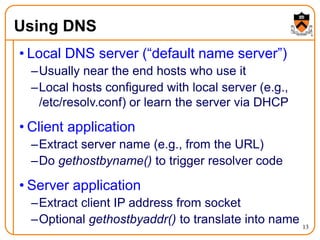
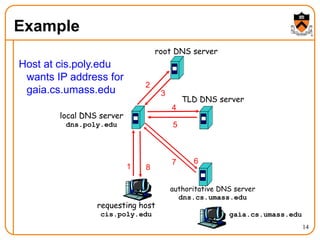
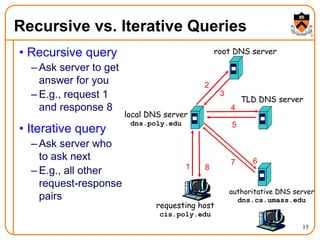
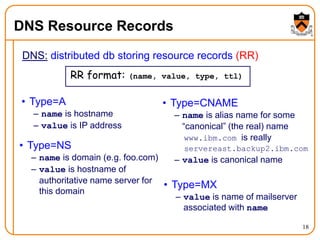
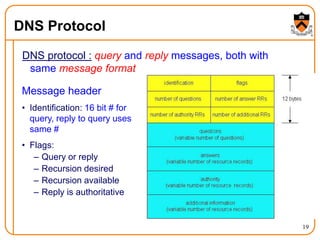
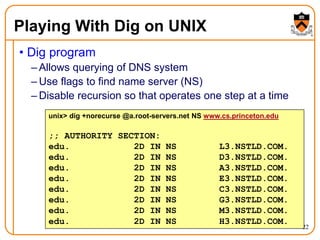
3. DNS uses a distributed database of name servers to lookup mappings between hostnames and