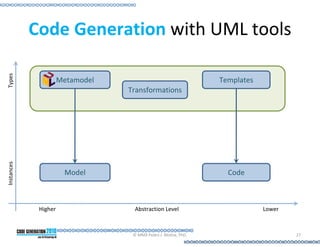
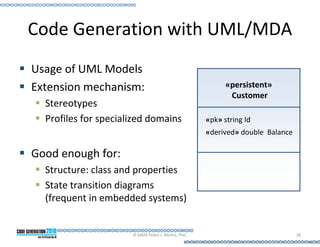
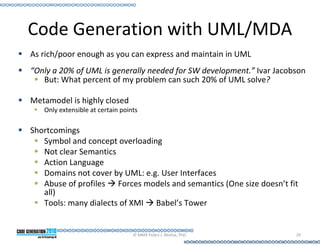
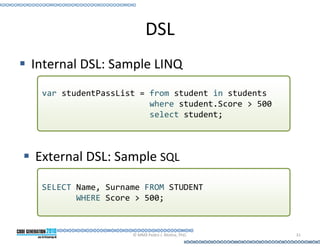
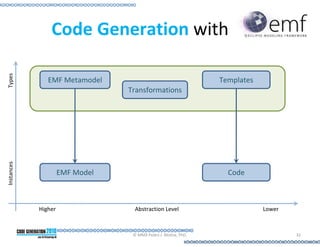
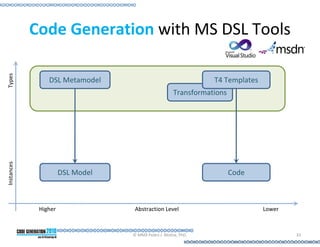
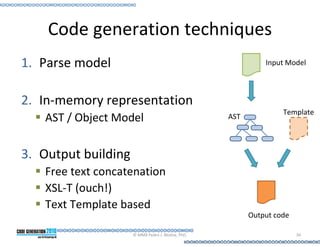
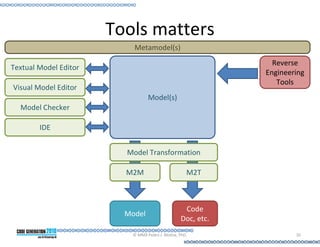
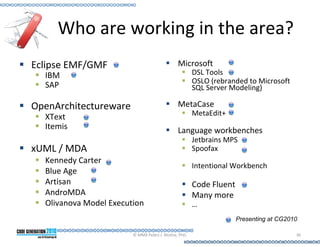
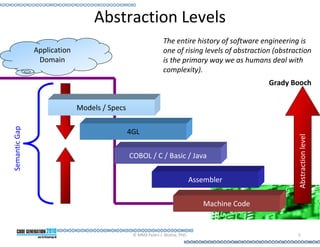
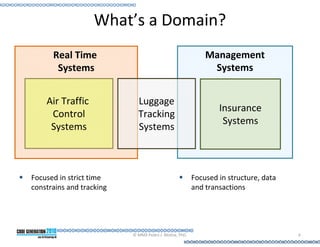
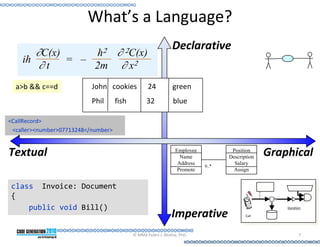
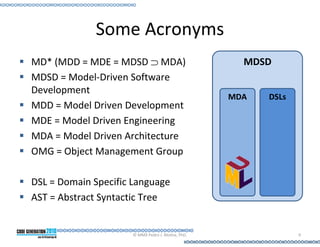
This document provides an introduction to model-driven software development (MDSD). It discusses what MDSD is, why organizations adopt it, and how it can be applied. Key aspects of MDSD covered include code generation, domain-specific languages, separation of concerns, and economic benefits such as reduced costs from economies of scale and scope. The document also reviews various tools and approaches used in MDSD, including those based on UML, EMF, and DSLs. It concludes by emphasizing that MDSD can help improve software productivity and help establish true software engineering practices.





![Economies of Scale
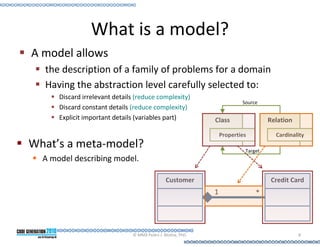
Economies of Scale
The condition where few inputs, as effort and time, are needed to
produce big quantities of a unique output. [Wit96]
But: Can’t be applied to SW!
Once the SW is produced
Copy cost is = 0 £!
Japanese Cookie Factory. Production Line.
© MMX Pedro J. Molina, PhD. 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cg2010introducingmdsd-100617020657-phpapp02/85/CG2010-Introducing-MDSD-16-320.jpg)

![Economies of Scope
Economies of Scope
The condition where few inputs, as effort and time, are
needed to produce a great variety of outputs. It is
produced more added value producing in the same line
different outputs. To produce each output independently
creates an overcost in the common parts.
Economy of Scope occurs when the cost of combining two
or more products in a unique product line is lower than
producing them independently. [Wit96]
© MMX Pedro J. Molina, PhD. 18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cg2010introducingmdsd-100617020657-phpapp02/85/CG2010-Introducing-MDSD-18-320.jpg)